Pseudostellarin BCAS# 156430-21-6 |
Quality Control & MSDS
Number of papers citing our products

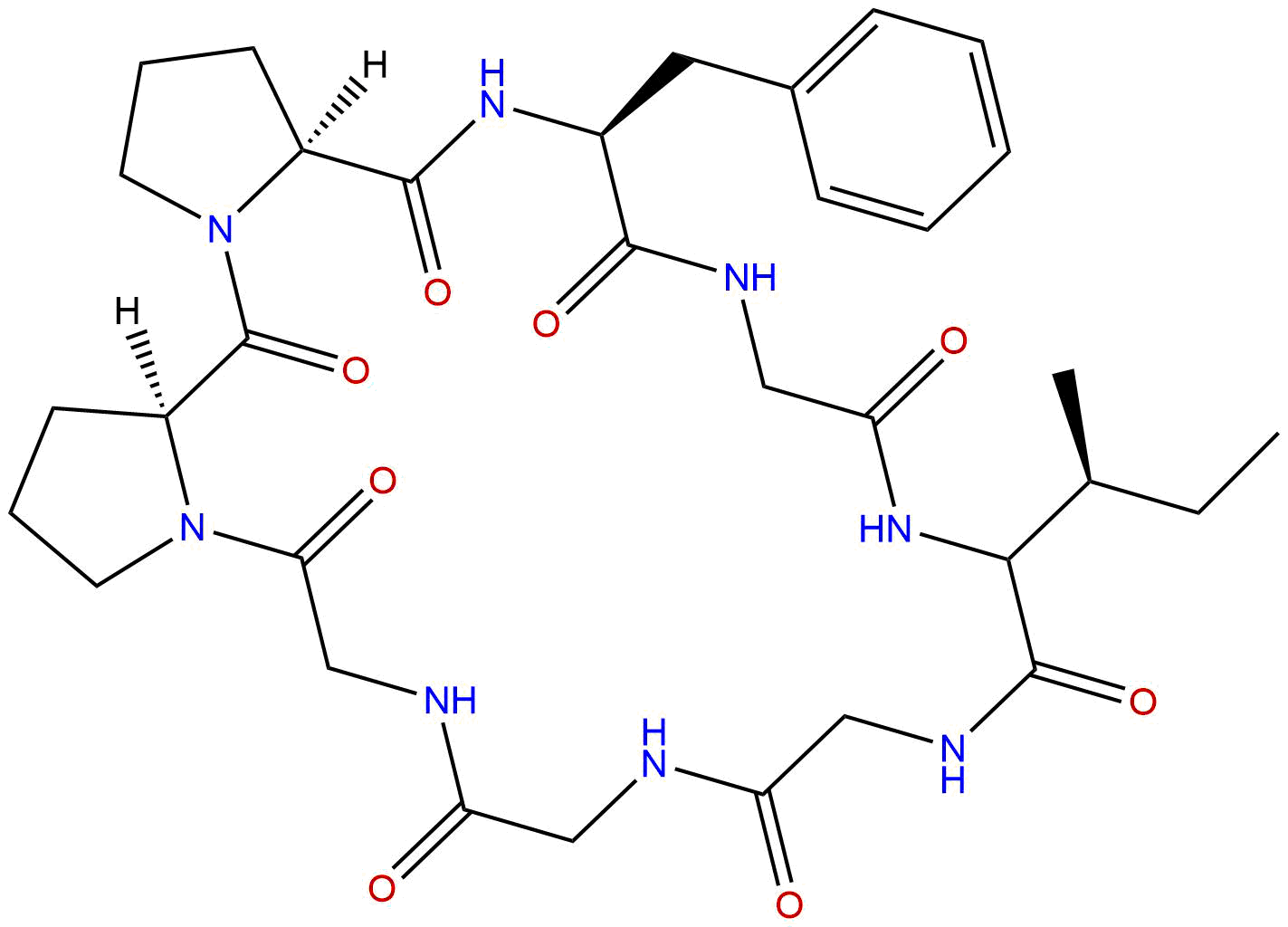
Chemical structure

| Cas No. | 156430-21-6 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | N/A | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C33H46N8O8 | M.Wt | 682.78 |
| Type of Compound | Botanical Cyclopeptides | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

Pseudostellarin B Dilution Calculator

Pseudostellarin B Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.4646 mL | 7.323 mL | 14.646 mL | 29.292 mL | 36.615 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.2929 mL | 1.4646 mL | 2.9292 mL | 5.8584 mL | 7.323 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.1465 mL | 0.7323 mL | 1.4646 mL | 2.9292 mL | 3.6615 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0293 mL | 0.1465 mL | 0.2929 mL | 0.5858 mL | 0.7323 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0146 mL | 0.0732 mL | 0.1465 mL | 0.2929 mL | 0.3662 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Rhamnetin 3-O-rutinoside
Catalog No.:BCX1080
CAS No.:34202-83-0
- 4-Deoxy-4α-phorbol
Catalog No.:BCX1079
CAS No.:37415-57-9
- 6-Methoxyldihydrochelerythrine chloride
Catalog No.:BCX1078
CAS No.:1071676-04-4
- Avenanthramide C
Catalog No.:BCX1077
CAS No.:116764-15-9
- Pseudoginsenoside Rh1
Catalog No.:BCX1076
CAS No.:97744-96-2
- γ-Tocopherol
Catalog No.:BCX1075
CAS No.:54-28-4
- Momilacton A
Catalog No.:BCX1074
CAS No.:51415-07-7
- Momilacton B
Catalog No.:BCX1073
CAS No.:51415-08-8
- Prunetinoside
Catalog No.:BCX1072
CAS No.:89595-66-4
- Stachyanthuside A
Catalog No.:BCX1071
CAS No.:864779-30-6
- 2-O-α-D-Glucopyranosyl-L-ascorbic acid
Catalog No.:BCX1070
CAS No.:129499-78-1
- Tamarixetin-3-O-rutinoside
Catalog No.:BCX1069
CAS No.:20550-05-4
- 6-Iodo Diosmin
Catalog No.:BCX1082
CAS No.:1431536-92-3
- 6'-Sialyllactose Sodium Salt
Catalog No.:BCX1083
CAS No.:157574-76-0
- 3'-Sialyllactose Sodium Salt
Catalog No.:BCX1084
CAS No.:128596-80-5
- Indican
Catalog No.:BCX1085
CAS No.:487-60-5
- Kuwanon W
Catalog No.:BCX1086
CAS No.:95518-95-9
- Avenanthramide E
Catalog No.:BCX1087
CAS No.:93755-77-2
- 4'-O-methyl-Neochlorogenic acid
Catalog No.:BCX1088
CAS No.:1234369-77-7
- 4'-O-methyl-Chlorogenic acid
Catalog No.:BCX1089
CAS No.:57496-29-4
- 4'-O-methylether-Homoeriodictyol 7-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCX1090
CAS No.:1612225-01-0
- 3-O-Coumaroylquinic acid
Catalog No.:BCX1091
CAS No.:1899-30-5
- Methyl lucidenate F
Catalog No.:BCX1092
CAS No.:98665-10-2
- 5-O-(3,4-dimethoxycinnamoyl)shikimic acid
Catalog No.:BCX1093
CAS No.:1338228-77-5
Investigating Potential GLP-1 Receptor Agonists in Cyclopeptides from Pseudostellaria heterophylla, Linum usitatissimum, and Drymaria diandra, and Peptides Derived from Heterophyllin B for the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes: An In Silico Study.[Pubmed:35736482]
Metabolites. 2022 Jun 15;12(6):549.
GLP-1 receptor agonists stimulate GLP-1R to promote insulin secretion, whereas DPP4 inhibitors slow GLP-1 degradation. Both approaches are incretin-based therapies for T2D. In addition to GLP-1 analogs, small nonpeptide GLP-1RAs such as LY3502970, TT-OAD2, and PF-06882961 have been considered as possible therapeutic alternatives. Pseudostellaria heterophylla, Linum usitatissimum, and Drymaria diandra are plants rich in cyclopeptides with hypoglycemic effects. Our previous study demonstrated the potential of their cyclopeptides for DPP4 inhibition. Reports of cyclic setmelanotide as an MC4R (GPCR) agonist and cyclic alpha-conotoxin chimeras as GLP-1RAs led to docking studies of these cyclopeptides with GLP-1R. Heterophyllin B, Pseudostellarin B, Cyclolinopeptide B, Cyclolinopeptide C, Drymarin A, and Diandrine C are abundant in these plants, with binding affinities of -9.5, -10.4, -10.3, -10.6, -11.2, and -11.9 kcal/mol, respectively. The configuration they demonstrated established multiple hydrogen bonds with the transmembrane region of GLP-1R. DdC:(cyclo)-GGPYWP showed the most promising docking score. The results suggest that, in addition to DPP4, GLP-1R may be a hypoglycemic target of these cyclopeptides. This may bring about more discussion of plant cyclopeptides as GLP-1RAs. Moreover, peptides derived from the HB precursor (IFGGLPPP), including IFGGWPPP, IFPGWPPP, IFGGYWPPP, and IFGYGWPPPP, exhibited diverse interactions with GLP-1R and displayed backbones available for further research.
[Chemical constituents of cyclic peptides from fibrous roots of Pseudostellaria heterophylla].[Pubmed:35178918]
Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2022 Jan;47(1):122-126.
Four cyclic peptides were isolated from the 75% ethanol extract of the fibrous roots of Pseudostellaria heterophylla by silica gel, Sephadex LH-20 column chromatography, and semi-preparative HPLC. Through mass spectrometry, NMR and other methods, they were identified as pseudostellarin L(1), heterophyllin B(2), Pseudostellarin B(3), and pseudostellarin C(4). Among them, compound 1 was a new cyclic peptide, and compounds 2-4 were isolated from the fibrous roots of P. heterophylla for the first time. None of these compounds displayed cytotoxic activities against MCF-7, A549, HCT-116, and SGC-7901 cells.
[Regional stability analysis of Pseudostellariae Radix new variety "Shitai No.1"].[Pubmed:28994530]
Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2017 Mar;42(5):882-889.
To provide guidance for certification, popularization and application of Pseudostellariae Radix new variety, the regional adaptation and stabilities of "Shitai No.1" were evaluated. The "Qian taizishen No.1" and "SB-C" varieties (strains) were used as the control varieties. The agronomic, medicinal material traits and medicine quality were used as evaluation index to compare the phenotypic difference of the three varieties (strains) in four planting areas. Compared to the control varieties, 10 agronomic traits of "Shitai No.1" had the smallest coefficient of variation among the 18 agronomic traits, and other 8 agronomic traits placed the middle level. Among 8 medicinal material traits and medicine quality indicators, the coefficient of variation of different regions of the extract content, Pseudostellarin B content, the number of 50 g root tuber, the plant medicinal materials weight and weight of single root of "Shitai No.1" were the smallest compare to other varieties (strains). It could be divided into three groups based on the phenotypic difference of the three varieties (strains) in four planting areas. The "Shitai No.1" was classified as one group, while the "Qian taizishen No.1" and "SB-C" had cross clustering. The regional stability of several index about agronomic traits, medicinal material traits and medicine quality of "Shitai No.1" were better than that of the control varieties (strains). "Shitai No.1" was suitable for planting, popularization and application in the appropriate ecological areas of Guizhou province.
[Research on quality regionalization of cultivated Pseudostellaria heterophylla based on climate factors].[Pubmed:28905557]
Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2016 Jul;41(13):2386-2390.
Maxent model was applied in the study to filtering the climate factors layer by layer. Polysaccharides and Pseudostellarin B the two internal quality evaluation index were combined to analyse the interlinkages between climate factors and chemical constituents in order to search for the critical climate factors of Pseudostellaria heterophylla. Then based on the key climate factors to explicit the quality spatial distribution of P. heterophylla. The results showed that polysaccharides and climatic factors had no significant correlation, suggesting that the indicator was not climate-driven metabolites. Pseudostellarin B could construct regression model with the precipitation. And quality regionalization results showed that Pseudostellarin B content presented firstly increased and then decreased trend from southeast to northwest, which was the consistent change with precipitation. It clearly proposed that precipitation was the key climate factor, which affected the accumulation of cyclopeptide compound for Pseudostellariae Radix.
[Effect of Basic Soil Nutrients and Inorganic Elements on Quality of Pseudostellaria heterophylla Root].[Pubmed:26672330]
Zhong Yao Cai. 2015 Apr;38(4):674-8.
OBJECTIVE: To study the effect of basic soil nutrients and inorganic elements on the quality of Pseudostellaria heterophylla root, in order to reveal the inner link and to provide the scientific basis for rational cultivation of Pseudostellaria heterophylla. METHODS: The medicinal materials of Pseudostellariae Radix and soil samples from 15 habitats were collected, and three essential nutrients, five inorganic elements in the soil and the medicinal contents of polysaccharides and Pseudostellarin B were determined. Then using SPSS software to analyze its relevance. RESULTS: Significant difference of Pseudostellarin B content was found in samples from different provinces, which was not detected in the sample of Fujian Province, but the difference of polysaccharides content was small, at around 30%. Basic nutrients and inorganic elements from the soil for comparison, Pseudostellaria heterophylla from different habitats and cultivation of soil nutrients and inorganic elements contents were very uneven. The contents of Pb, Cu and B in the soil sample of Guizhou Province were the highest, and Cr and available phosphorus content in the soil sample of Shandong Province, Zn and effective potassium in the soil sample of Fujian Province all were the highest. With reference to the Soil Environment Quality Standard (GB15618-1995), most of Pseudostellaria heterophylla soil reached the national standard. From the point of soil elements and medicinal materials quality correlation, Pseudostellarin B content and polysaccharide content had no significant correlation between each element in the soil. CONCLUSION: The ammonium nitrogen, effective potassium, available phosphorus and elements of Pb, Cr, Cu, Zn and B in the soil have no direct effect on effective component content of medicinal materials. 60% of Pseudostellaria heterophylla origin is generally lack of B in soil. It should be appropriate to increase the percentage of boron in the fertilizer management to ensure the quality of Pseudostellaria heterophylla root.
Quantitative determination of Phakellistatin 13, a new cyclic heptapeptide, in rat plasma by liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry: application to a pharmacokinetic study.[Pubmed:19760191]
Anal Bioanal Chem. 2009 Nov;395(5):1461-9.
A sensitive liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) method, followed by a 96-well protein precipitation, has been developed and fully validated for the determination of Phakellistatin 13 (PK13), a new cyclic heptapeptide isolated from the sponge Phakellia fusca Thiele, in rat plasma. After protein precipitation of the plasma samples (50 microL) in a 96-well plate by methanol (200 microL) containing the internal standard Pseudostellarin B (20 ng/mL), the plate was vortex mixed for 3 min. Following filtration for 5 min, the filtrate was directly injected into the LC-MS/MS system. The analytes were separated on an XB-C18 analytical column (5 microm, 50 mm x 4.6 mm i.d.) using an eluent of methanol-water (85:15, v/v) and detected by electrospray ionization mass spectrometry in the negative multiple reaction monitoring mode with a chromatographic run time of 5.0 min. The method was sensitive with a lower limit of quantification (LLOQ) of 0.1 ng/mL, with good linearity (r > 0.999) over the quantitation range of 0.1-5 ng/mL. The validation results demonstrated that this method was significantly specific, accurate, precise, and was successfully applied in measuring levels of PK13 in rat plasma following intravenous administration of 20, 50, and 100 microg/kg of peptide in rats, respectively, which was suitable for the preclinical pharmacokinetic studies on PK13.
Isolation and purification of Pseudostellarin B (cyclic peptide) from Pseudostellaria heterophylla (Miq.) Pax by high-speed counter-current chromatography.[Pubmed:19071377]
Talanta. 2007 Feb 15;71(2):801-5.
Pseudostellarin B (cyclic peptide) was isolated and purified from the herbs of Pseudostellaria heterophylla (Miq.) Pax for the first time by high-speed counter-current chromatography (HSCCC) using a two-phase solvent system consisting of n-butanol-ethyl acetate-water (0.6:4.4:5, v/v). The technique can isolate mg levels of the target compound per run with purity better than 96%. The chemical structure of the compound has been positively confirmed by electrospray ionization time of flight (TOF) MS, (1)H-NMR, (13)C-NMR and (1)H-(13)C-COSY analyses.
Synthesis and biological evaluation of pseudostellarin B.[Pubmed:11421263]
Farmaco. 2001 Apr;56(4):331-4.
A new potent bioactive cyclic peptide Pseudostellarin B has been synthesised. The structure was elucidated by elemental analyses, IR, 1H NMR, 13C NMR and FAB mass spectral data. The synthesised compound was also screened for its antibacterial, antifungal, antiinflammatory and anthelmintic activities.


