Carbonic Anhydrase
Carbonic anhydrases (CAs) are a family of zinc containing metalloproteins that catalyze the reversible conversion of carbon dioxide (CO2) to bicarbonate with the releasing of a proton. Being encoded by three distinct and evolutionarily unrelated gene families, CA enzymes are divided into three subfamilies, α-CAs (in vertebrates, eubacteria, algae and cytoplasm of green plants), β-CAs (in eubacteria, algae and chloroplasts of both mono- and di-cotyledons) and γ-CAs (in Archaea and some eubacteria). Through extensive studies, fourteen different CA isozymes have been identified in mammals, including four cytosolic isozymes (CA I-III and CA VII), four membrane-bound isozymes (CA IV, CA IX, CA XII and CA XIV), one mitochondrial isozyme (CA V) and one secreted isozyme (CA VI).
Products for Carbonic Anhydrase
- Cat.No. Product Name Information
-
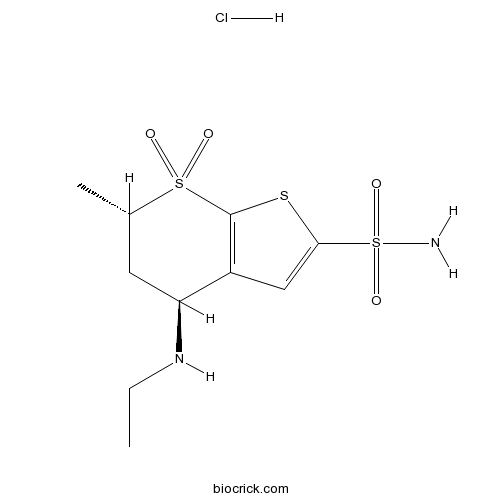
BCC2311
Dorzolamide HClCarbonic anhydrase inhibitor
-
BCC2312
U-104Potent carbonic anhydrase (CA) IX and XII inhibitor

-
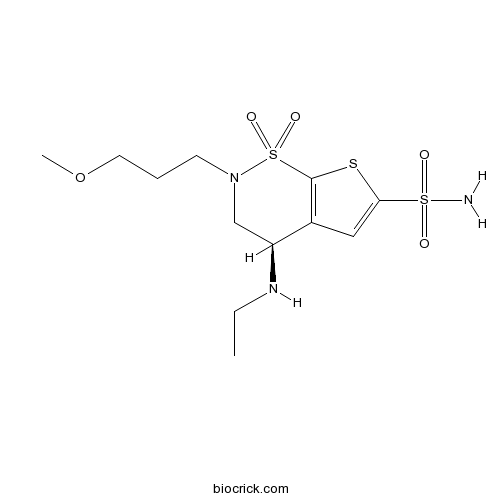
BCC2313
BrinzolamideCA II inhibitor
-
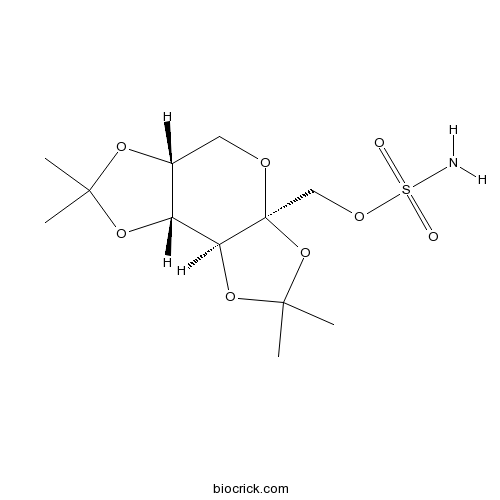
BCC2314
TopiramateGluR5 antagonist; inhibits carbonic anhydrase (CA) II and IV
-
BCC2318
MethazolamideCarbonic anhydrase inhibitor



