Agrimonia pilosa
Agrimonia pilosa
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Agrimonia pilosa
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
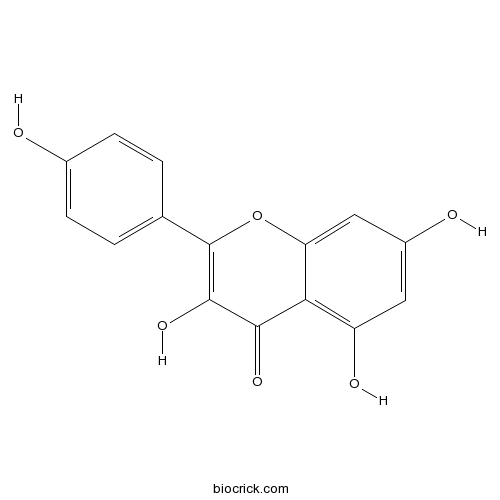
BCN4889
Tiliroside20316-62-5
Instructions

-
BCN5338
Luteolin-7-O-glucuronide29741-10-4
Instructions

-
BCN6386
Pseudoaspidin478-28-4
Instructions

-
BCN0310
trans-p-Coumaric acid501-98-4
Instructions

-
BCN5653
Kaempferol520-18-3
Instructions
-
BCN4171
Wogonin632-85-9
Instructions

Anti-Nociceptive Effect and Standardization from Mixture of Agrimonia pilosa Ledeb and Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge Extracts.[Pubmed: 29847228]
Agrimonia pilosa Ledeb has been previously reported to produce an anti-nociceptive effect in ICR mice in both tail-flick and hot-plate tests. Studies have shown that Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge, also renowned in traditional Chinese medicine, is an effective anti-inflammatory treatment. Among the extraction solvents investigated, a 50% ethanol (EtOH) extract of A. pilosa produced the highest anti-nociceptive effect in monosodium uric acid-induced gout pain models and the greatest yield. The 80% EtOH extract of S. miltiorrhiza moderately inhibited lipopolysaccharide-induced nitric oxide release from RAW 264.7 murine macrophages and exhibited outstanding yield. The mixture of optimized A. pilosa and S. miltiorrhiza extracts were evaluated for enhanced anti-nociceptive effects in gout arthritis treatment. To control extract quality, four marker compounds were determined using an HPLC-DAD method. A 1:1 mixture of A. pilosa 50 and S. miltiorrhiza 80% EtOH extracts of produced better results than when the extracts were administered individually.
The isolation, structural characterization and anti-osteosarcoma activity of a water soluble polysaccharide from Agrimonia pilosa.[Pubmed: 29486840]
A homogenous polysaccharide (APP), with a molecular weight of 120 kDa, was isolated from the dried aerial parts of Agrimonia pilosa. Gas chromatography (GC) and GC-MS analysis revealed that APP has a backbone of 1,3-linked Glcp and 1,3, 6-linked Glcp, and branched with 1-linked Glcp terminal along the main chain in a relative ratio of 2:1:1. We investigated the response of human osteosarcoma U-2 OS cells to APP treatment. MTT result showed that APP significantly inhibited cell viability in a concentration dependent manner via induction of apoptotic death in U-2 OS cells, as determined by annexin V/propidium iodide (PI) staining. Western blot analysis also indicated that APP CRA increased in Bax/Bcl-2 ratios by up-regulating Bax expression and triggered the release of cytochrome c from mitochondria into the cytoplasm. Moreover, APP supplement induced the activation of caspase-3, and -9, but not caspase-8 in U-2 OS cells. Likewise, APP administration significantly suppressed tumor growth in BALB/C nude mice bearing U-2 OS xenograft tumors. All these results indicate that APP-induced apoptosis is associated with the activation of a caspase-3-mediated mitochondrial pathway.
Morphological changes of bacterial cells upon exposure of silver-silver chloride nanoparticles synthesized using Agrimonia pilosa.[Pubmed: 29339306]
Facile, eco-friendly synthesis of metal nanoparticles has been proposed as a cost effective method. In the present study, we propose the facile synthesis of silver-silver chloride (Ag-AgCl) nanoparticles (NPs) using the medicinally important Agrimonia pilosa plant extract without addition of capping or stabilizing agents. The Ag-AgCl NPs synthesis was observed at 40 °C after 10 min incubation; the synthesis of Ag-AgCl NPs was indicated by color change and confirmed by UV-vis spectroscopic peak at 454 nm. TEM analysis confirmed Ag-AgCl NPs were 10-20 nm in size and spherical, and oval in shape. Elemental composition was determined by energy dispersive X-ray analysis, and crystalline structure was confirmed by X-ray diffraction spectroscopy. Different phytocomponents present in the plant extract were analyzed by Gas Chromatography-Mass spectrometry, and the interaction of biomolecules in reduction process was analyzed by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy studies. The synthesized Ag-AgCl NPs showed significant antibacterial efficiency, analyzed by well diffusion assay against pathogenic bacteria including Bacillus cereus, Listeria monocytogenes, Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus saprophyticus, Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas putida. Minimum inhibitory concentration and minimum bactericidal concentration were evaluated by microbroth dilution, and spread plate method, respectively. The possible mechanism of bacterial growth inhibition is due to changes in bacterial cell wall morphology that was studied by FE-SEM analysis.
Agrimonia pilosa Ledeb. aqueous extract improves impaired glucose tolerance in high-fat diet-fed rats by decreasing the inflammatory response.[Pubmed: 28870184]
Agrimonia pilosa Ledeb. is a medicinal plant with physiological activities such as anti-cancer, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory activities and in vitro anti-diabetic activity. However, the effects of aqueous extracts from A. pilosa on insulin-resistant rats have not yet been examined. We investigated the effects of aqueous extract from A. pilosa on impaired glucose metabolism induced by a high-fat diet in rats.


