Ainsliaea fragrans
Ainsliaea fragrans
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Ainsliaea fragrans
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
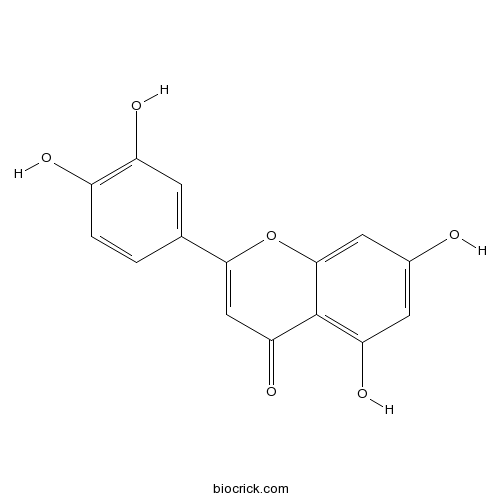
BCN5600
Luteolin491-70-3
Instructions
-
BCN6307
Arbutin497-76-7
Instructions

-
BCN5658
Apigenin520-36-5
Instructions

An integrative investigation of the therapeutic mechanism of Ainsliaea fragrans Champ. in cervicitis using liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry based on a rat plasma metabolomics strategy.[Pubmed: 29729635]
Cervicitis is an extremely common gynecological disease and can be induced by diverse factors such as Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Chlamydia trachomatis, and Mycoplasma genitalium infections. Long-term unhealed cervicitis may lead to a series of diseases including endometritis, salpingitis, pelvic inflammatory disease, and chorioamnionitis. However, the pathogenesis of cervicitis remains unknown. Ainsliaea fragrans Champ. (AFC) has been widely used in clinical treatment of cervicitis. In the present study, we performed an integrative investigation involving histopathology analysis and non-target plasma metabolomics analysis in a cervicitis rat model induced by phenol mucilage, using ultra-performance liquid chromatography coupled with a tandem quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry approach. Based on the integrative investigation, marked metabolomic differences were identified between the cervicitis and control groups using multivariate analysis. As a result, 32 potential biomarkers were identified in the response to cervicitis, and were involved in arachidonic acid metabolism, linoleic acid metabolism, primary bile acid biosynthesis, taurine and hypotaurine metabolism, pantothenate and CoA biosynthesis, and glycerophospholipid metabolism. After treatment, a total of 27 potential biomarkers exhibited altered levels in the AFC group compared to the model group, and 12 metabolites including 1-stearoylglycerophosphoinositol, bolasterone, lysoPC(16:0), lysoPC(20:4), lysoPC(P-16:0), lysoPC(P-18:0), lysoPC(P-18:1), stearoylcarnitine, taurine, lysoPC(17:0), 20-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid, and 1-arachidonoylglycerophosphoinositol returned to their normal levels. This study suggested that the therapeutic mechanism of AFC is related to those altered endogenous metabolites.
[Study on differences of Ainsliaea fragrans from different sources based on UFLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS and PCA analysis].[Pubmed: 29271156]
A rapid and accurate method of UFLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS combined with multivariate statistical analysis was established for the identification of Ainsliaea fragrans from different origins in this study. The A. fragrans from different producing areas of Jiangxi, Yunnan, Henan and Jiangsu were determined by UFLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS in the negative ion mode. And the data of the study were analyzed by the Markerview and other software for the PCA and OPLS-DA cluster analysis as well as t test. The results of the principal component analysis(PCA)showed that the main components from different origins were well distinguished. And the results of multivariate statistical showed the differences and similarities between different producing areas. Besides, 40 different compounds were identified in the negative ion mode. This method for identifying A. fragrans from different producing areas has the advantages of rapid accuracy and simplicity, which laid the foundation for the evaluation of the quality of the A. fragrans.
A robust platform based on ultra-high performance liquid chromatography Quadrupole time of flight tandem mass spectrometry with a two-step data mining strategy in the investigation, classification, and identification of chlorogenic acids in Ainsliaea fragrans Champ.[Pubmed: 28477946]
The chlorogenic acids are the major bioactive constituents of the whole plant of Ainsliaea fragrans Champ. (Xingxiang Tuerfeng). These compounds are usually present as isomeric forms in Xingxiang Tuerfeng. Therefore, an efficient approach should be developed for the rapid discovery and identification of chlorogenic acids isomers through the fragmentation pathway and rules. In this study, the collision induced dissociation tandem mass spectrometry (CID-MS/MS) fragmentation routes of chlorogenic acids were systematically investigated by UHPLC-QTOF-MS/MS in the negative ion mode using eight chlorogenic acids standards. As a result, diagnostic product ions for rapid discovery and classification of chlorogenic acids isomers were determined according to their MS/MS fragmentation patterns and intensity analysis. Based on these findings, a novel two-step data mining strategy was established. The first key step was to screen different kinds of substitution and the skeleton of the quinic acid using the characteristic product ions and neutral losses. The second key step was to screen and classify different types of chlorogenic acids using their diagnostic product ions. It was apply to the rapid investigation, classification, and identification of chlorogenic acids. And the same carbon skeletons from a complex extract of Ainsliaea fragrans Champ. were effectively identified. 88 constituents, including 14 chlorogenic acids types, were rapidly discovered and identified, and in particular, 12 types of chlorogenic acids, including p-CoQC, FQA, BQC, CQA-Glu, CFQA, p-Co-CQC, di-p-CoQC, BCQA, di-CQA-Glu, PCQA, tri-QCA, and P-di-CQA, were first discovered in Ainsliaea fragrans Champ. In conclusion, UHPLC-QTOF-MS/MS method together with a systematic two-step data mining strategy was established as a feasible, effective, and rational technique for analyzing chlorogenic acids. Additionally, this study laid a foundation for the study of the active substances and quality control of Ainsliaea fragrans Champ.
Coumarin derivatives from Ainsliaea fragrans and their anticoagulant activity.[Pubmed: 26315062]
Coumarin derivatives are an important class of C6-C3 plant metabolites that show a variety of bioactivities. Currently, most clinical anticoagulant agents are coumarins, such as warfarin, dicoumarol and acenocoumarol, and patients taking these drugs must be monitored for adverse reactions. In a search for safe and effective anticoagulant compounds from Chinese herbal medicine, a screening procedure on the whole plant of Ainsliaea fragrans was performed. The phytochemical investigation of this plant afforded five new coumarin derivatives, including a pair of natural 4-hydroxycoumarin enantiomers (1), a pair of coumarin enantiomers with a rare polycyclic pyrano[3-2c] carbon skeleton (2) and a 7-hydroxycoumarin derivative (3), together with 5 known biogenetically related compounds (4-8). Enantioseparation of 1 and 2 produced optically pure compounds 1a, 1b, 2a and 2b. The absolute configurations of the new compounds were confirmed by single-crystal X-ray diffraction analysis. In addition, we evaluated the anticoagulant activity of all isolates via activated partial thromboplastin time (APTT), thrombin time (TT) and prothrombin time (PT) assays in vitro and in vivo. Of note, compound 3 displayed potent anticoagulant activity and no significant hepatic or renal toxicity, which could make it a promising agent for further preclinical evaluation for preventing abnormal blood clotting.
The anti-inflammatory activities of Ainsliaea fragrans Champ. extract and its components in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW264.7 macrophages through inhibition of NF-κB pathway.[Pubmed: 25975516]
Ainsliaea fragrans Champ. (A. fragrans) is a traditional Chinese herbal that contains components like 3,5-dicaffeoylquinic acid and 4,5-dicaffeoylquinic acid. It exhibits anti-inflammatory activities which has been used for the treatment of gynecological diseases for many years in China. The aims of the present study were to investigate the anti-inflammatory activities of A. fragrans and elucidate the underlying mechanisms with regard to its molecular basis of action for the best component.
[Quantitative analysis of phenolic acids in ainsliaea fragrans from different habitats].[Pubmed: 25726638]
The contents of major phenolic acids in Ainsliaea fragrans from different habitats were determined,in order to improve quality standards of Ainsliaea fragrans and provide reference for optimization its daodi habitat.
Comparative pharmacokinetics and tissue distribution study of mono-, and di-caffeoylquinic acids isomers of Ainsliaea fragrans Champ by a fast UHPLC-MS/MS method.[Pubmed: 25256061]
Ainsliaea fragrans Champ, as a well-known herb in Traditional Chinese Medicine, was often used in the treatment of gynecological diseases. Caffeoylquinic acids (CQAs) were the bioactive constituents of this plant medicine which primarily contains mono-CQAs (MCQA) and di-CQAs (DCQA). The biosynthesis showed that MCQAs were the precursor of DCQAs. Recent literatures manifested some particular features of DCQAs, different from MCQAs. Therefore it is apparent that a complete and scientific assessment of DCQAs and MCQAs should include not only the DCQAs' pharmacokinetics and distribution but also its degradation products. So an efficient, sensitive rapid resolution liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry (UHPLC-MS/MS) method for the simultaneous determination of the active ingredients in rat plasma and different tissues had been developed and validated. Mass spectrometric detection was performed by selected reaction monitoring mode (MRM) via an electrospray ionization source operating in negative ionization mode. The method was validated in plasma and tissue samples, which showed good linearity over a wide concentration range (r(2)>0.99), and obtained lower limit of quantification (LLOQ) was 2.34 ng·mL(-1) for the analytes in biological samples. The intra- and inter-day assay variability was less than 15%, and the accuracy was between -8.8% and 5.7%. This study provided the pharmacokinetic profiles and the tissue regional distribution of MCQAs, DCQAs and caffeic acid. The results indicated that the DCQAs isomers were absorbed quickly after oral administration and degradation products MCQAs were mostly found in tissues, not in plasma. Besides, 1,5-DCQA was the prior configuration for the isomerization phenomenon. The small intestine was the main absorption site for DCQAs. Interestingly, the content of the DCQA and MCQA isomers was all high in the ovary and uterus, and some could pass through the barrier between the blood and brain obviously.
High-performance liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry for simultaneous determination of four dicaffeoylquinic acids in rat plasma.[Pubmed: 22854127]
A specific and reliable HPLC-MS/MS method was developed and validated for the simultaneous determination of four dicaffeoylquinic acids (DCQA): 3,4-DCQA, 1,5-DCQA, 3,5-DCQA and 4,5-DCQA. The analytes were separated on a C₁₈ column (150 mm × 2.1 mm, 1.8 μm) and a triple-quadrupole mass spectrometry equipped with an electrospray ionization (ESI) source was applied for detection. The plasma sample was prepared by a liquid-liquid extraction method and the recovery for the four analytes was around 80%. The calibration curves were linear over a concentration range of 10.6-1060.0 ng/mL for 3,4-DCQA, 19.2-1920.0 ng/mL for 1,5-DCQA, 14.0-2900.0 ng/mL for 3,5-DCQA, 9.7-970.0 ng/mL for 4,5-DCQA. The intra-day and inter-day precision was less than 15% and the relative error (RE) were all within ±15%. The validated method was successfully applied to a pharmacokinetics study in rats after oral administration of the extracts of Ainsliaea fragrans cham (a traditional Chinese herb).
Two novel sesquiterpenoids from Ainsliaea fragrans Champ.[Pubmed: 20183246]
A new sesquiterpene lactone, 3beta-O-beta-D-glucopyranosyl-8alpha-hydroxy-11alpha,13-dihydrozaluzanin C (1), and a novel trinorguaiane-type sesquiterpene, 4beta,10alpha-dimethyl-1beta,5alpha-bicycle[3,5,0]dec-6-en-4alpha,10beta-diol (2), together with three known compounds, glucozaluzanin C (3), 11alpha,13-dihydrozaluzanin C (4), and 8alpha-hydroxy-11alpha,13-dihydrozaluzanin C (5), were isolated from the whole plant of Ainsliaea fragrans Champ. The structures of 1 and 2 were elucidated on the basis of detailed spectral analysis. Structures of the known compounds were identified by comparison of its spectral data with those values in the literature.


