Clematis tangutica
Clematis tangutica
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Clematis tangutica
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
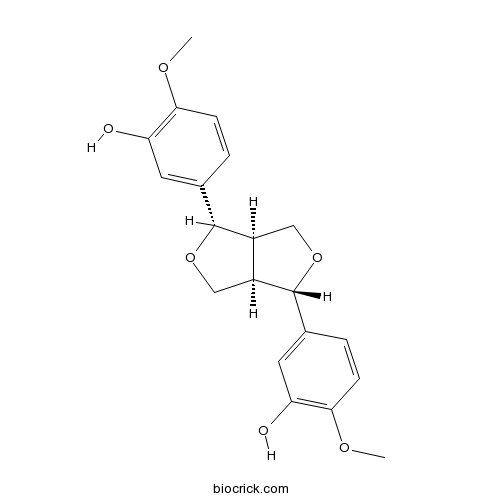
BCN7834
Clemaphenol A362606-60-8
Instructions
Apigenin-7-O-β-d-(-6″-p-coumaroyl)-glucopyranoside pretreatment attenuates myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury via activating AMPK signaling.[Pubmed: 29705352]
Apigenin-7-O-β-d-(-6″-p-coumaroyl)-glucopyranoside (APG) was considered as the major active compound derived from Clematis tangutica. Though we have demonstrated that APG exerts cardioprotective effects, the mechanism of APG-mediated cardioprotection remains largely unknown. Numerous studies indicate that endoplasmic reticulum stress (ERS) is a vital injury factor in myocardial ischemia reperfusion (MI/R). In this study, we mainly investigated whether modulation of the ERS and AMPK were involved in the cardioprotective action of APG during MI/R injury.
A new flavonoid glycoside (APG) isolated from Clematis tangutica attenuates myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury via activating PKCε signaling.[Pubmed: 28024940]
Clematis tangutica has been shown to be beneficial for the heart; however, the mechanism of this effectremains unknown. Apigenin-7-O-β-D-(-6″-p-coumaroyl)-glucopyranoside (APG) is a new flavonoid glycoside isolated from Clematis tangutica. This study investigates the effects of APG on myocardial ischemia/reperfusion (IR) injury (IRI). An IRI model of primary myocardial cells and mice was used in this study. Compared with the IR group, APG preconditioning is protective against IRI in primary myocardial cells and in mice hearts in a dose-dependent manner. The cardioprotective mechanisms of APG may involve a significant PKCε translocation into the mitochondria and an activation of the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway, which respectively suppressesmitochondrial oxidative stress and inhibits apoptosis. In addition, PKCε-targeted siRNA and a PKCε specialized inhibitor (ε-V1-2) were used to inhibit PKCε expression and activity. The inhibition of PKCε reversed the cardioprotective effect of APG, with an inhibition of Nrf2/HO-1 activation and increased mitochondrial oxidative stress and cardiomyocyte apoptosis. In conclusion, PKCε activation plays an important role in the cardioprotective effects of APG. PKCε activation induced by APG preconditioning reduces mitochondrial oxidative stress and promotes Nrf2/HO-1-mediated anti-apoptosis signaling.
Cytotoxic triterpenoid saponins from Clematis tangutica.[Pubmed: 27262876]
Eight previously undescribed oleanane-type triterpenoid saponins, clematangoticosides A-H, together with eight known saponins, were isolated from the whole plants of Clematis tangutica (Maxim.) Korsh. Their structures were elucidated by extensive spectroscopic analysis, in combination with chemical methods (acid hydrolysis and mild alkaline hydrolysis). Clematangoticosides D-G were found to be unusual 23, 28-bidesmosidic glycosides. The cytotoxic activities of all of the isolated saponins were evaluated against the four human cancer cell lines SGC-7901, HepG2, HL-60 and U251MG. Clematoside S, sapindoside B, kalopanax saponin A, and koelreuteria saponin A exhibited cytotoxicity against all of the test cancer cell lines with IC50 values in the range of 1.88-27.20 μM, while clematangoticoside D and F showed selective cytotoxicity against SGC-7901 with IC50 values of 24.22 and 21.35 μM, respectively.
Triterpenoid saponins with anti-myocardial ischemia activity from the whole plants of Clematis tangutica.[Pubmed: 23670628]
Four new triterpenoid saponins named clematangosides A-D (1-4) along with six known saponins (5-10) were isolated from the whole plants of Clematis tangutica. Their structures were determined by extensive spectral analysis and chemical evidences. All saponins were evaluated for their protective effects in hypoxia-induced myocardial injury model. Compounds 2-4, 6, and 10 exhibited anti-myocardial ischemia activities with ED50 values in the range of 75.77-127.22 µM.
Triterpenoid saponins from Clematis tangutica and their cardioprotective activities.[Pubmed: 23266737]
Phytochemical investigation of the whole plants of Clematis tangutica led to the isolation of three new triterpenoid saponins (1-3), together with four known saponins (4-7). Their structures were determined by extensive spectral analysis and chemical evidences. Compounds 1-7 were evaluated for their cardioprotective activities in cardiomyocytes anoxia/reoxygenation (A/R) model. The results showed that those saponins exhibited cardioprotective effects by decreasing the levels of creatine kinase-MB (CK-MB) and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH).
Two new antifungal saponins from the Tibetan herbal medicine Clematis tangutica.[Pubmed: 12865975]
Bioassay-guided fractionation of the ethanol extract of the aerial parts of Clematis tangutica led to the isolation of two new antifungal triterpene saponins. Their structures were determined to be 3- O-alpha- L-arabinopyranosyl hederagenin 28- O-alpha- L-rhamnopyranosyl ester ( 1) and 3- O-beta- D-glucopyranosyl-(1--> 4)-alpha- L-arabinopyranosyl hederagenin 28- O-alpha- L-rhamnopyranosyl ester ( 2) on the basis of spectral data and chemical evidence. Inhibitory activities of the two saponins against seven fungal strains were evaluated. Compounds 1 and 2 showed evident antifungal activity (MIA approximately 2.5 micrograms/disc) against Saccharomyces cerevisiae, similar to the positive control amphotericin B and ordinary activities (MIA approximately 10 micrograms/disc) against Penicillium avellaneum UC-4376, Candida glabrata, Trichosporon beigelii and Pyricularia oryzae. Compound 2 is a better antifungal agent than compound 1 against most of the fungal strains that were tested.
Triterpenoid saponins from Clematis tangutica.[Pubmed: 11488472]
Two new triterpenoid saponins, tanguticoside A and B along with seven known saponins vitalboside B, alpha-hederin, saponin PK, beta-hederin, saponin PJ3, saponin PE, and ciwujianoside A were isolated from aerial part of Clematis tangutica. By chemical and spectral evidences methods, the structures of tanguticoside A and B were elucidated as 3-O-beta-D-glucopyranosylhederagenin 28-O-alpha-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1-->4)-beta-D-glucopyranosyl-(1-->6)-beta-D-glucopyranoside and 3-O-beta-D-glucopyranosyl-(1-->2)-beta-D-glucopyranosylhederagenin 28-O-alpha-D-rhamnopyranosyl-(1-->4)-beta-D-glucopyranosyl-(1-->6)-beta-D-glucopyranoside, respectively.


