Cuscuta chinensis
Cuscuta chinensis
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
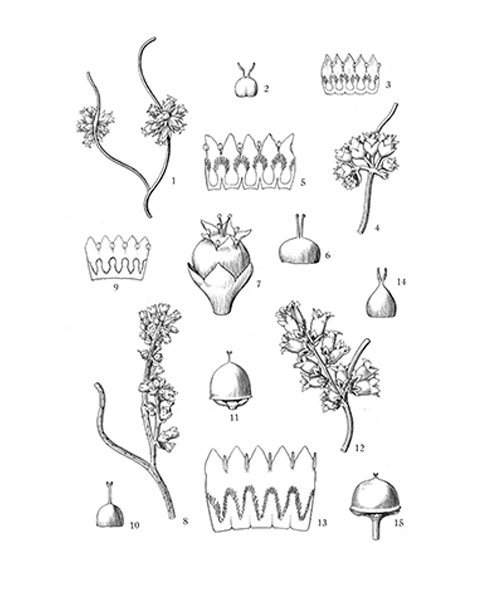
Natural products/compounds from Cuscuta chinensis
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
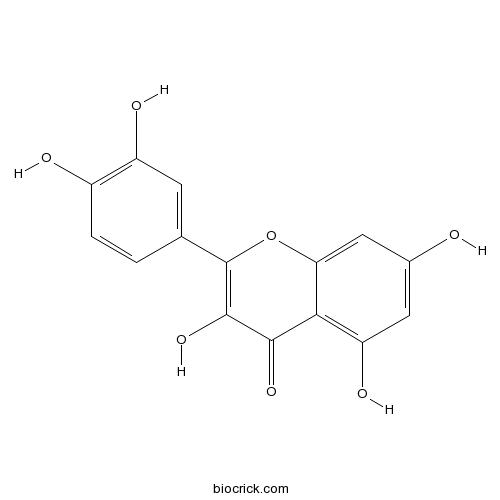
BCN6049
Quercetin117-39-5
Instructions
-
BCN5549
Astragalin480-10-4
Instructions

-
BCN5551
Isorhamnetin480-19-3
Instructions

-
BCN5570
Hyperoside482-36-0
Instructions

-
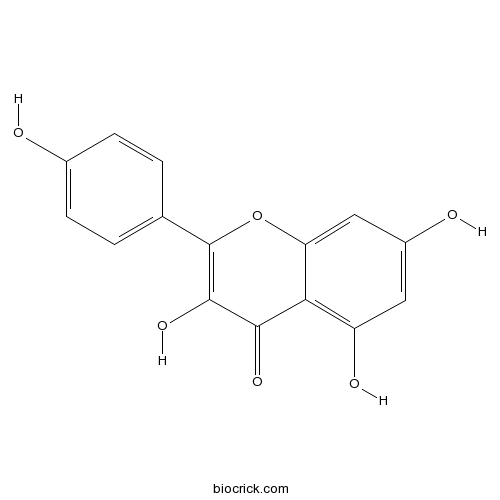
BCN5653
Kaempferol520-18-3
Instructions
-
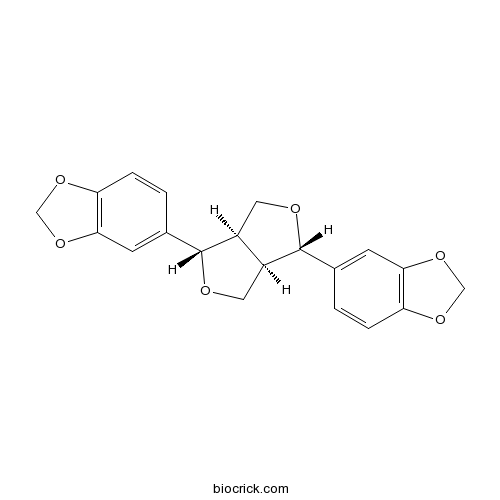
BCN4123
Sesamin607-80-7
Instructions
-
BCN5907
Cryptochlorogenic acid905-99-7
Instructions

-
BCN4450
Neochlorogenic acid906-33-2
Instructions

Improved antimelanogenesis and antioxidant effects of polysaccharide from Cuscuta chinensis Lam seeds after enzymatic hydrolysis.[Pubmed: 29846408]
Cuscuta chinensis polysaccharide (CPS) was extracted using hot water and enzymatically hydrolyzed C. chinensis polysaccharide (ECPS) was produced by the mannase enzymatic hydrolysis process. The purpose of this research was to investigate the antimelanogenic activity of ECPS and CPS in B16F10 melanoma cells. The in vitro antioxidant activity was assessed by their ferric iron reducing power and DPPH free radical scavenging activities. The molecular mass distribution of polysaccharides was determined using SEC-MALLS-RI. CPS was successfully enzymatically degraded using mannase and the weighted average molecular weights of CPS and ECPS were 434.6 kDa and 211.7 kDa. The results of biological activity assays suggested that the enzymatically hydrolyzed polysaccharide had superior antimelanogenic activity and antioxidant effect than the original polysaccharide. ECPS exhibited antimelanogenic activity by down-regulating the expression of tyrosinase, MITF, and TRP-1 without cytotoxic effects in B16F10 melanoma cells. In conclusion, ECPS have the potential to become a skin whitening product.
Protective effect of MOTILIPERM in varicocele-induced oxidative injury in rat testis by activating phosphorylated inositol requiring kinase 1α (p-IRE1α) and phosphorylated c-Jun N-terminal kinase (p-JNK) pathways.[Pubmed: 29316840]
MOTILIPERM was prepared as a mixture of extracts of three medicinal herbs [roots of Morinda officinalis How (Rubiaceae), outer scales of Allium cepa L. (Liliaceae) and seeds of Cuscuta chinensis Lamark (Convolvulaceae)].
[Varieties textual research, resource investigation and identification of commercial drugs on Cuscutae Semen].[Pubmed: 29235303]
Through the textual research, resource investigation, literature reviews (including Flora of China, municipal Flora, pharmacopoeia of China and municipal drug standards) and identification of commercial drugs on Cuscutae Semen, it was found the species described in the herbal textual was Cuscuta chinensis, with good quality from Shandong and Henan Province. The identification of commodities showed the majority drugs were from C. australis, varied from the ancient herbal textuals .Mordern literature reviews indicate that it was necessary to strengthen the research on Cuscutae Semen from C. australis, C. chinensis and C. japonica because of their differences in resources, macroscopical and microscopical characters, while wrong descriptions in some literatures. It was suggested that the two species (C. australis and C. chinensis) should be separated in pharmacopoeia of China. The study provides scientific basis for the development and utilization of Cuscutae Semen.
Selected hepatoprotective herbal medicines: Evidence from ethnomedicinal applications, animal models, and possible mechanism of actions.[Pubmed: 29047177]
Insight into the hepatoprotective effects of medicinally important plants is important, both for physicians and researchers. Main reasons for the use of herbal medicine include their lesser cost compared with conventional drugs, lesser undesirable drug reactions and thus high safety, and reduced side effects. The present review focuses on the composition, pharmacology, and results of experimental trials of selected medicinal plants: Silybum marianum (L.) Gaertn., Glycyrrhiza glabra, Phyllanthus amarus Schumach. & Thonn., Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge., Astragalus membranaceus (Fisch.) Bunge, Capparis spinosa (L.), Cichorium intybus (L.), Solanum nigrum (L.), Sapindus mukorossi Gaertn., Ginkgo biloba (L.), Woodfordia fruticosa (L.) Kurz, Vitex trifolia (L.), Schisandra chinensis (Turcz.) Baill., Cuscuta chinensis (Lam.), Lycium barbarum, Angelica sinensis (Oliv.) Diels, and Litsea coreana (H. Lev.). The probable modes of action of these plants include immunomodulation, stimulation of hepatic DNA synthesis, simulation of superoxide dismutase and glutathione reductase to inhibit oxidation in hepatocytes, reduction of intracellular reactive oxygen species by enhancing levels of antioxidants, suppression of ethanol-induced lipid accumulation, inhibition of nucleic acid polymerases to downregulate viral mRNA transcription and translation, free radical scavenging and reduction of hepatic fibrosis by decreasing the levels of transforming growth factor beta-1, and collagen synthesis in hepatic cells. However, further research is needed to identify, characterize, and standardize the active ingredients, useful compounds, and their preparations for the treatment of liver diseases.
Oral administration of kaempferol inhibits bone loss in rat model of ovariectomy-induced osteopenia.[Pubmed: 29031689]
Postmenopausal osteoporosis and osteoporotic fractures constitute an increasing problem in developing countries. Kaempferol, isolated from seeds of Cuscuta chinensis, is an active flavonoid inhibiting in vitro osteoclast activity. The aim of the presented research was an assessment of kaempferol effect on estrogen-deficiency-induced bone structure disturbances in rats.
In Silico Prediction of the Anti-Depression Mechanism of a Herbal Formula (Tiansi Liquid) Containing Morinda officinalis and Cuscuta chinensis.[Pubmed: 28954415]
None
Anti-fibrotic effects of Cuscuta chinensis with in vitro hepatic stellate cells and a thioacetamide-induced experimental rat model.[Pubmed: 28651481]
Cuscuta chinensis Lam. (Convolvulaceae) has been used as a traditional herbal remedy for treating liver and kidney disorders.


