Dendrobium crystallinum
Dendrobium crystallinum
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Dendrobium crystallinum
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
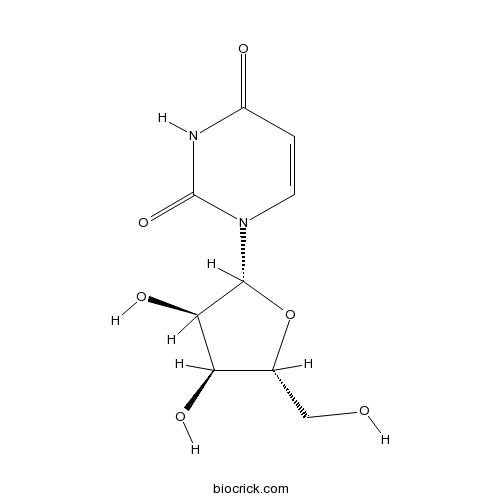
BCN4090
Uridine58-96-8
Instructions
-
BCN9061
(±)-Naringenin67604-48-2
Instructions
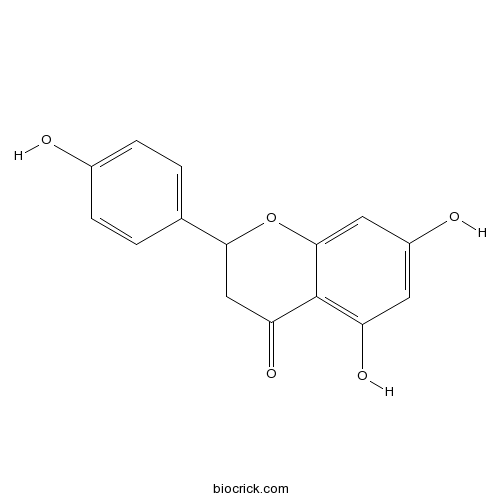
Discrimination of the rare medicinal plant Dendrobium officinale based on naringenin, bibenzyl, and polysaccharides.[Pubmed: 23233224]
The aim of this study was to establish a method for discriminating Dendrobium officinale from four of its close relatives Dendrobium chrysanthum, Dendrobium crystallinum, Dendrobium aphyllum and Dendrobium devonianum based on chemical composition analysis. We analyzed 62 samples of 24 Dendrobium species. High performance liquid chromatography analysis confirmed that the four low molecular weight compounds 4',5,7-trihydroxyflavanone (naringenin), 3,4-dihydroxy-4',5-dime-thoxybibenzyl (DDB-2), 3',4-dihydroxy-3,5'-dimethoxybibenzyl (gigantol), and 4,4'-dihydroxy-3,3',5-trimethoxybibenzy (moscatilin), were common in the genus. The phenol-sulfuric acid method was used to quantify polysaccharides, and the monosaccharide composition of the polysaccharides was determined by gas chromatography. Stepwise discriminant analysis was used to differentiate among the five closely related species based on the chemical composition analysis. This proved to be a simple and accurate approach for discriminating among these species. The results also showed that the polysaccharide content, the amounts of the four low molecular weight compounds, and the mannose to glucose ratio, were important factors for species discriminant. Therefore, we propose that a chemical analysis based on quantification of naringenin, bibenzyl, and polysaccharides is effective for identifying D. officinale.
Enzymatic fingerprints of polysaccharides of Dendrobium officinale and their application in identification of Dendrobium species.[Pubmed: 22261857]
Enzymatic fingerprinting of polysaccharides from Dendrobium officinale was studied and applied to authenticate Dendrobium species. Results showed that Dendrobium officinale species from Anhui province, Fujian province, Yunnan province, Guangdong province and Guangxi province of China, could be identified by polysaccharide analysis using carbohydrate gel electrophoresis (PACE). However, the fingerprints of Dendrobium officinale from Jiangxi province, Hu'nan province and Wenzhou, Yandangshan and Fuyang in Zhejiang province were very similar. As far as the fingerprints of different Dendrobium species were concerned, the differences between Dendrobium officinale, Dendrobium huoshanense, Dendrobium moniliforme, Dendrobium devonianum, Dendrobium aphyllum, Dendrobium wilsonii and Dendrobium crystallinum were obvious. Moreover, the genetic relationships between different samples were analyzed by using principal component analysis and unweighted pair group method with arithmetic mean cluster analysis. Results suggested that polysaccharide fingerprint analysis by PACE has the potential to become a valuable new method for the identification and control of quality of herbal medicines in future.
Five new compounds from Dendrobium crystallinum.[Pubmed: 20183252]
Five new compounds, dencryol A (1), dencryol B (2), crystalltone (3), crystallinin (4), and 3-hydroxy-2-methoxy-5,6-dimethylbenzoic acid (5), together with six known compounds, dendronobilin B (6), syringic acid (7), apigenin (8), isoviolanthin (9), 6'''-glucosyl-vitexin (10), and palmarumycin JC2 (11), have been isolated from the stems of Dendrobium crystallinum, of which compounds 9-11 were isolated from the genus Dendrobium for the first time, and all the other compounds were first obtained from this plant. Their structures were established on the basis of spectroscopic analysis and literature data.
[Studies on chemical constituents of Dendrobium crystallinum].[Pubmed: 19007013]
To study the chemical constituents of Dendobium crystallinum.


