Elaeagnus umbellata
Elaeagnus umbellata
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Elaeagnus umbellata
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
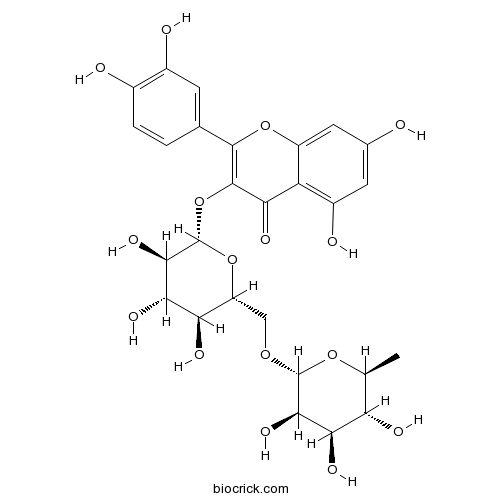
BCN1684
Rutin153-18-4
Instructions
Peltate trichomes on biogenic silvery leaves of Elaeagnus umbellata.[Pubmed: 29675911]
External and internal features of Elaeagnus umbellata leaves were investigated by optical and electron microscopy. The adaxial (upper) and abaxial (lower) leaf surfaces appeared green and silver in color, respectively. There were peltate trichomes on both the adaxial and abaxial leaf surfaces. The peltate trichomes were 200-300 μm in diameter and shield or umbrella-shaped. They had a central dome and 20-30 radiating rays that were fused to form a circular cap in the center and tapered at the end. The density of peltate trichomes was apparently higher on the abaxial leaf surface than on the adaxial leaf surface. At least two layers of peltate trichomes were commonly observed on the abaxial leaf surface. The epidermal cells on the abaxial leaf surface had convex lens-like shape in cross sections. No distinct chloroplasts were found in the cytoplasm of peltate trichomes. These results suggest that the silver coloration on the abaxial leaf surface is mostly due to structural coloration associated with the profuse overlapping peltate trichomes having a circular cap of radially fused rays. The shrub did not show any pigmentary cellular features associated with the silver coloration. With the silvery leaves as a reflective surface for shaded leaves in canopy, E. umbellata is likely to adapt to the harsh non-native light-demanding environments.
From endogenous to exogenous pattern formation: Invasive plant species changes the spatial distribution of a native ant.[Pubmed: 28231634]
Invasive species are a significant threat to global biodiversity, but our understanding of how invasive species impact native communities across space and time remains limited. Based on observations in an old field in Southeast Michigan spanning 35 years, our study documents significant impacts of habitat change, likely driven by the invasion of the shrub, Elaeagnus umbellata, on the nest distribution patterns and population demographics of a native ant species, Formica obscuripes. Landcover change in aerial photographs indicates that E. umbellata expanded aggressively, transforming a large proportion of the original open field into dense shrubland. By comparing the ant's landcover preferences before and after the invasion, we demonstrate that this species experienced a significant unfavorable change in its foraging areas. We also find that shrub landcover significantly moderates aggression between nests, suggesting nests are more related where there is more E. umbellata. This may represent a shift in reproductive strategy from queen flights, reported in the past, to asexual nest budding. Our results suggest that E. umbellata may affect the spatial distribution of F. obscuripes by shifting the drivers of nest pattern formation from an endogenous process (queen flights), which led to a uniform pattern, to a process that is both endogenous (nest budding) and exogenous (loss of preferred habitat), resulting in a significantly different clustered pattern. The number and sizes of F. obscuripes nests in our study site are projected to decrease in the next 40 years, although further study of this population's colony structures is needed to understand the extent of this decrease. Elaeagnus umbellata is a common invasive shrub, and similar impacts on native species might occur in its invasive range, or in areas with similar shrub invasions.
Biological screening of Elaeagnus umbellata Thunb.[Pubmed: 25553686]
The bark and fruit extracts of Elaeagnus umbellata have been investigated for their antibacterial, anti-fungal, insecticidal and phytotoxic activities. The petroleum ether extracts of the plant showed significant activity against E. faecalis. The activity of dichloromethane extract was also determined significant against S. aureus. The chloroform extract indicated low activity against E. coli, K. pneumoniae, B. subtilis and S. flexenari. The ethyl acetate fraction demonstrated significant activity against K. pneumoniae while methanolic extract exhibited significant activity against E. coli. All extracts showed low phytotoxic activity. The dichloromethane extract exhibited moderate insecticidal activity while other extract indicated low activity.
Organization of nif gene cluster in Frankia sp. EuIK1 strain, a symbiont of Elaeagnus umbellata.[Pubmed: 21769644]
The nucleotide sequence of a 20.5-kb genomic region harboring nif genes was determined and analyzed. The fragment was obtained from Frankia sp. EuIK1 strain, an indigenous symbiont of Elaeagnus umbellata. A total of 20 ORFs including 12 nif genes were identified and subjected to comparative analysis with the genome sequences of 3 Frankia strains representing diverse host plant specificities. The nucleotide and deduced amino acid sequences showed highest levels of identity with orthologous genes from an Elaeagnus-infecting strain. The gene organization patterns around the nif gene clusters were well conserved among all 4 Frankia strains. However, characteristic features appeared in the location of the nifV gene for each Frankia strain, depending on the type of host plant. Sequence analysis was performed to determine the transcription units and suggested that there could be an independent operon starting from the nifW gene in the EuIK strain. Considering the organization patterns and their total extensions on the genome, we propose that the nif gene clusters remained stable despite genetic variations occurring in the Frankia genomes.
Proteomic analysis of up-accumulated proteins associated with fruit quality during autumn olive (Elaeagnus umbellata) fruit ripening.[Pubmed: 21175188]
Fruit ripening is a complex phenomenon that makes berries attractive and also determines their nutritional value. Autumn olive ( Elaeagnus umbellata Thunb.) fruit is a rich source of many human health-related nutrients. The changes in pericarp color are initiated at early developmental stages, coinciding with the fast increase in fruit size. Fruit quality traits with special emphasis on soluble sugars, organic acids, lycopene, and total protein contents were assayed during the fruit ripening. In the fully ripe fruit, glucose and fructose were the principal sugars, malic acid was the most abundant organic acid, and lycopene concentration was extremely high. A proteomic analysis was used to identify up-accumulated proteins induced by the ripening. Among 63 up-accumulated protein spots, 43 were successfully identified by MALDI-TOF/TOF-MS. All 43 proteins were novel for autumn olive, and 8 were first reported in the fruit. Twenty-one proteins of known function were involved in sugar metabolism, citric acid cycle, isoprenoid metabolism, fatty acid synthesis, and protein hydrolysis. The possible roles of these 21 accumulated proteins in autumn olive fruit quality are discussed.
Soil and groundwater nitrogen response to invasion by an exotic nitrogen-fixing shrub.[Pubmed: 20400603]
Autumn-olive (Elaeagnus umbellata Thunb.) is an invasive, exotic shrub that has become naturalized in the eastern United States and can fix nitrogen (N) via a symbiotic relationship with the actinomycete Frankia. Fixed N could potentially influence nutrient cycling rates and N leaching into soil water and groundwater. In situ net N mineralization, net nitrification, and net ammonification rates, as well as soil water and groundwater nitrate N (NO(3)-N) and ammonium N (NH(4)-N) concentrations, were measured under autumn-olive-dominated and herbaceous open field areas in southern Illinois. Soil net N mineralization and net nitrification rates were higher under autumn-olive compared with open field (p < 0.05) and could be driven, in part, by the relatively low C/N ratio (11.41 +/- 0.29) of autumn-olive foliage and subsequent litter. Autumn-olive stands also had greater soil water NO(3)-N (p = 0.003), but soil water NH(4)-N concentrations were similar between autumn-olive and open field. Groundwater NO(3)-N and NH(4)-N concentrations were similar beneath both types of vegetation. Groundwater NO(3)-N concentrations did not reflect patterns in soil N mineralization and soil water NO(3)-N most likely due to a weak hydrologic connection between soil water and groundwater. The increased N levels in soil and soil water indicate that abandoned agroecosystems invaded by autumn-olive may be net sources of N to adjacent terrestrial and aquatic systems rather than net sinks.
Cloning and expression analysis of carotenogenic genes during ripening of autumn olive fruit (Elaeagnus umbellata).[Pubmed: 19459638]
Autumn olive ( Elaeagnus umbellata Thunb.) is an extremely lycopene-rich natural source, and lycopene concentration of ripe wild autumn olive fruit was 12 times higher than that of tomato. Lycopene formation was found to increase with significant reduction of other carotenoids and chlorophylls during fruit ripening. To elucidate the molecular basis of massive lycopene accumulation in autumn olive fruit, seven cDNA fragments were cloned encoding enzymes of the main steps of carotenoid biosynthetic pathway, which were geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate synthase (EutGgps), phytoene synthase (EutPsy), phytoene desaturase (EutPds), zeta-carotene desaturase (EutZds), lycopene beta-cyclase (EutLcy-b), lycopene epsilon-cyclase (EutLcy-e), and beta-carotene hydroxylase (EutBch). The accumulation of lycopene in the fruit was concomitant with the up-regulation of upstream genes of lycopene synthesis (EutGgps, EutPsy, EutPds, and EutZds) and down-regulation of downstream genes (EutLcy-b and EutBch) and in particular with the silence of EutLcy-e throughout fruit ripening. Thus, lycopene accumulation in autumn olive fruit was highly regulated by the coordination of the expression among carotenogenic genes and by fruit ripening.


