Elephantopus scaber
Elephantopus scaber
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Elephantopus scaber
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
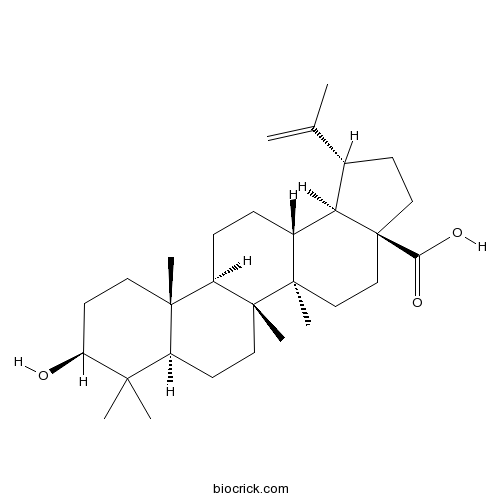
BCN5524
Betulinic acid472-15-1
Instructions
-
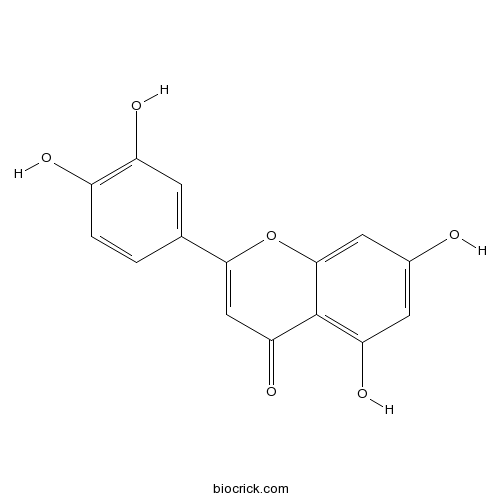
BCN5600
Luteolin491-70-3
Instructions
-
BCN2356
Diosmetin520-34-3
Instructions

-
BCN5725
Lupeol545-47-1
Instructions

Deoxyelephantopin ameliorates lipopolysaccharides (LPS)-induced memory impairments in rats: Evidence for its anti-neuroinflammatory properties.[Pubmed: 29792878]
Neuroinflammation is a critical pathogenic mechanism of most neurodegenerative disorders especially, Alzheimer's disease (AD). Lipopolysaccharides (LPS) are known to induce neuroinflammation which is evident from significant upsurge of pro-inflammatory mediators in in vitro BV-2 microglial cells and in vivo animal models. In present study, we investigated anti-neuroinflammatory properties of deoxyelephantopin (DET) isolated from Elephantopus scaber in LPS-induced neuroinflammatory rat model.
Preclinical Hepatoprotective Effect of Herbalism against Ethanol Induced Hepatotoxicity: A Review.[Pubmed: 29600757]
Liver ailments including alcoholic liver disease (ALD), still remain the main reason for morbidity & mortality worldwide. In fact, ALD is a multifactorial disease with complex pathophysiology which is linked to several types of liver damages including steatohepatitis, fibrosis and cirrhosis. This review emphasizes on 30 herbal medicinal plants with their extracts studied for protective effect against ALD and current scientific evidence of ALD cure by thirty Indian Materia Medica including Tilia Platyphyllos, Amomum subulatum, Carica papaya, Pogostemon patchouli, Commelina benghalensis, Bacopamonnieri, Pecan nut, Allium cepa, Beta Vulgaris, Adina cordifolia, Ocimum gratissimum, Vernonia amygdalina, Sida veronicaefolia, Chenopodium album, Korean red ginseng, Elephantopus scaber, Tecomella undulata, Prunus armeniaca, Sea tangle (Laminaria japonica), Emblica officinalis, Saccharum officinarum, Cocculus hirsutus, Cassia roxburghii, Zhi-Zi-Da-Huang, Phyllanthus amarus, Aegle marmelos, Agrimonia eupatoria, Flaveria trinervia, Curcuma longa and Garcinia indica. Reduction in oxidative stress, improvement in inflammation, reduction in degeneration of fat and necrosis are some of the mechanisms of action of these medicinal plants observed in alcohol-induced in-vivo and in-vitro liver injury models. Accordingly, this review provides several evidences which show that these medicinal plants could be used for the treatment and prevention of ALD.
Development of a Novel Herbal Formulation To Inhibit Biofilm Formation in Toxigenic Vibrio cholerae.[Pubmed: 29053421]
Vibrio cholerae, a causative agent of the waterborne disease cholera, still threatens a large proportion of world's population. The role of biofilm formation in V. cholerae pathogenesis is well established, as it provides the bacterium enhanced tolerance to antimicrobial agents and increased transmission. In the present study, four medicinal plants used in traditional medicines with antidiarrheal properties were evaluated for its antibiofilm activity. Methanol extracts of these plants (Centella asiatica, Elephantopus scaber, Camellia sinensis, and Holarrhena antidysenterica) showed promising antibiofilm activity against V. cholerae with crystal violet and air-liquid interface coverslip assays. Results revealed that C. asiatica, E. scaber, C. sinensis, and H. antidysenterica extracts significantly inhibited biofilm formation by approximately 75, 76, 78, and 55% at concentrations of 3, 2, 1, and 0.6 mg/mL, respectively. A promising antibiofilm activity of ∼89% inhibition at 1.5 mg/mL concentration was observed when a combination of E. scaber and C. sinensis was used. The herbal extracts were thermostable at a temperature range of 40 to 100°C. The 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay revealed that the viability of bacteria was not affected by treatment with these plant extracts. Gene expression studies revealed that extracts of H. antidysenterica leaf, H. antidysenterica bark, and the whole plant of E. scaber and C. asiatica down-regulate aphA or aphB, the major regulator genes modulating both virulence and biofilm formation. Hence, we propose that these herbal combinations could serve as a multifaceted approach to combat the pathogen and also, in turn, reduce antimicrobial resistance development.
Deoxyelephantopin Induces Reactive Oxygen Species-Mediated Apoptosis and Autophagy in Human Osteosarcoma Cells.[Pubmed: 28750364]
Osteosarcoma is the predominant form of primary bone malignancy. Although the combinational application of neoadjuvant chemotherapy and surgical resection significantly increases the survival rate, the therapeutic outcome remains unsatisfactory. Deoxyelephantopin (DET), an active ingredient of Elephantopus scaber, has been reported to have an anti-tumor effect in recent publications. This study aimed to investigate whether DET has antineoplastic effects on osteosarcoma cells and its underlying mechanism.


