Fritillaria pallidiflora
Fritillaria pallidiflora
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Fritillaria pallidiflora
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
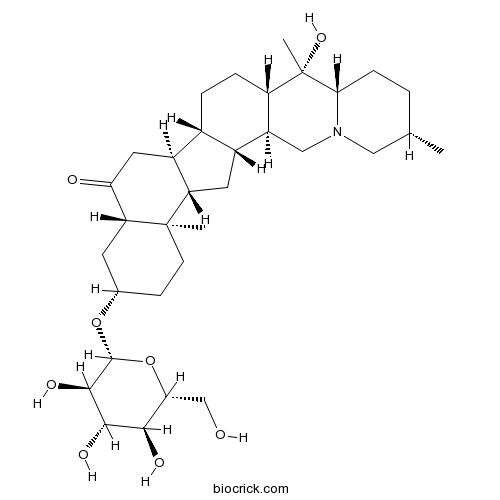
BCN6771
Edpetiline32685-93-1
Instructions
Characterization of the Isosteroidal Alkaloid Chuanbeinone from Bulbus of Fritillaria pallidiflora as Novel Antitumor Agent In Vitro and In Vivo.[Pubmed: 26584458]
Bulbus of Fritillaria pallidiflora, the dried bulb of F. pallidiflora, is widely used in Chinese folk medicine due to its powerful biological activities. The aim of this study was to investigate in vitro and in vivo antitumor activity of different fractions and isosteroidal alkaloids from bulbus of F. pallidiflora and clarify its putative mechanism of antitumor activity. Firstly, we assayed in vitro antitumor effects of different fractions from bulbus of F. pallidiflora and found that chloroform extracts and purified total alkaloids of bulbus of F. pallidiflora showed higher cytotoxic activity than other tested extracts. We further isolated four main alkaloids, chuanbeinone, imperialine-β-N-oxide, isoverticine and isoverticine-β-N-oxide, from the total alkaloids of bulbus of F. pallidiflora and found that they display significant cytotoxicity, whereby chuanbeinone showed the highest activity against Lewis lung carcinoma cells. Moreover, we found that chuanbeinone induced S phase arrest and further increased apoptosis of Lewis lung carcinoma cells. The results of Western blotting experiments showed that the expression of the antiapoptotic Bcl-2 was reduced by chuanbeinone treatment, while the proapoptotic protein Bax and caspase-3 were increased. Moreover, we investigated the in vivo antitumor activity of chuanbeinone and characterized its putative antitumor mechanism of action by the TUNEL assay and by histological and immunohistochemical analyses. Our results showed that chuanbeinone exhibited significant antitumor activity in vivo, while notably inhibiting tumor angiogenesis and inducing apoptosis characterized by an increased expression of caspase-3. Our findings show that chuanbeinone exhibits significant antitumor activity in vitro and in vivo, and points to possible therapeutic potential for this compound as well as for its natural source, bulbus of F. pallidiflora.
Steroidal saponins from Fritillaria pallidiflora Schrenk.[Pubmed: 22450263]
Five new steroidal saponins, Pallidifloside D (1), Pallidifloside E (2), Pallidifloside G (5), Pallidifloside H (6) and Pallidifloside I (7), together with seven other steroidal saponins (3, 4, 8-12) were isolated from the dry bulbs of Fritillaria pallidiflora Schrenk. Their structures were established by spectroscopic techniques (IR, MS, 1D and 2D NMR) and chemical means. The isolated steroidal saponins were evaluated for cyotoxic activity against human C6 brain gliomas and Hela cervix cancer cell lines using MTT assays. Compounds 1, 10, 11, 12 showed cytotoxicity against C6 and Hela cell lines with IC(50) values in the range of 5.1-75.8μM.
Three new steroidal saponins from Fritillaria pallidiflora.[Pubmed: 22008065]
Three new steroidal saponins, pallidiflosides A (1), B (2), and C (3), have been isolated from the dry bulbs of Fritillaria pallidiflora Schrenk. Their structures were elucidated as 26-O-β-d-glucopyranosyl-(25R)-furost-5,20(22)-dien-3β,26-diol-3-O-β-d-xylopyranosyl(1 → 4)-[α-l-rhamnopyranosyl(1 → 2)]-β-d-glucopyranoside (1); 26-O-β-d-glucopyranosyl-3β,26-dihydroxyl-20,22-seco-25(R)-furost-5-en-20,22-dione-3-O-α-l-rhamnopyranosyl(1 → 2)-β-d-glucopyranoside (2); and (25R)-spirost-5-ene-3β,17α-diol-3-O-β-d-glucopyranosyl(1 → 4)-β-d-galactopyranoside (3) by spectroscopic techniques and chemical means.
[Simultaneous determination of peimisine and sipeimine in Fritillaria walujewii regel and Fritillaria pallidiflora Schrenk by UPLC-ELSD].[Pubmed: 21351494]
The paper reports the establishment of a method for simultaneous determination of peimisine and sipeimine contents in Fritillaria walujewii Regel and Fritillaria pallidiflora Schrenk. The analyses were performed on an ultra-performance liquid chromatography with evaporative light scattering detection (UPLC-ELSD), equipped with a binary solvent manager, a sampler manager and a column compartment, and connected to Waters Empower 2 software. An Acquity UPLC BEH C18 column (100 mm x 2.1 mm, 1.7 microm) was used for all analysis. The investigated compounds were separated with gradient mobile phase consisting of acetonitrile-0.02% triethylamine-water. The temperature of sample manager was set at 25 degrees C. Drift tube temperature was 40 degrees C, and spray parameter was 40% with injection volume of 1 microL. The investigated compounds including peimisine and sipeimine had good linearity (r > or = 0.9991) over the tested ranges. The average recovery was 94.5% and 98.1% with RSD < or = 2.36%. The UPLC-ELSD method is simple, sensitive and accurate with good repeatability, which is available for quality control of F. walujewii Regel and F. pallidiflora Schrenk.
Identification of Fritillaria pallidiflora using diagnostic PCR and PCR-RFLP based on nuclear ribosomal DNA internal transcribed spacer sequences.[Pubmed: 15856423]
Fritillaria pallidiflora Schrenk (Liliaceae) is a commonly used antitussive herb. There are 9 species of Fritillaria recorded as herbal drugs in the Chinese Pharmacopoeia. The other species are often marketed as F. pallidiflora, and thus, the therapeutic effects of F. pallidiflora are not achieved. Methods to distinguish F. pallidiflora from the 8 other species of Fritillaria are limited by the current morphological and chemical methods. In this study, we report two molecular authentication methods based on the sequences of nuclear ribosomal DNA internal transcribed spacer (nrDNA ITS) regions. For diagnostic PCR, we designed a pair of species-specific primers to authenticate F. pallidiflora. The PCR program consisted of only two steps for every repeated cycle. For PCR-RFLP, we identified a distinctive site which can be recognized by the restriction endonuclease Eco81I in the nrDNA ITS1 region of F. pallidiflora. PCR-RFLP analysis was established to differentiate F. pallidiflora from the other species of Fritillaria. These methods provide effective and accurate identification of F. pallidiflora.


