Gardenia sootepensis
Gardenia sootepensis
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Gardenia sootepensis
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
BCN1427
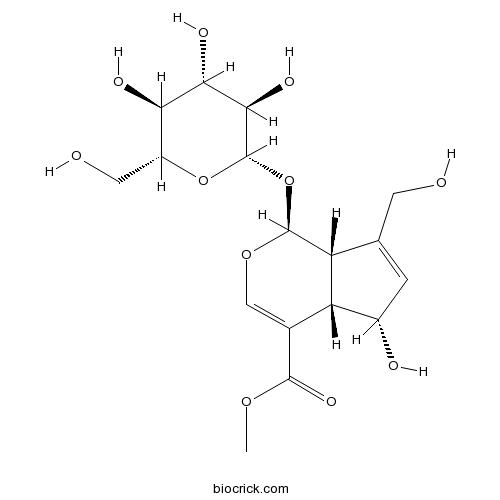
Deacetylasperulosidic acid methyl ester52613-28-2
Instructions
Three new 3,4-seco-cycloartane triterpenes from Gardenia sootepensis.[Pubmed: 29251512]
The plants in the genus Gardenia (Rubiaceae) have long been used as traditional medicines in China. In this study, two new 3,4-seco-cycloartane triterpenes, sootepin J (1) and sootepin K (2), and a novel nor-3,4-seco-cycloartane triterpenes, sootepin L (3), together with two known compounds (4-5), were isolated from the methanolic extract of the leaves and twigs of Gardenia sootepensis. The structures of the new compounds were elucidated by combinations of 1D, 2D NMR experiments and HR-MS data, while the known compounds were identified by comparison of the NMR data with previously published data.
Anti-inflammatory triterpenes from the apical bud of Gardenia sootepensis.[Pubmed: 27575322]
None
New 3,4-seco-cycloartane triterpenes from Gardenia sootepensis.[Pubmed: 26848635]
Two new 3,4-seco-cycloartane triterpenes, named sootepins H (1) and I (2), were isolated from the ethyl acetate extract of the leaves and twigs of Gardenia sootepensis. Their structures were elucidated on the basis of 1D- and 2D-nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) analysis, as well as high-resolution mass spectrometry (HR-MS), infrared (IR), and ultra violet (UV).
Cytotoxic and anti-angiogenic properties of minor 3,4-seco-cycloartanes from Gardenia sootepensis exudate.[Pubmed: 23207634]
Gardenia plants have long been used as traditional medicines in various countries including Thailand. In this study, two new 3,4-seco-cycloartane triterpenes, sootependial (1) and sootepenoic acid (2), were isolated from bud exudate of G. sootepensis, together with five known compounds. Their structures were elucidated on the basis of spectroscopic data. Sootependial (1) showed potent cytotoxicity selective to Hep-G2 cell lines and anti-angiogenic activity in ex vivo model (a rat aortic ring sprouting) assay. Furthermore, its angiogenic effect was found to occur mainly by suppressing endothelial cell proliferation and tubule formation, suggesting the potential of 1 as a lead compound for cancer treatment.
Antiangiogenic activity of 3,4-seco-cycloartane triterpenes from Thai Gardenia spp. and their semi-synthetic analogs.[Pubmed: 22142538]
Twelve naturally occurring 3,4-seco-cycloartane triterpenes (1-12) isolated from Gardenia sootepensis and Gardenia obtusifolia, and eight semi-synthetic derivatives (13-20) were evaluated for their antiangiogenic activity on a rat aortic sprouting assay, an ex vivo model of angiogenesis. Among these compounds, sootepin B (1) displayed the most potent activity in terms of the inhibition of microvessel sprouting from rat aortic rings in a dose-dependent manner with IC(50) value of 4.46 μM. Its angiogenic effect was found to occur via suppression of endothelial cell proliferation and tubular formation, and was likely mediated by regulation (inhibition) of the Erk1/2 signaling pathway.
Cytotoxic 3,4-seco-cycloartane triterpenes from Gardenia sootepensis.[Pubmed: 19456120]
Five new 3,4-seco-cycloartanes, sootepins A-E (1-5), along with four known triterpenes (6-9), were isolated from the apical buds of Gardenia sootepensis. Their structures were elucidated on the basis of spectroscopic methods (1D and 2D NMR, HRESIMS, and X-ray crystallography), and the compounds were tested for in vitro cytotoxic activity against human breast (BT474), lung (CHAGO), liver (Hep-G2), gastric (KATO-3), and colon (SW-620) cancer cell lines. Generally, the compounds possessing an exomethylene gamma-lactone ring showed broad cytotoxicity for all cell lines tested.
[A study on chemical composition of Gardenia sootepensis Hutch--quantitative determination of iridoid compounds by RP-HPLC].[Pubmed: 12205960]
To determine the iridoid contents in Gardenia sootepensis.
[Chemical constituents of fruits of Gardenia sootepensis Hutch].[Pubmed: 12078152]
To demonstrate the chemical constituents of the fruits of Gardenia sootepensis.


