Hemerocallis citrina
Hemerocallis citrina
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Hemerocallis citrina
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
BCN2537
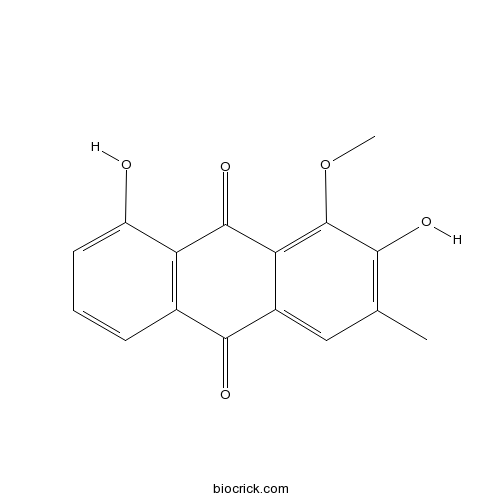
Obtusifolin477-85-0
Instructions
-
BCN5567
Chrysophanol481-74-3
Instructions

Evaluation of the toxicological properties and anti-inflammatory mechanism of Hemerocallis citrina in LPS-induced depressive-like mice.[Pubmed: 28460225]
Hemerocallis citrina Baroni (Liliaceae), a Liliaceae plant, has been widely used in food and traditional medicine. This study investigated the safety of ethanol extracts from Hemerocallis citrina (HCE) after oral treatment (p.o.) and evaluating the anti-inflammatory mechanism of HCE in a lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced depressive-like model. First, in an 8-week experimental procedure, blood and tissue samples collected from mice were used for biochemical and histopathological analysis every two weeks. Neither the body weight nor relative organ weights were affected by HCE administration. Only the total cholesterol levels were decreased by HCE administration. Histopathological analysis showed no significant liver and kidney changes caused by HCE. In addition, in an LPS-induced mouse depressive-like model, HCE significantly reversed the reduction of sucrose preference with LPS. The results also indicated that LPS activated the nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB), inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) and cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) expression in the prefrontal cortex. In contrast, these activations were normalized by HCE pretreatment. In summary, our study provided essential evidence for the safety of Hemerocallis citrina in both food and medicine. The results also demonstrated that HCE exhibited antidepressant-like effects that might be related to inhibition of the NF-κB signaling pathway.
Identification and validation of reference genes for quantitative real-time PCR studies in long yellow daylily, Hemerocallis citrina Borani.[Pubmed: 28362875]
Gene expression analysis using reverse transcription quantitative real-time PCR (RT-qPCR) requires the use of reference gene(s) in the target species. The long yellow daylily, Hemerocallis citrina Baroni. is rich in beneficial secondary metabolites and is considered as a functional vegetable. It is widely cultivated and consumed in East Asian countries. However, reference genes for use in RT-qPCR in H. citrina are not available. In the present study, six potential reference genes, actin (ACT), AP-4 complex subunit (AP4), tubulin (TUB), ubiquitin (UBQ), 18S and 60S ribosomal RNA, were selected and their expression stability in different developmental stages, organs and accessions was evaluated using four statistical software packages (geNorm, NormFinder, BestKeeper, and RefFinder). For commercial flower buds of different landraces, the combination of 60S, TUB, and AP4 was appropriate whereas ACT and 60S was suitable for normalization of different organs. In addition, AP4 exhibited the most stable expression in flower buds among different developmental stages. UBQ was less stable than the other reference genes under the experimental conditions except under different organs was 18S. The relative expression levels of two genes, primary-amine oxidase (HcAOC3) and tyrosine aminotransferase (HcTAT) which play important roles in alkaloid biosynthesis were also examined in different organs of the 'Datong' landrace, which further confirmed the results of selected reference genes. This is the first report to evaluate the stability of reference genes in the long yellow daylily that can serve as a foundation for RT-qPCR analysis of gene expression in this species.
Effects of phenolic constituents of daylily flowers on corticosterone- and glutamate-treated PC12 cells.[Pubmed: 28109297]
Daylily flowers, the flower and bud parts of Hemerocallis citrina or H. fulva, are well known as Wang-You-Cao in Chinese, meaning forget-one's sadness plant. However, the major types of active constituents responsible for the neurological effects remain unclear. This study was to examine the protective effects of hydroalcoholic extract and fractions and to identify the active fractions.
Antidepressant-like effects and cognitive enhancement of the total phenols extract of Hemerocallis citrina Baroni in chronic unpredictable mild stress rats and its related mechanism.[Pubmed: 27623554]
Depression induce distressed emotional state and cognitive deficits simultaneously, which both should be improved in the treatment. Hemerocallis citrina Baroni (HC) is a traditional herbal medicine in Eastern-Asia areas and the total phenols extract of HC (HCPE) contains the main active ingredients. It has been reported that HC has the emotional improvement effect. But the cognitive effect of HC was seldom researched.
Ultrasound-synergized electrostatic field extraction of total flavonoids from Hemerocallis citrina baroni.[Pubmed: 27773282]
The total flavonoids from Hemerocallis citrina baroni are regarded as a green and natural health care product with many beneficial impacts on human health. In this study, ultrasound-synergized electrostatic field extraction (UEE) of the total flavonoids (TF) from H. citrina was investigated. Significant independent variables of the extraction, including the electrostatic field, ultrasonic power, ethanol concentration and extraction time, were optimized using the Box-Behnken (BB) method, and the optimal extraction conditions were obtained by response surface methodology (RSM). The extraction yield using UEE was compared with the yields obtained using only ultrasound extraction (UE) and water bath extraction (WE), using a UV-vis spectrophotometer. The best extraction yield of 1.536% using UEE was achieved under the following optimal conditions: electrostatic field of 7kV, ultrasonic power of 500W, ethanol concentration of 70% and extraction time of 20min. The optimal solid-liquid ratio (1:25g/mL) and extraction temperature (55°C) were determined by single factor experiments. Compared to other extraction methods, UEE not only increases the extraction yield of TF but also exhibits an excellent antioxidant activity in assays of the scavenging capacity for DPPH, hydroxyl and superoxide anion radicals. The availability of the UEE method can be supported by the ultrasonic cavitation effect, which plays the most important role in the UEE method. The electrostatic field can be regarded as a random disturbance for sonication, which can strengthen the cavitation effect and increase the cavitation yield. Moreover, the amount of iodine release in potassium iodide solution well validated the synergetic effect between the ultrasound and electrostatic field.
ERK-dependent brain-derived neurotrophic factor regulation by hesperidin in mice exposed to chronic mild stress.[Pubmed: 27018164]
A previous study found that the antidepressant-like effects of ethanolic extracts from Hemerocallis citrina are predominantly related to the flavonoid, hesperidin. The study herein aimed to explore the antidepressant-like mechanism of hesperidin in mice induced by chronic mild stress (CMS). The results indicated that hesperidin reversed the reduction of sucrose preference and the elevation of immobility time in mice induced by CMS. In addition, the increase in serum corticosterone levels and decrease in hippocampal extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) phosphorylation and brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) levels in CMS mice were also ameliorated by hesperidin treatment. In contrast, improvement by hesperidin was suppressed by pretreatment with ERK inhibitor SL327. Taken together, our findings confirmed the antidepressant-like effect of hesperidin and indicated that hesperidin-induced BDNF up-regulation was mediated in an ERK-dependent manner.
[Effects of Hemerocallis citrine baroni flavonids on CCl4-induced liver fibrosis of rats].[Pubmed: 26234134]
This study is designed to explore the possible effects of Hemerocallis citrina baroni flavonids (HCBF) on liver fibrosis induced by CCl4 in rats. The liver fibrosis model was induced by CCl4, and HCBF were administered by gastric perfusion at 25 and 50 mg x kg(-1) qd for 50 days, while the contents of alanine transaminase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), gamma glutamyl transpeptidase (GGT), alkaline phosphatase (ALP), superoxide dismutase (SOD), maleic dialdehyde (MDA) and transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1) were measured and the contents of PINP were measured in liver tissue, and the expression of TGF-β1 were observed by immunohistochemisty and Western blot. The pathological changes of liver tissue were examined by HE. The results showed that HCBF (25, 50 mg x kg(-1)) improved the liver function significantly through reducing the level of ALT, AST, GGT and ALP (P < 0.05 or P < 0.01), and increasing the content of SOD (P < 0.01), while reducing the content of MDA (P < 0.05 or P < 0.01), the expression of TGF-β1 (P < 0.05) and the content of PINP (P < 0.05). The results suggest that HCBF (25, 50 mg x kg(-1)) may inhibit the liver injury induced by CCl4 by decreasing the oxidative stress.
Antidepressant-like effects of the hydroalcoholic extracts of Hemerocallis citrina and its potential active components.[Pubmed: 25179173]
Herbal therapies are potential alternatives and adjuncts for depression treatment. The present study aims to investigate the antidepressant-like effects of hydroalcoholic Hemerocallis citrina extracts and its potential neuropharmacological components.
Ethanol extracts from Hemerocallis citrina attenuate the upregulation of proinflammatory cytokines and indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase in rats.[Pubmed: 24632017]
Hemerocallis citrina, a traditional herbal medicine, has been used for the improvement of behavioral and emotional status in Eastern-Asia countries. Previous studies in our laboratory demonstrated that ethanol extracts from Hemerocallis citrina (HCE) enhanced monoamines and brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) in depression-like model of rodents.


