Hirudo nipponica
Hirudo nipponica
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Hirudo nipponica
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
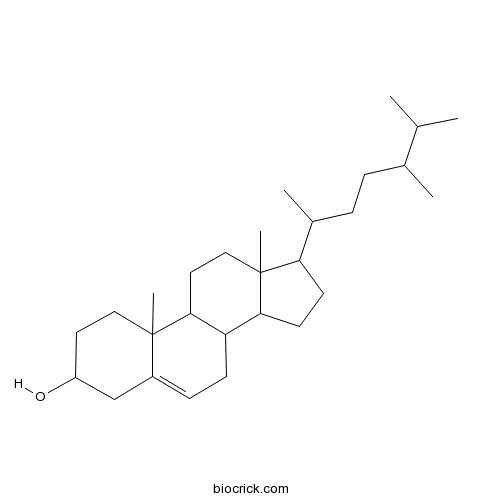
BCN3181
Campesterol474-62-4
Instructions
-
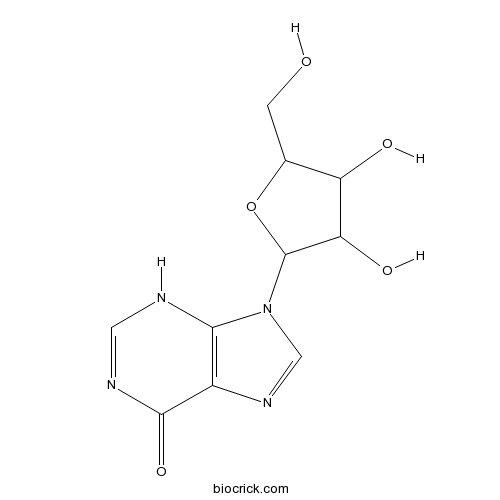
BCN3841
Inosine58-63-9
Instructions
[Studies on effects of water temperature, stocking density and feeding cycle on growth and feeding in Hirudo nipponica].[Pubmed: 28840681]
Effects of different water temperature, stocking density and feeding cycle on growth, feeding and survival of Hirudo nipponica have been studied, six temperature gradients were set: 18, 22, 26, 30, 34 and 38 ℃, five stocking density gradients were set: 30, 60, 120, 180 and 240 leech/L, four feeding cycle gradients were set: 2, 5, 10 and 20 d, respectively. The results showed that there exists a significant regression relationship between water temperature and specific growth rate: y=-0.016 5x²+0.836 9x-6.847 5(R²=0.990 8)(P<0.05), a regression analysis indicated that specific growth rate reached the maximum (3.76) at 25.36 ℃. When water temperature was beyond 30 ℃, the survival rate significantly decreased as water temperature increased (P<0.05). The specific growth rate and survival rate decreased as stocking density increased. A linear relationship exists between the feeding cycle and the SGR: y=-0.094 1x+3.832 9(R²=0.992 7). From this study, it can be concluded that the optimal water temperature and stocking density for the growth of H. nipponica is 22-26 ℃ and 30-120 leech/L, respectively.
[Study on Reproductive Performance of Hirudio nipponica].[Pubmed: 26762051]
To investigate the reproductive performance of Hirudo nipponica under artificial cultivation, in order to provide reference for the commercial rearing and breeding industry of this species.
Genetic variation in Whitmania pigra, Hirudo nipponica and Poecilobdella manillensis, three endemic and endangered species in China using SSR and TRAP markers.[Pubmed: 26743128]
Leeches are not only important medicinal animals worldwide but also are endangered. We aimed to (i) explore the level of genetic diversity within/among populations of three leeches, (ii) assess genetic differentiation among these three leeches, and (iii) discuss an appropriate strategy for conserving leech germplasm. A total of 315 individuals of Whitmania pigra, Hirudo nipponica and Poecilobdella manillensis from 21 populations were collected in China and Vietnam. The genetic structure and genetic diversity among and within the 21 populations were evaluated using target region amplified polymorphism (TRAP) and simple sequence repeat (SSR) markers. Sixteen pairs of TRAP primers generated a total of 398 fragments, of which 396 (99.50%) were polymorphic; fourteen pairs of SSR primers generated a total of 60 fragments, of which 59 (98.33%) were polymorphic. Shannon's index (I) and Nei's gene diversity index (H) for the three leeches were high at the species level (I=0.4980 and H=0.3323 for TRAPs, I=0.4487 and H=0.2969 for SSRs in W. pigra; I=0.4147/0.3769, H=0.2788/0.2566 for H. nipponica; and I=0.4616/0.4717, H=0.3099/0.3203 for P. manillensis). However, low genetic diversity was determined at the population level; the average genetic diversity measures within populations were H=0.1767/0.1376, I=0.2589/0.2043 for W. pigra, H=0.2149/0.2021, I=0.3184/0.3000 for H. nipponica and H=0.2850/0.2724, I=0.4152/0.3967 for P. manillensis. We conclude that there was limited gene exchange within/among populations and species, as the gene flow number (Nm) was 0.5493/0.5807. However, for all three species, the genetic diversity was different at the population level. Gene differentiation (Gst) and Nm were 0.4682 /0.5364 and 0.5678/0.4321 for W. pigra, 0.2294/0.2127 and 1.6797/1.8512 for H. nipponica and 0.1214/0.1496 and 3.6202/2.8412 for P. manillensis. STRUCTURE analysis, Unweighted Pair-Group Method with Arithmetic means (UPGMA) cluster analysis and Principal Coordinates Analysis (PCOA) all yielded similar results. The isolation-by-distance pattern was not significant for any of the three species by the Mantel test. These data emphasize the need for management, conservation, and rehabilitation of this animal species. Finally, an appropriate strategy for conserving leech is proposed.
Peptides from two sanguinovorous leeches analyzed by ultra-performance liquid chromatography coupled with electrospray ionization quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometric detector.[Pubmed: 25709207]
Hirudo nipponica Whitman and Poecilobdella manillensis Lesson fall into the family of Hirudinidae Whitman, both of them are sanguinovorous leeches and used a anticoagulant medicines in China. Their medicinal parts are the dried bodies. However, the peptides in the dried body of the two leeches have not been very clear up to now.
Mechanisms of inhibiting proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells by serum of rats treated with Dahuang Zhechong pill.[Pubmed: 19527826]
Dahuang Zhechong pill (DHZCP), a famous and classical Chinese herbal prescription, consists of twelve traditional Chinese drugs: Eupolyphaga sinensis Walker., Rheum officinale Baill., Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi., Glycyrrhiza uralensis Fisch., Prunus persica Batsch., Prunus armeniaca L., Paeonia lactiflora Pall., Rehmannia glutinosa Libosch., Toxicodendron vernicifluum F.A. Barkl., Tabanus bivittatus Mats., Hirudo nipponica Whitman. and Holotrichia diomphalia Bates., and is clinically used to treat hepatic diseases, gynecopathy and atherosclerosis in China. Our previous studies confirm that DHZCP is able to significantly inhibit proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) in vivo and in vitro.
Six trigalactosylceramides from the leech (Hirudo nipponica).[Pubmed: 8689724]
Six neutral glycosphingolipids were isolated in the pure state from the leech, Hirudo nipponica (Annelida). In contrast to the zwitterionic monogalactosylceramides carrying a choline phosphate group so far obtained, all compounds are non-zwitterionic glycosphingolipids, trigalactosylceramides. Five compounds possess a Ga1 alpha 1-6Ga1 alpha 1-6Ga1 beta 1-Cer core, and one is unique in having a Ga1 alpha 1-6Ga1 beta 1-Cer structure. Their full structures have been determined on the bases of chemical and spectral evidence.
[Effects of leech and ground beetle powder on hemorheology and blood lipid of ischemic stroke].[Pubmed: 7647529]
In order to improve blood supply for the brain, restore the functions of the cerebral cells and the limbs, and increas the curative rate, the leech (Hirudo nipponica and ground beetle Eupolyphage sinensis), powder (LGBP) to the patients according to the principle of promoting the blood circulation to remove the stasis was administered, and the clinical observation and experimental study was conducted. Its effects were compared with those of Western medicines. The results showed that after medication of LGBP, the blood flow of brain significantly increased, the hypoxia was improved, blood viscosity and blood lipid were lowered and thrombosis was inhibited in vitro or in vivo. No toxic side-effects caused by LGBP was found.


