Holarrhena pubescens
Holarrhena pubescens
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Holarrhena pubescens
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
BCN5796
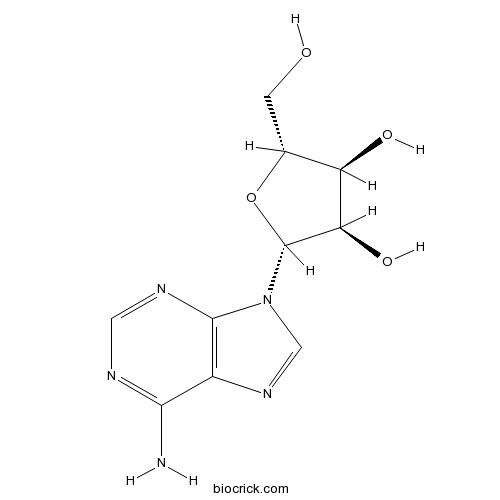
Adenosine58-61-7
Instructions
Antimalarial and cytotoxic activities of pregnene-type steroidal alkaloids from Holarrhena pubescens roots.[Pubmed: 29172699]
None
In vivo antimalarial activity of extracts of Tanzanian medicinal plants used for the treatment of malaria.[Pubmed: 27144154]
Plants used in traditional medicine have been the source of a number of currently used antimalarial medicines and continue to be a promising resource for the discovery of new classes of antimalarial compounds. The aim of this study was to evaluate in vivo antimalarial activity of four plants; Erythrina schliebenii Harms, Holarrhena pubescens Buch-Ham, Phyllanthus nummulariifolius Poir, and Caesalpinia bonducella (L.) Flem used for treatment of malaria in Tanzania. In vivo antimalarial activity was assessed using the 4-day suppressive antimalarial assay. Mice were infected by injection via tail vein with 2 × 10(7) erythrocytes infected with Plasmodium berghei ANKA. Extracts were administered orally, once daily, for a total of four daily doses from the day of infection. Chloroquine (10 mg/kg/day) and solvent (5 mL/kg/day) were used as positive and negative controls, respectively. The extracts of C. bonducella, E. schliebenii, H. pubescens, and P. nummulariifolius exhibited dose-dependent suppression of parasite growth in vivo in mice, with the highest suppression being by C. bonducella extract. While each of the plant extracts has potential to yield useful antimalarial compounds, the dichloromethane root extract of C. bonducella seems to be the most promising for isolation of active antimalarial compound(s). In vivo antimalarial activity presented in this study supports traditional uses of C. bonducella roots, E. schliebenii stem barks, H. pubescens roots, and P. nummulariifolius for treatment of malaria.
Acetylcholinesterase inhibitory activity and molecular docking study of steroidal alkaloids from Holarrhena pubescens barks.[Pubmed: 26850468]
An alkaloidal extract of the bark of Holarrhena pubescens showed several inhibition zones of acetylcholinesterase (AChE) inhibitor, using a bioautographic assay. Activity-guided fractionation afforded three new steroidal alkaloids, mokluangins A-C (1-3), together with three known compounds, antidysentericine (4), holaphyllamine (5), methylholaphyllamine (6). All structures were elucidated by analysis of NMR and MS spectroscopic data. Compound 2 showed moderate antibacterial activity against Bacillus subtilis and Escherichia coli with the MIC value of 16 μg/mL, while compound 3 exhibited moderate selective activity against E. coli with the MIC value of 16 μg/mL. In addition, compounds 1-4 also showed strong AChE inhibiting activity with IC50 values ranging from 1.44 to 23.22 μM. Molecular docking calculations were also performed and the results demonstrated that all compounds can bind at the aromatic gorge of AChE with estimated binding free energies correlated well with the in vitro inhibitory profiles. Hydrophobic and hydrogen bonding interactions contribute mainly to the binding of the alkaloids where the substituents at C-3 serving as key functional groups for the AChE inhibition. Our results will allow the development of new AChE-inhibitors based on steroidal alkaloid skeleton bearing the cyclic amide moiety.
Evaluation of antioxidative and antidiabetic activity of bark of holarrhena pubescens wall.[Pubmed: 25386454]
The objectives of the study are to screen out various phytochemicals and to evaluate the antioxidant and antidiabetic potential of the stem bark of Holarrhena pubescens Wall (Holarrhena antidysenterica).


