Ilex centrochinensis
Ilex centrochinensis
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Ilex centrochinensis
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
BCN5559
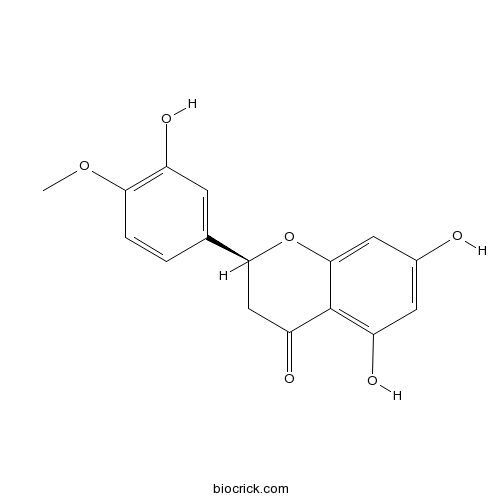
Isosakuranetin480-43-3
Instructions

-
BCN5657
Hesperetin520-33-2
Instructions
A pair of new diastereoisomeric phenylpropanoid-substituted flavan from the leaves of Ilex centrochinensis.[Pubmed: 29553829]
None
[In vitro anti-inflammatory and free radical scavenging activities of flavans from Ilex centrochinensis].[Pubmed: 26281592]
This study was carried out to evaluate the anti-inflammatory and free radical scavenging activities of flavans from flex centrochinensis S. Y. Hu in vitro and their structure-activity relationship. LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophage was used as inflammatory model. MTT assay for cell availability, Griess reaction for nitric oxide (NO) production, the content of TNF-alpha, IL-1beta, IL-6 and PGE, were detected with ELISA kits; DPPH, superoxide anion and hydroxyl free radicals scavenging activities were also investigated. According to the result, all flavans tested exhibited anti-inflammatory effect in different levels. Among them, compounds 1, 3, 4 and 6 showed potent anti-inflammatory effect through the inhibition of NO, TNF-alpha, IL-lp and IL-6, of which 1 was the most effective inhibitor, however, 2 and 5 were relatively weak or inactive. The order of free radical scavenging activities was similar to that of anti-inflammatory activities. Therefore, these results suggest that 3, 4 and 6, especially of 1, were,in part responsible for the anti-inflammatory and free radical scavenging activity of Ilex centrochinensis. Hydroxyl group at 4'-position of B-ring plays an important role in the anti-inflammatory and free radical scavenging capacities.
[Chemical constituents and their antitumor cytotoxic activity in leaves of Ilex centrochinensis].[Pubmed: 23668008]
To investigate the chemical constituents in leaves of Ilex centrochinensis and their antitumor bioactivity.
Appraisal of anti-inflammatory and free radical scavenging activities of ethanol extract of Ilex ficoidea Hemsl and Ilex centrochinensis S.Y. Hu.[Pubmed: 21843790]
This study was to appraise the anti-inflammatory and free radical scavenging activities of ethanol extracts of Ilex ficoidea Hemsl (EIFH) and Ilex centrochinensis S.Y. Hu (EICC). Anti-inflammatory activities were evaluated using xylene-induced ear edema and the cotton pellet granuloma tests. Some antioxidants produced during chronic inflammation were quantitated and the DPPH, superoxide anion and hydroxyl free radicals scavenging activities in vitro were also investigated. EICC showed a significant anti-inflammatory effect during the acute inflammation and chronic inflammation without any acute oral toxicity. However, EIFH exhibited a negligible anti-acute inflammatory and a moderate anti-chronic inflammatory activity. EICC significantly inhibited the formation of MDA and markedly raised the activities of SOD, CAT and GSH-Px. EIFH could reduce the level of MDA and elevate the activity of SOD only at the high dose. The free radical scavenging activities of EICC are higher than that of EIFH. These results suggest that EICC possesses significant anti-inflammatory and free radical scavenging activities. The anti-inflammatory mechanism is attributed, in part, to enhance the activities of antioxidant enzymes.
Flavans from the leaf of Ilex centrochinensis.[Pubmed: 21462042]
Phytochemical investigation of the leaf of Ilex centrochinensis led to the isolation and characterization of four flavans, one flavanone (5), and one flavone (6), including a new compound whose structure was elucidated as (2S)-5,3',4'-trihydroxy-7-methoxyflavan (1) and a new natural product whose structure was elucidated as (2S)-5-hydroxy-7,3',4'-trimethoxyflavan (4) on the basis of spectroscopic methods especially 1D and 2D NMR, CD, and mass spectral analyses. Compounds 1 and 4 exhibited weak cytotoxic activity against Huh7 cell line and no cytotoxic activity against Caco-2 cell line.
Two new 5,8-quinoflavans from the leaf of Ilex centrochinensis.[Pubmed: 21462037]
Two new 5,8-quinoflavans were isolated from the leaf of Ilex centrochinensis, and their structures were elucidated as (2R)-7,3',4'-trimethoxy-5,8-quinoflavan and (2S)-7-methoxy-4'-hydroxy-5,8-quinoflavan on the basis of spectroscopic methods, especially 1D and 2D NMR, CD, and mass spectral analyses. Both of them exhibited weak cytotoxic activity against HuH7 cell lines and no cytotoxic activity against CaCO-2 cell lines.


