Ilex rotunda
Ilex rotunda
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Ilex rotunda
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
BCN6059
Syringin118-34-3
Instructions

-
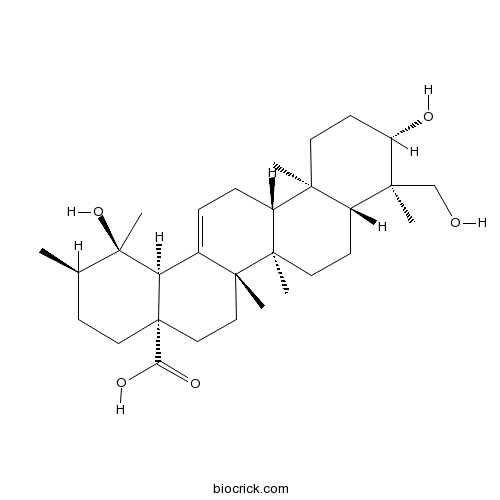
BCN5370
Rutundic acid20137-37-5
Instructions
-
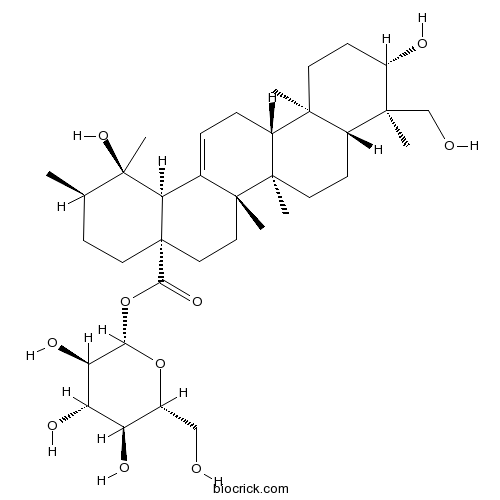
BCN1191
Pedunculoside42719-32-4
Instructions
-
BCN5747
Friedelin559-74-0
Instructions

-
BCN3820
Stearic Acid57-11-4
Instructions

A facile and selective approach to the qualitative and quantitative analysis of triterpenoids and phenylpropanoids by UPLC/Q-TOF-MS/MS for the quality control of Ilex rotunda.[Pubmed: 29758469]
None
Pedunculoside, a novel triterpene saponin extracted from Ilex rotunda, ameliorates high-fat diet induced hyperlipidemia in rats.[Pubmed: 29518607]
Pedunculoside (PE) is a novel triterpene saponin extracted from the dried barks of Ilex rotunda Thunb. The present study aims to explore lipid-lowering effects of PE on hyperlipidemia rat induced by high-fat diet. The rats were fed with the high-fat diet and subjected to intragastric administration of PE at doses of 30, 15, or 5 mg/kg daily for 7 weeks. The results demonstrated that treatment with PE for 7-week dramatically decreased serum total cholesterol (TC) and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) and reduced liver TC in hyperlipidemia rat induced by high-fat diet. Furthermore, the results also showed that PE modulated the expression of enzymes involved in lipid metabolism including peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α (PPAR-α), sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1 (SREBP-1), fatty acid synthase (FAS) and stearoyl CoA desaturase-1 (SCD-1) mRNA in liver. Besides, PE-treated group decreased weights and diameters of epididymal adipose hyperlipidemia rat. Mechanism study demonstrated that PE regulated PPAR-γ, CCAAT/Enhancer-binding Protein α (C/EBPα)、and SREBP-1 expression as well as inhibited phosphorylation of AMPK in MDI (methylisobutylxanthine, dexamethasone, insulin) induced-3T3L1 cells. Molecular Docking confirmed interaction between PE with proteins involving PPAR-γ, C/EBPα and SREBP-1. In summary, these findings may support that PE is a novel lipid-lowering drug candidate.
Triterpenoids with antiplatelet aggregation activity from Ilex rotunda.[Pubmed: 29169092]
None
Triterpenoid Saponins with Potential Cytotoxic Activities from the Root Bark of Ilex rotunda Thunb.[Pubmed: 27447119]
None
LC-MS/MS Determination and Pharmacokinetic Study of Pedunculoside in Rat Plasma after Oral Administration of Pedunculoside and Ilex rotunda Extract.[Pubmed: 25996213]
Ilex rotunda is widely used to treat many disorders as a traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) containing 4%-5% pedunculoside (PDC). A rapid, selective, and sensitive liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method (LC-MS/MS) was developed and validated to determine PDC in rat plasma by using 3β,19α-dihydroxyurs-12-en-28-oic acid 28-β-D-glucopyranosyl ester (DEOG) as an internal standard. The analytes were extracted by protein precipitation and eluted on a C18 chromatography column using a mobile phase of methanol-H2O (70:30, v/v) delivered at a flow rate of 0.6 mL/min. Detection was performed using positive ion electrospray ionization in multiple reaction monitoring modes. The assay was linear over the concentration range of 0.60 ng/mL to 200 ng/mL, with a quantification limit of 0.60 ng/mL. Intra-day and inter-day precisions (%RSD) ranged from 2.12 to 9.51 for PDC, whereas the accuracy was within -7.83%~9.40%. The validated method was successfully applied to the pharmacokinetic study of PDC in rat plasma after oral administration of pure PDC and Ilex rotunda extract (IRE). Pharmacokinetic parameters of PDC in IRE, such as Cmax, AUC0-t, AUC0-∞, t1/2z, and CLz/F, statistically differed from those of the pure monomer (p < 0.01). However, Tmax and MRT showed no significant differences between the two groups. Results suggested that other coexisting components in IRE may decrease the absorption of PDC. Compound-compound interactions between PDC and other herbal extract components can alter the pharmacokinetic behavior of PDC. The study will be helpful in providing references for understanding the action mechanism and clinical application of Ilex rotunda.
Antiplatelet aggregation triterpene saponins from the barks of Ilex rotunda.[Pubmed: 25447155]
Four new triterpene saponins, rotundinosides A-D (1-4) and seven known triterpene saponins (5-11) were isolated from a methanol extract of the barks of Ilex rotunda Thunb. The new saponins were characterized as 3-O-β-d-glucopyranosy1-(1→2)-β-d-xylopyranosyl siaresinolic acid 28-O-β-d-glucopyranoside (1), 3-O-[β-d-glucopyranosy1-(1→2)-β-d-xylopyranosyl]-3β,19α-dihydroxyurs-12-en-28-oic-O-β-d-glucopranosy1ester (2), 3-O-[α-l-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→2)-β-d-glucopyranosy1-(1→2)-α-l-arabinopyranosyl]-3β,19α-dihydroxyurs-12-en-28-oic-O-β-d-glucopyranosy1 ester (3), and 3-O-α-l-rhamanopyranosyl-(1→2)-β-d-glucopyranosy1-(1→2)-α-l-arabinopyranosyl ilexgenin B 28-O-β-d-glucopyranosy1 ester (4), respectively. Their structures were established by extensive spectroscopic analysis, including HSQC, HMBC, (1)H-(1)H COSY, NOESY and acid hydrolysis, and also by the comparison of their spectroscopic data with those of related compounds. The known compounds 5-11 were all obtained from this species for the first time. The biological activity of compounds 1-11 against ADP induced platelet aggregation in rabbit plasma was determined. Among the tested compounds 1, 3, 5 and 10 exhibited strong inhibition of platelet aggregation in vitro, with IC50 values of 11.4±2.2, 10.4±1.3, 13.2±2.4, and 15.1±3.4μM, respectively.


