Isodon coetsa
Isodon coetsa
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Isodon coetsa
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
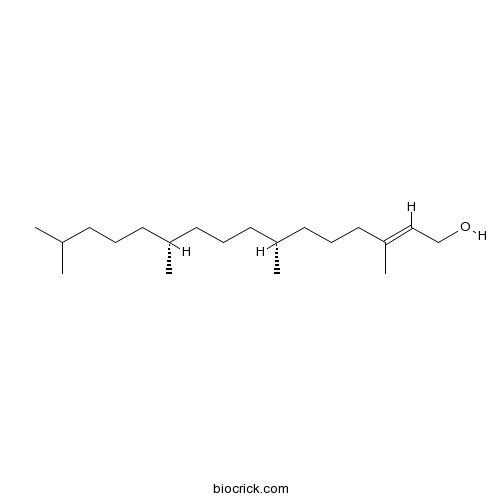
BCN1673
Phytol150-86-7
Instructions
-
BCN5407
Maoecrystal A96850-30-5
Instructions

Chemical constituents from the aerial parts of Isodon coetsa and their cytotoxicity.[Pubmed: 22210024]
Three new compounds (1-3), including a neolignan, a triterpenoid, and a diterpenoid, together with twenty known compounds (4-23), were isolated from the aerial parts of Isodon coetsa. Their structures and relative configurations were elucidated on the basis of spectroscopic data. Compounds 1, 3, 5-9, 11-13, 16-17, and 19-23 were evaluated for their cytotoxicity against HT-29, BEL-7402, and SK-OV-3 human tumor cell lines. Compound 7 showed significant inhibitory effects on all three types of cells, with IC50 values of 2.52, 3.06, 2.14 μM, respectively.
Research on Isodon species: still going strong.[Pubmed: 22210022]
Isodon species have been much studied for their biologically active ingredients, and Sun and co-workers report the isolation, characterization, and biological activities of twenty three compounds, including three new ones. The new compounds from Isodon coetsa are neolignan, triterpenoid, and diterpenoid types, showing that Isodon species have diverse types of compounds, in addition to the much-explored kaurane type diterpenoids. They determined the chemical structures based on extensive spectroscopic analyses and comparison with related compounds. Their report is expected to be yet another stepping stone for more exciting compounds from Isodon species.
[Rabdocoetsin B, a diterpenoid isolated from Isodon coetsa, is a potential proteasome inhibitor and induced apoptosis of t(8;21) leukemia cells].[Pubmed: 19938460]
Effects of Rabdocoetsin B (Rabd-B), a diterpenoid extracted from Isodon coetsa, on t(8;21) leukemic cells was tested by CCK-8 assay and Flow cytometry. The A549 cells stably expressing pGC-E1-ZU1-GFP were treated with Rabd-B for 4 h, and the accumulation of GFP was detected by fluorescence microscope. Using Western blotting, we investigated the expression of Casp-3, PARP, S6', which is a subunit of the 19S regulatory complex of the 26S proteasome, and cellular ubiqutinated proteins. We found that Rabd-B induced growth inhibition and apoptosis of Kasumi-1 cells in a dose-dependent manner. In Kasumi-1 cells treated with 2.5 micromol/L Rabd-B for 24 h, pro-caspase-3 was processed into its active form. The substrate of Casp-3, poly ADP-ribose polymerase (PARP), was cleaved with generation of an 85 kD fragment. The increased GFP fluorescence intensity, cleavage of S6' and the accumulation of ubiquitinated proteins were found in Kasumi-1 cells treated with Rabd-B. These results suggested that Rabd-B is a potential proteasome inhibitor which induces programmed cell death of t(8;21) cells. Further study might provide evidence for employing Rabd-B in treating human t(8;21) leukemia.
Two new rearranged abietane diterpenoids from tropical Isodon coetsa.[Pubmed: 17145653]
Two new rearranged abietane diterpenoids, sincoetsin A (1) and sincoetsin B (2), were isolated from the aerial part of Isodon coetsa (Buth-Ham ex D.Don) Hara collected in Singapore, and their structures were determined by spectroscopic methods, especially 2D NMR techniques.


