Isodon excisus
Isodon excisus
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Isodon excisus
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
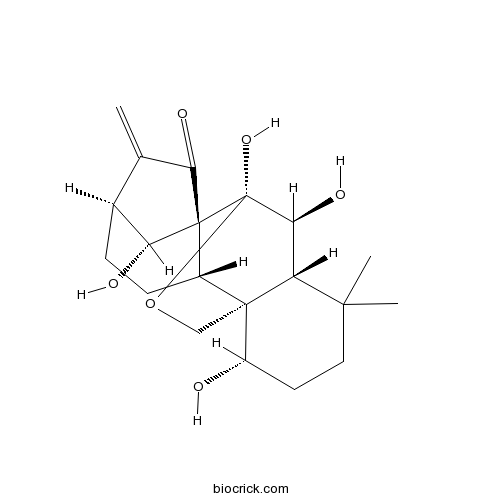
BCN5953
Oridonin28957-04-2
Instructions
-
BCN4327
Ursolic acid77-52-1
Instructions

ORI2 inhibits coxsackievirus replication and myocardial inflammation in experimental murine myocarditis.[Pubmed: 25273388]
We purified ORI2 [3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)acrylic acid 1-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-2-methoxycarbonylethyl ester] from an extract of the plant Isodon excisus. We tested the antiviral effect of ORI2 in a coxsackievirus-induced myocarditis model. Coxsackievirus B3 (CVB3) is a common cause of myocarditis and dilated cardiomyopathy. Activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) and Akt signaling in virus-infected cells is essential for CVB3 replication. Antiviral compounds were screened by HeLa cell survival assay. Several purified natural compounds were added to HeLa cells cultured in 96-well plates for 30 min after 1 multiplicity of infection (m.o.i) CVB3 infection. ORI2 significantly improved HeLa cell survival in a dose-dependent manner. For in vivo studies, BALB/c mice (n=20) were infected with CVB3, then 10 of the mice were treated by daily intraperitoneal injections of ORI2 (100 mM) for 3 consecutive days. ORI2 treatment significantly improved early survival in the treated mice compared to untreated mice (85% vs. 50%, respectively). Organ virus titers and myocardial damage were significantly lower in the ORI2-treated mice than in untreated mice. These results demonstrate that ORI2, delivered by intraperitoneal injection after CVB3 infection, has a significant antiviral effect by markedly inhibiting virus replication, resulting in a decrease in organ virus titer and myocardial damage. ORI2 may be developed as a potential therapeutic agent for the treatment of CVB3 infections.
Dimeric ent-kaurane diterpenoids from Isodon excisus.[Pubmed: 22066578]
Five new dimeric ent-kauranoids, biexcisusins A-E (1-5), were isolated from the aerial parts of Isodon excisus. The structures and relative configurations of these compounds were determined on the basis of spectroscopic data interpretation. Of these, biexcisusins C-E (3-5) are dimeric ent-kaurane diterpenoids exhibiting an unprecedented linkage through a nine-membered lactone ring between two ent-kaurane subunits. Compounds 1-5 showed no inhibitory effects on the LPS-induced production of nitric oxide in murine macrophage RAW264.7 cells, up to a dose of 50 μM.
Pyrrolidinone diterpenoid from Isodon excisus and inhibition of nitric oxide production in lipopolysaccharide-induced macrophage RAW264.7 cells.[Pubmed: 21273070]
A new pyrrolidinone diterpenoid, excisusin F (1), was isolated from the aerial parts of Isodon excisus (Lamiaceae), together with four known compounds, and their structures were determined mainly by NMR (1D and 2D) and mass spectrometry. Excisusin F (1) and inflexarabdonin E (3) showed potent inhibitory effects of LPS-induced nitric oxide production in RAW264.7 cells with the IC(50) value of 10.4 and 3.8 μM, respectively.
Inflexin attenuates proinflammatory responses and nuclear factor-kappaB activation in LPS-treated microglia.[Pubmed: 20159010]
Activated microglia participate in neuroinflammation which contribute to neuronal damage. Suppression of microglial activation would have therapeutic benefits, which lead to alleviation of the progression of neurodegeneration. In this study, the inhibitory effects of inflexin, a putative antiinflammatory agent isolated from Isodon excisus (Max.) Kudo (Labiateae), on the production of proinflammatory mediators were investigated in the lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated microglia. Inflexin significantly inhibited the release of nitric oxide (NO). Consistently, both the mRNA and the protein levels for the inducible NO synthase were decreased by inflexin in a concentration-dependent manner. Inflexin also inhibited the expression of cyclooxygenase (COX)-2, but not the COX-1 and effectively reduced the LPS-induced expression of proinflammatory cytokines in a dose-dependent manner. Furthermore, inflexin inhibited the degradation of IkappaB-alpha and the activation of NF-kappaB, p65 and Akt, while the MAPKs signal pathway was not affected. Our data suggest that inflexin was able to suppress neuroinflammation via inhibition of NF-kappaB activation and Akt pathway indicating that inflexin may be developed as a potent therapeutic agent in treating neuroinflammatory diseases.
Inhibitory effect of inflexinol on nitric oxide generation and iNOS expression via inhibition of NF-kappaB activation.[Pubmed: 17541474]
Inflexinol, an ent-kaurane diterpenoid, was isolated from the leaves of Isodon excisus. Many diterpenoids isolated from the genus Isodon (Labiatae) have antitumor and antiinflammatory activities. We investigated the antiinflammatory effect of inflexinol in RAW 264.7 cells and astrocytes. As a result, we found that inflexinol (1, 5, 10 microM) suppressed the expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) and cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) as well as the production of nitric oxide (NO) in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 cells and astrocytes. Consistent with the inhibitory effect on iNOS and COX-2 expression, inflexinol also inhibited transcriptional and DNA binding activity of NF-kappaB via inhibition of IkappaB degradation as well as p50 and p65 translocation into nucleus. These results suggest that inflexinol inhibits iNOS and COX-2 expression through inhibition of NF-kappaB activation, thereby inhibits generation of inflammatory mediators in RAW 264.7 cells and astrocytes, and may be useful for treatment of inflammatory diseases.
Kaurane diterpenoids from Isodon excisus inhibit LPS-induced NF-kappaB activation and NO production in macrophage RAW264.7 cells.[Pubmed: 17338565]
As part of an ongoing search for plant-derived compounds that inhibit the activation of NF-kappaB, the methanol extract of the aerial parts of Isodon excisus was found to have significant inhibitory effects on the activation of NF-kappaB in murine macrophage RAW264.7 cells. Bioactivity-guided isolation of the extract yielded five new diterpenoids, excisusin A-E (1-5), along with seven known compounds, inflexarabdonin I (6), inflexarabdonin G (7), inflexin (8), inflexanin A (9), inflexanin B (10), inflexinol (11), and inflexarabdonin A (12). The structures were determined by analysis of the spectroscopic data including 2D NMR. All of the isolates were evaluated for their inhibitory effects on LPS-induced NF-kappaB activation and nitric oxide production in RAW264.7 cells.
A novel synthetic analogue of a constituent of Isodon excisus inhibits transcription of CYP1A1, -1A2 and -1B1 by preventing activation of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor.[Pubmed: 17183067]
We investigated the effect of a novel synthetic analogue of a constituent from the Chinese medicinal herb Isodon excisus, 3-(3-methoxy-phenyl)-N-(3, 4, 5-trimethoxy-phenyl)-acrylamide (compound 343), on the carcinogen activation pathway mediated by the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) in human hepatoma HepG2 cells. We found that compound 343 inhibited the upregulation of cytochrome P-450 (CYP) enzyme activity in cells treated with the AhR ligands and potent carcinogens, dimethylbenz[a]anthracene (DMBA) or 2, 3, 7, 8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD). Compound 343 also inhibited the DMBA- or TCDD-induced increase in CYP1A1, -1A2 and -1B1 mRNA levels. Carcinogen-induced transcription of CYP genes was also suppressed by compound 343, as measured by a reporter gene controlled by the xenobiotic-responsive element (XRE). This was confirmed by measuring the amount of carcinogen-induced CYP1A1 heterogeneous nuclear RNA. Compound 343 blocked the DMBA- or TCDD-induced activation of the AhR DNA-binding capacity for the XRE, as measured by a chromatin immunoprecipitation assay. Compound 343 also inhibited CYP enzyme activity in microsomes isolated from DMBA- or TCDD-treated cells, as well as the activity of recombinant CYP1A1, -1A2 and -1B1, indicating that compound 343 directly inhibits CYP enzymes. These results indicate that compound 343 is both a potent inhibitor of carcinogen-induced CYP enzyme expression, as well as a direct inhibitor of CYP enzymes.
Two new constituents of Isodon excisus and their evaluation in an apoptosis inhibition assay.[Pubmed: 11374970]
Investigation of the whole plant of Isodon excisus resulted in the isolation of two new apoptosis inhibitors (1 and 2). Compounds 1 and 2 inhibited etoposide-induced apoptosis in U937 cells with IC50 values of 10.2 and 52.4 microg/mL, respectively. The structures of 1 and 2 were determined by spectral data interpretation.
Aromatase inhibitors from Isodon excisus var. coreanus.[Pubmed: 10896056]
The diethyl ether extract of Isodon excisus var. coreanus exhibited significant inhibitory activity in aromatase assay. Bioactivity-guided fractionation of the extract led to the isolation of three active compounds: inflexin (ent-1alpha-hydroxy-3beta,6a-diacetoxykaur-16-en-11,15-dione ) (1), ursolic acid (2), and ursolic acid 3-O-acetate (3).


