Jasminum grandiflorum
Jasminum grandiflorum
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Jasminum grandiflorum
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
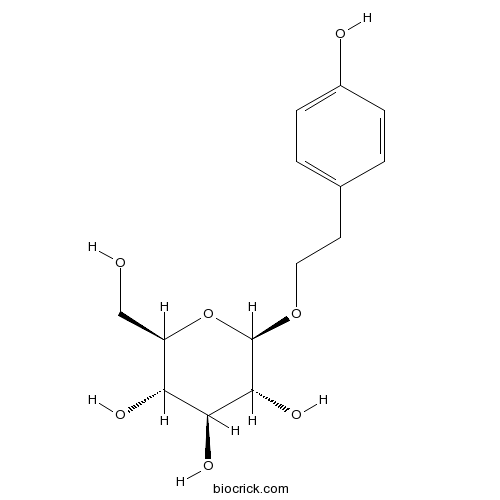
BCN5966
Salidroside10338-51-9
Instructions
Antidepressant-like activity of methyl jasmonate involves modulation of monoaminergic pathways in mice.[Pubmed: 28818747]
The efficacy of current antidepressant drugs has been compromised by adverse effects, low remission and delay onset of action necessitating the search for alternative agents. Methyl jasmonate (MJ), a bioactive compound isolated from Jasminum grandiflorum has been shown to demonstrate antidepressant activity but its mechanism of action remains unknown. Thus, the role of monoaminergic systems in the antidepression-like activity of MJ was investigated in this study.
Scent from Jasminum grandiflorum flowers: Investigation of the change in linalool enantiomers at various developmental stages using chemical and molecular methods.[Pubmed: 28463687]
Jasminum species are among the most preferred fresh cut flowers in India since ancient times. The plant produces small and fragrant flowers, which are of great demand in the preparation of fragrant garlands and also in perfume industries. Floral volatile of Jasminum grandiflorum L. (Family: Oleaceae) was extracted using solid-phase microextraction and analyzed in enantioselective gas chromatography. Chemical classes of identified volatiles revealed the presence of terpenoids, phenylpropanoids, and fatty acid derivatives. Marker constituent of flower volatiles, linalool was selected for analytical characterization on ethyl- and acetyl-β-cyclodextrin stationary phase. (R)-(-)-Linalool was found as major enantiomer in volatiles of floral buds whereas (S)-(+)-linalool predominated in the volatiles of matured flowers. Simultaneously, a quantitative real-time PCR was performed to find the gene expression of linalool synthase to investigate the mechanism of enantiomeric inversion. The emission pattern of (R)-(-)-linalool at different flower developmental stages was well correlated (P = 0.01) with the gene expression of the cloned linalool synthase from J. grandiflorum. We observed that the successive change in (R)- to (S)-linalool ratio from bud to mature flower was mainly due to the enantio- specific transformation and temporal decline of (R)-linalool producing gene in J. grandiflorum. This enantiomeric change also leads to the difference in flower aroma. Furthermore, this is probably the reason behind consumer's acceptance for jasmine buds rather than bloomed flowers in cut flower segments.
Exploratory Studies on the in Vitro Anti-inflammatory Potential of Two Herbal Teas (Annona muricata L. and Jasminum grandiflorum L.), and Relation with Their Phenolic Composition.[Pubmed: 28256049]
None
Phytopharmacological Profile of Jasminum grandiflorum Linn. (Oleaceae).[Pubmed: 25847780]
Plants are the real basis towards animal life and are also central to people's livelihood. The contributions of the plants in performing varied religious celebrations and in other multiple beneficiaries like medicine, human happiness as well as in treating deadly diseases can never be neglected. In treating diseases, the plants and their constituents are better choice than any other synthetic chemical. The nature has been kind enough to provide the human beings with various types of medicinal plants and in the real sense these form the storehouse of curing almost all the ailments. Consequently, most of the drugs which are being used in preparing formulations have their origin and roots in the plants which form the chief natural source of medicines. Even in modern era, the plant-derived drugs are being extensively used, either in their original or semi-synthetic form. It is because their natural phytoconstituents are highly innocuous posing relatively fewer or no side effects. Based upon their observations, analysis and experience, our ancestors used many plants for medicinal purposes and thus their efforts need to be supported by scientific evidence. Jasminum grandiflorum Linn. is one of such important plants. It has been extensively used by the tribes all over India to treat different diseases which mainly include body pains, toothache, stomach ache, ulcers, and sexual impotency. Chemistry of the plant revealed the presence of mainly secoiridoids, terpenoids, flavonoids and tannins. Not much scientific support was given to the folklore claims for this plant but some of its traditional uses were investigated like spasmolytic, wound healing, antimicrobial, angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor, antiulcer and antioxidant activities. This article is the review of research works done on the plant Jasminum grandiflorum Linn. to date. As a part of it the local names, morphology, traditional claims, chemistry and pharmacological activities have been discussed.
Inter-specific variation in headspace scent volatiles composition of four commercially cultivated jasmine flowers.[Pubmed: 25583067]
Jasmines are commercially grown for their fragrant flowers and essential oil production. The flowers of jasmine emit sweet-smelling fragrance from evening till midnight. This study was designed to study the composition and inter-specific variation of the emitted scent volatiles from flowers of four commercially cultivated Jasminum species namely, Jasminum sambac, Jasminum auriculatum, Jasminum grandiflorum and Jasminum multiflorum. Gas chromatography-mass spectrometry analysis revealed that the scent volatiles composition of these flowers was predominantly enriched with both terpenoid and benzenoid compounds. Linalool and (3E,6E)-α-farnesene were identified as the major monoterpene and sesquiterpene in all the four species, respectively. The most abundant benzenoid detected in all flowers was benzyl acetate. Comparison of volatile profiles indicated a variation in fragrance contents and types emitted from these four jasmine flowers. The outcome of this study shall help in elucidating the enzymes and genes of fragrance biosynthesis in jasmines and in aiming to create flowers with improved scent quality.
Application of ISSR markers to analyze molecular relationships in Iranian jasmine (Jasminum spp.) accessions.[Pubmed: 25189463]
There are many species of jasmines in different regions of Iran in natural or cultivated form, and there is no information about their genetic status. Therefore, inter-simple sequence repeat (ISSR) analysis was used to evaluate genetic variations of the 53 accessions representing eight species of Jasminum collected from different regions of Iran. A total of 21 ISSR primers were used which generated 981 bands of different sizes. Mean percentage of polymorphic bands was 90.64 %. Maximum resolving power, polymorphic information content average, and marker index values were 21.55, 0.35, and 14.42 for primers of 3, 4, and 3 respectively. The unweighted pair group method with arithmetic mean dendrogram based on Jaccard's coefficients indicated that 53 accessions were divided into two major clusters. The first major cluster was divided into two subclusters; the subcluster A included Jasminum grandiflorum L., J. officinale L., and J. azoricum L. and the subcluster B consisted of three forms of J. sambac L. (single, semi-double, and double flowers). The second major cluster was divided into two subclusters; the first subcluster (C) included J. humile L., J. primulinum Hemsl., J. nudiflorum Lindl. and the second subcluster (D) consisted of J. fruticans L. At the species level, the highest percentage of polymorphism (34.05 %), numbers of effective alleles (1.16), Shannon index (0.151), and Nei's genetic diversity (0.098) were observed in J. officinale. The lowest values of percentage polymorphism (0.011), number of effective alleles (1.009), Shannon index (0.007), and Nei's genetic diversity (0.005) were obtained for J. nudiflorum. Based on pairwise population matrix of Nei's unbiased genetic identity, the highest identity (0.85) was found between J.officinale and J. azoricum and the lowest identity (0.69) was between J. grandiflorum and J. perimulinum. Based on analysis of molecular variance, the amount of genetic variations among the eight populations was 83 %. This study demonstrated that the ISSR is an useful tool in jasmine genomic diversity studies and to detect their relationships.
Antinociceptive and anticonvulsant activities of hydroalcoholic extract of Jasminum grandiflorum (jasmine) leaves in experimental animals.[Pubmed: 24174823]
Jasminum grandiflorum belongs to the family Oleaceae and is known to have anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, antioxidant, and antiulcer activities. The present study was undertaken to study its analgesic and anticonvulsant effects in rats and mice. The antinociceptive activity of the hydroalcoholic extract of J. grandiflorum leaves (HEJGL) was studied using tail flick and acetic acid - induced writhing method. Similarly, its anticonvulsant activity was observed by maximal electroshock (MES) method and pentylenetetrazol (PTZ) method. Statistical analysis was performed using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by Dunnett's test. At doses of 50, 100, and 200 mg/kg, HEJGL showed significant analgesic and anticonvulsant effects in experimental animals. In view of its analgesic and anticonvulsant activity, the JGL extract can be used in painful conditions as well as in seizure disorders.


