Ligustrum quihoui
Ligustrum quihoui
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Ligustrum quihoui
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
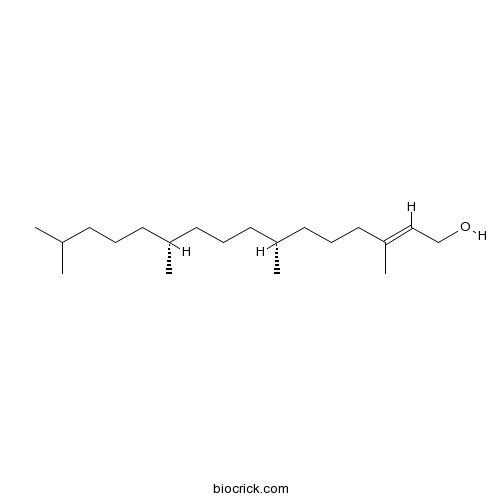
BCN1673
Phytol150-86-7
Instructions
[Gene cloning and prokaryotic expression of glycosyltransferase from Ligustrum quihoui].[Pubmed: 29600644]
None
Feeding on different attractive flowering plants affects the energy reserves of Culex pipiens pallens adults.[Pubmed: 29177970]
Mosquito adults usually need to ingest sugar from nectar host plants to sustain their metabolic needs. Mosquitoes could be differentially attracted by various flowering plant species, and the volatiles were thought to be important factors attributed to the differential attractiveness. However, whether mosquitoes' preference for host plants correlates with their nutritional rewards from sugar sources remains unclear. In the present study, the preference of newly emerged Culex pipiens pallens to three kinds of flowering plants (Ligustrum quihoui, Abelia chinensis, and Nerium indicum) was determined in the olfactometer. Besides, when the newly emerged mosquitoes were provided with these flowering plants as sugar sources, the content of their metabolic reserves (glycogen, lipid, and protein) was determined. The results revealed that Cx. pipiens pallens could be differentially attracted by the odors emitted by the inflorescences of the tested flowering plants, and the nutritional rewards of mosquitoes were significantly affected by feeding on different inflorescences. The present study demonstrated that feeding on nectar host plants with differential attraction could affect the energy reserves of Cx. pipiens pallens.
Demographic analysis of the fitness of Problepsis superans (Lepidoptera: Geometridae) feeding on three ligustrum (Lamiales: Oleaceae) species.[Pubmed: 25026663]
Using the age-stage, two-sex life table, the effects of three ligustrum species, Ligustrum x vicaryi Hort., Ligustrum quihoui Carrière, and Ligustrum lucidum Aiton, on the fitness of Problepsis superans (Butler, 1885) (Lepidoptera: Geometridae) were assayed by considering life table parameters of P. superans at 27 +/- 1 degrees C, 70 +/- 5% relative humidity, and a photoperiod of 16:8 (L: D) h. The means and SEs of population parameters were calculated using the jackknife and bootstrap methods. The total developmental time of larval stage of P. superans on L. x vicaryi was significantly shorter than that on L. x vicaryi and L. quihoui, whereas higher fecundity was observed on L. x vicaryi. The highest value of the finite rate of increase was observed on L. x vicaryi. The intrinsic rate of increase of P. superans on L. x vicaryi, L. quihoui, and L. lucidum, was 0.147 +/- 0.004, 0.130 +/- 0.004, and 0.112 +/- 0.005, respectively, which differed significantly among the three ligustrum species. The net reproductive rate varied from 122.8 +/- 24.7 female offspring on L. lucidum to 242.2 +/- 36.2 female offspring on L. x vicaryi. The lowest mean generation time was observed on L. x vicaryi. The gross reproductive rate of P. superans on the three ligustrum species did not significantly differ. Based on growth and population parameters, the suitability of the three ligustrum species to P. superans is ranked from high to low in the order as L. x vicaryi, L. quihoui, and L. lucidum.
[Models for biomass estimation of four shrub species planted in urban area of Xi'an city, Northwest China].[Pubmed: 24765849]
Four common greening shrub species (i. e. Ligustrum quihoui, Buxus bodinieri, Berberis xinganensis and Buxus megistophylla) in Xi'an City were selected to develop the highest correlation and best-fit estimation models for the organ (branch, leaf and root) and total biomass against different independent variables. The results indicated that the organ and total biomass optimal models of the four shrubs were power functional model (CAR model) except for the leaf biomass model of B. megistophylla which was logarithmic functional model (VAR model). The independent variables included basal diameter, crown diameter, crown diameter multiplied by height, canopy area and canopy volume. B. megistophylla significantly differed from the other three shrub species in the independent variable selection, which were basal diameter and crown-related factors, respectively.
[Analysis of the chemical constituents of essential oil from Ligustrum quihoui by GC-MS].[Pubmed: 22066401]
[corrected] To study the chemical constituents of essential oil from Ligustrum quihoui.


