Macrosolen cochinchinensis
Macrosolen cochinchinensis
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Macrosolen cochinchinensis
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
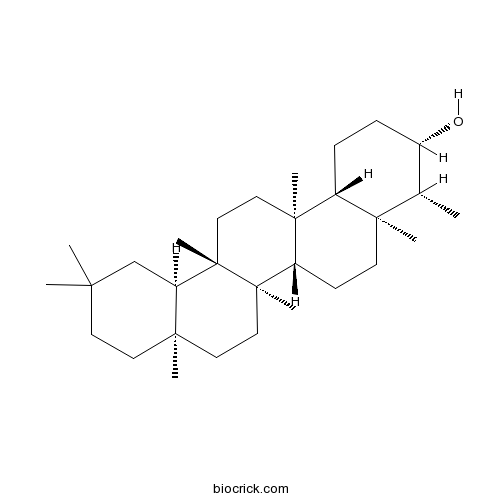
BCN1104
Epifriedelanol16844-71-6
Instructions
-
BCN4984
Orientin28608-75-5
Instructions

Understanding plastome evolution in Hemiparasitic Santalales: Complete chloroplast genomes of three species, Dendrotrophe varians, Helixanthera parasitica, and Macrosolen cochinchinensis.[Pubmed: 29975758]
Santalales is a large order, with over 2200 species, most of which are root or aerial (stem) hemiparasites. In this study, we report the newly assembled chloroplast genome of Dendrotrophe varians (140,666 bp) in the family Amphorogynaceae and the cp genomes of Helixanthera parasitica (124,881 bp) and Macrosolen cochinchinensis (122,986 bp), both in the family Loranthaceae. We compared the cp genomes of 11 Santalales including eight currently available cp genomes. Santalales cp genomes are slightly or not reduced in size (119-147 kb), similar to other hemiparasitic species, when compared with typical angiosperm cp genomes (120-170 kb). In a phylogeny examining gene content, the NADH dehydrogenase gene group is the only one among eight functional gene groups that lost complete functionally in all examined Santalales. This supports the idea that the functional loss of ndh genes is the initial stage in the evolution of the plastome of parasitic plants, but the loss has occurred independently multiple times in angiosperms, while they are not found in some parasites. This suggests that the functional loss of ndh genes is not essential for the transition from autotroph to parasite. We additionally examined the correlation between gene content and type of parasitism (obligate/facultative and stem/root parasites) of all hemiparasitic species in which cp genomes have been reported to date. Correlation was not found in any types of parasitism.
Diversity of endophytic fungi associated with the foliar tissue of a hemi-parasitic plant Macrosolen cochinchinensis.[Pubmed: 25154477]
Foliar fungal endophytes are an important plant-associated fungal group. However, little is known about these fungi in hemi-parasitic plants, a unique plant group which derive nutrients from living plants of its hosts by haustoria while are photosynthetic to some degree. In this paper, the endophytic fungi in the leaves of a species of hemi-parasitic plant, Macrosolen cochinchinensis, were studied by both culture-dependent and culture-independent methods. By culture-dependent method, a total of 511 isolates were recovered from 452 of 600 leaf fragments (colonization rate = 75.3 %) and were identified to be 51 taxa. Valsa sp. was the most abundant (relative abundance = 38.4 %), followed by Cladosporium sp. 1 (13.5 %), Ulocladium sp. (4.3 %), Phomopsis sp. 2 (3.7 %), Hendersonia sp. (3.5 %), and Diaporthe sp. 4 (3.5 %). The Shannon index (H') of the isolated endophytic fungi was 2.628, indicating a moderate diversity. By culture-independent method, Aspergillus spp., Cladosporium sp., Mycosphaerella sp., Acremonium strictum, and Tremella sp. were detected. To our knowledge, the Tremella species have never been detected as endophytes so far. In addition, a cloned sequence was not similar with any current sequence in the Genbank, which may represent a novel species. Altogether, this study documented endophytic fungal assemble in the leaves of M. cochinchinensis which was worthy of our attention, and may expand our knowledge about endophytic fungi within the photosynthetic tissues of plants.


