Melilotus officinalis
Melilotus officinalis
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Melilotus officinalis
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
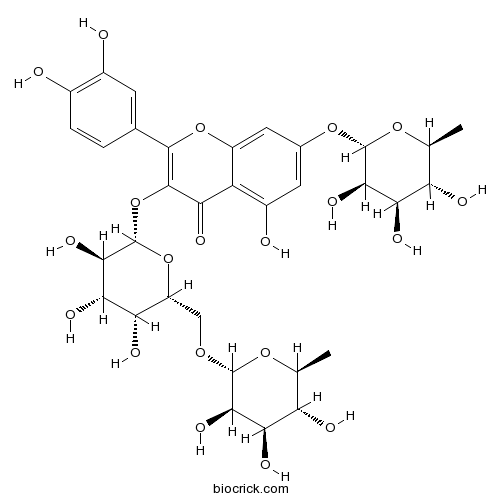
BCN5208
Robinin301-19-9
Instructions

-
BCN7817
Clovin81970-00-5
Instructions
-
BCN6309
Coumarin91-64-5
Instructions

Traditional and ethnobotanical dermatology practices in Romania and other Eastern European countries.[Pubmed: 29908576]
The geographic and ecologic specificity of Romania and other Eastern European countries has resulted in the development of an exceptional diversity of medicinal plants. The purpose of this study was to provide an overview of the ethnobotanical dermatology practices based on the use of medicinal plants in this region. The indications, ethnopharmacologic activities, parts used, and administration of 106 medicinal plants are provided. We also discuss the relative importance of these species, using two modified indices of quantitative ethnobotany: Use Value Index and Relative Dermatologic Importance, which were calculated on the basis of etic constructions (indications and ethnopharmacologic activities). The species identified to have the highest dermatologic importance (on a scale of 100) were Brassica oleracea L. (100), Matricaria chamomilla L. (79.17), Arctium lappa L. (74.82), Daucus carota L. (72.28), Equisetum arvense L. (70.47), Juglans regia L. (69.93), Populous nigra L. (65.94), Symphytum officinale L. (63.59), Chelidonium majus L. (57.78), Calendula officinalis L. (57.78), Achillea millefolium L. (57.43), Melilotus officinalis L. (55.25), Allium cepa L. (51.45), Quercus robur L. (51.08), and Betula spp. (50.91). This preliminary study on ethnobotanical dermatology practices indicates that Eastern European traditional medical knowledge represents an important heritage that is currently underexploited.
A new isoflavane-4-ol derivative from Melilotus officinalis (L.) Pall.[Pubmed: 29772948]
A new isoflavane derivative, melilofficinaside together with seven other metabolites including coumarin, uridine, methyl-α-d-fructofuranoside, and flavonoid glucosides were isolated from the aerial parts of Melilotus officinalis (L.) Pall.
EVALUATION OF HEPATOPROTECTIVE ACTIVITY OF MELILOTUS OFFICINALIS L. AGAINST PARACETAMOL AND CARBON TETRACHLORIDE INDUCED HEPATIC INJURY IN MICE.[Pubmed: 29513960]
Hepatic diseases are becoming common day by day and pose serious health threats to the life of humans. In order to treat these diseases, the attention of man is diverting towards herbal drugs, which are much safer and cost effective than synthetic drugs. The aim of present study was to investigate hepatoprotective activity of methanolic extract of Melilomus officinalis against paracetamol and carbon tetrachloride induced hepatic damage. Melilotus officinalis at selected oral doses of 50 mg/kg and 100 mg/kg showed significant hepatoprotective effects by decreasing the levels of serum marker enzymes such as total bilirubin, SGOT, SGPT, ALP, albumin and total protein, when compared with standard drug (silymarin) and negative control. Similarly, histopathological studies also supported biochemical estimations. It was concluded that extract of Melilotus officinali has strong hepatoprotective activity against paracetamol and carbon tetrachloride induced hepatotoxicity, which might be due to free radical scavenging mechanisms exhibited by flavonoids and phenolics, thus affirming its traditional therapeutic role in liver injury.
Determination of dicoumarol in Melilotus officinalis L. by using molecularly imprinted polymer solid-phase extraction coupled with high performance liquid chromatography.[Pubmed: 29395163]
None
Chemical Constituents and Antioxidant, Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Tumor Activities of Melilotus officinalis (Linn.) Pall.[Pubmed: 29382154]
None


