Mosla chinensis
Mosla chinensis
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Mosla chinensis
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
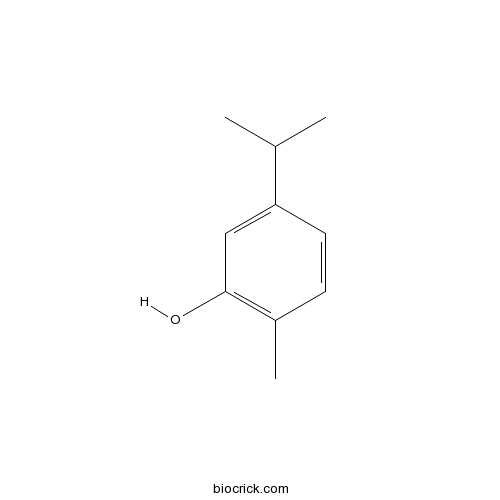
BCN2633
5-Isopropyl-2-methylphenol499-75-2
Instructions
-
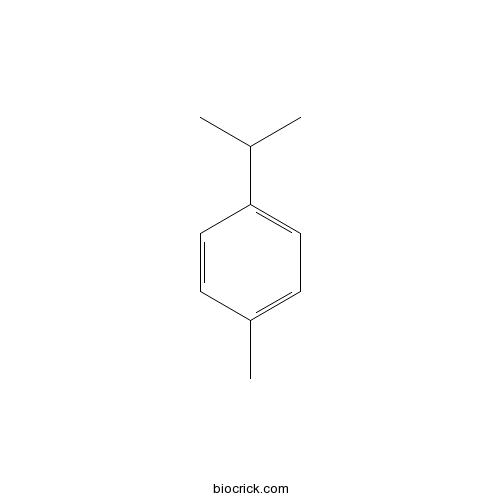
BCC8282
4-Isopropyltoluene99-87-6
Instructions
Inhibitory effects and related molecular mechanisms of total flavonoids in Mosla chinensis Maxim against H1N1 influenza virus.[Pubmed: 29177921]
The Shixiangru (Mosla chinensis Maxim) total flavonoids (STF) mainly contain luteolin and apigenin. The study aims to examine the inhibitory effects of STF on anti-H1N1 influenza virus and its related molecular mechanisms in pneumonia mice.
Structure and biological activities of a pectic polysaccharide from Mosla chinensis Maxim. cv. Jiangxiangru.[Pubmed: 24708981]
A water-soluble pectic polysaccharide (MP-A40) was isolated and purified from Mosla chinensis Maxim. cv. Jiangxiangru for the first time, with a molecular weight of 32,600Da. MP-A40 was comprised of 68.63% galacturonic acid and 13.05% neutral sugar. In addition, arabinose, galactose, rhamnose, mannose and glucose composed the neutral sugar in a relative ratio of 4.94, 3.07, 2.13, 1.62 and 1.29% of the dry weight of MP-A40, respectively. Structural characterization of MP-A40 was investigated by methylation analysis and 1D/2D NMR spectroscopy. From the results, the structure of MP-A40 was revealed as follows: 1,4-linked α-d-GalpA and 1,4-linked α-d-GalpA6Me interspersed with rare t-Araf (0.60%), t-Rhap (1.67%) and t-GalpA (10.15%). Esterification assay showed that about 32% of the carboxylic groups in GalA residues existed as methyl ester. In addition, MP-A40 could inhibit the growth of human leukemic cell line K562 and stimulate nitric oxide production from RAW 264.7 macrophages both in dose-dependent manners.
Chemical composition and antioxidant activities in immumosuppressed mice of polysaccharides isolated from Mosla chinensis Maxim cv. jiangxiangru.[Pubmed: 23796859]
Polysaccharide MP was isolated from Mosla chinensis Maxim cv. jiangxiangru. It was composed of rhamnose, arabinose, xylose, mannose, glucose and galactose in a molar ratio of 5.364:12.260:3.448:12.260:32.567:30.651, with 11.00%±0.24% uronic acid and 9.046%±0.04% protein. Its antioxidant activity on the cyclophosphamide-induced immunosuppressed mice was investigated. The spleen and the thymus indices were investigated, and the biochemical parameters were evaluated in three organs (liver, heart and kidney). MP was able to overcome the cyclophosphamide-induced immunosuppression and can significantly raise the T-AOC, CAT, SOD and GSH-PX level. It also raised the spleen and thymus indices and decreased the MDA level in mice. MP could play an important role during the prevention process of oxidative damage in immunological system.
Aqueous extract of Mosla chinensis inhibits mast cell-mediated allergic inflammation.[Pubmed: 23227796]
Allergic inflammatory diseases such as food allergy, asthma, sinusitis, and atopic dermatitis are increasing worldwide. In this study, we investigated the effects of aqueous extract of Mosla chinensis Max. (AMC) on mast cell-mediated allergic inflammation and studied the possible mechanism of this action. AMC inhibited compound 48/80-induced systemic and immunoglobulin E (IgE)-mediated local anaphylaxis. AMC reduced intracellular calcium levels and downstream histamine release from rat peritoneal mast cells activated by compound 48/80 or IgE. In addition, AMC decreased gene expression and secretion of proinflammatory cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, interleukin (IL)-6 and IL-8 in human mast cells. The inhibitory effect of AMC on cytokine expression was nuclear factor (NF)-κB dependent. Our results indicate that AMC inhibits mast cell-mediated allergic inflammatory reaction by suppressing histamine release and expression of proinflammatory cytokines and the involvement of calcium and NF-κB in these effects. AMC might be a possible therapeutic candidate for allergic inflammatory disorders.
[Polar constituents of Mosla chinensis].[Pubmed: 22032144]
To study polar constituents of Mosla Chinensis.
[Study on the flavonoids from Mosla chinensis 'jiangxiangru'].[Pubmed: 20575414]
To study the chemical constituents of Mosla chinensis 'jiangxiangru'.
[Study on extraction technology of Mosla chinensis volatile oil].[Pubmed: 18236760]
To study the techniques of organic solvent extraction method and supercritical CO2 extraction for extracting Mosla chinensis Maxim volatile oil (MCMVO), and to analyze its chemical compositions.
[Optimization of the extraction technology for the essential oil from Mosla chinensis Maxim].[Pubmed: 16850729]
To make sure the best extraction technology of essential oil from Mosla chinensis Maxim.
[Determination of carvacrol and thymol in Mosla chinensis by HPLC].[Pubmed: 15656129]
To establish a quantitative method of determination of carvacrol and thymol in Mosla chinensis.


