Oxalis pes-caprae
Oxalis pes-caprae
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Oxalis pes-caprae
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
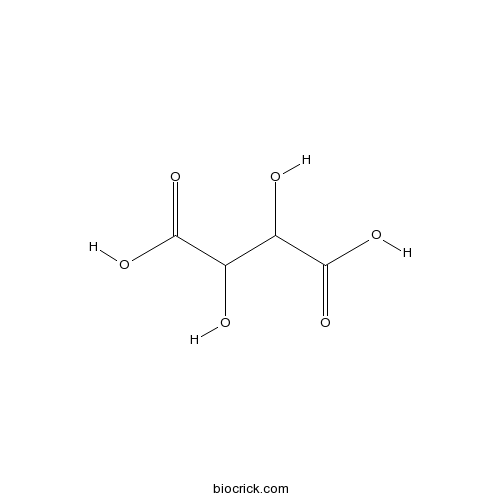
BCN9052
DL-Tartaric acid133-37-9
Instructions
-
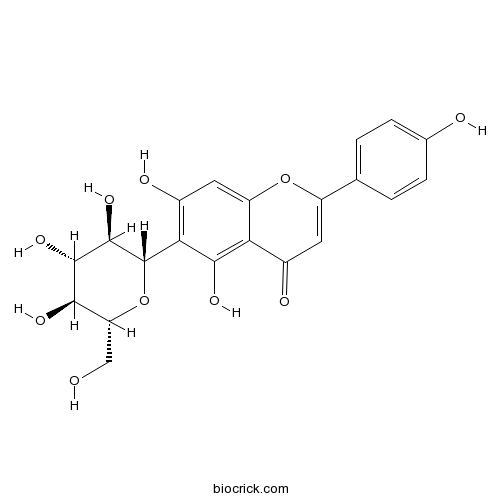
BCN5208
Robinin301-19-9
Instructions

-
BCN5423
Vitexin3681-93-4
Instructions

-
BCN5441
Isovitexin38953-85-4
Instructions
-
BCN5560
Acacetin480-44-4
Instructions

-
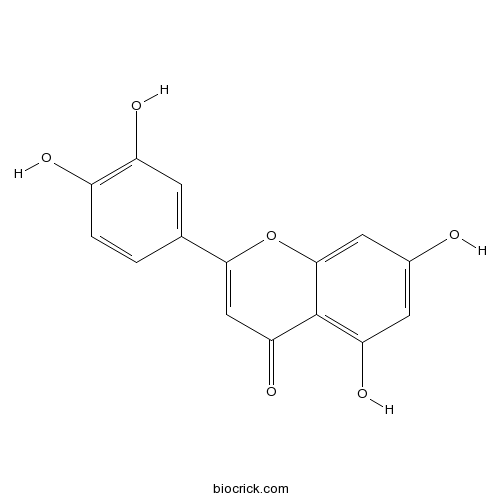
BCN5600
Luteolin491-70-3
Instructions
History vs. legend: Retracing invasion and spread of Oxalis pes-caprae L. in Europe and the Mediterranean area.[Pubmed: 29287103]
Oxalis pes-caprae L. is a South African geophyte that behaves as an invasive in the eurimediterranean area. According to a long-established hypothesis, O. pes-caprae may have invaded Europe and the Mediterranean area starting from a single plant introduced in the Botanical Garden of Malta at the beginning of the 19th century. The aim of this work was to test this hypothesis, to track the arrival of O. pes-caprae in different countries of the Euro-Mediterranean area and to understand the pathways of spreading and particularly its starting point(s). Historical data attesting the presence of the plant in the whole Euro-Mediterranean region were collected from different sources: herbarium specimens, Floras and other botanical papers, plant lists of gardens, catalogs of plant nurseries and plant dealers. First records of the plant (both cultivated and wild) for each Territorial Unit (3rd level of NUTS) were selected and used to draw up a diachronic map and an animated graphic. Both documents clearly show that oldest records are scattered throughout the whole area, proving that the plant arrived in Europe and in the Mediterranean region more times independently and that its spreading started in different times from several different centers of invasion. Botanical gardens and other public or private gardens, nurseries and plant dealers, and above all seaside towns and harbors seemingly played a strategic role as a source of either intentional and unintentional introduction or spread. A geographic profiling analysis was performed to analyse the data. We used also techniques (Silhouette, Kmeans and Voronoi tessellation) capable of verifying the presence of more than one independent clusters of data on the basis of their geographical distribution. Microsatellites were employed for a preliminary analysis of genetic variation in the Mediterranean. Even if the sampling was insufficient, particularly among the populations of the original area, our data supported three main groups of populations, one of them corresponding to the central group of populations identified by GP analysis, and the other two corresponding, respectively, to the western and the eastern cluster of data. The most probable areas of origin of the invasion in the three clusters of observations are characterized by the presence of localities where the invasive plant was cultivated, with the exception of the Iberian cluster of observation where the observations in the field predate the data about known cultivation localities. Alternative possible reasons are also suggested, to explain the current prevalence of pentaploid short-styled plants in the Euro-Mediterranean area.
Polyphenolic characterisation and bioactivity of an Oxalis pes-caprae L. leaf extract.[Pubmed: 28627294]
The present work is focused on the characterisation of the polyphenolic content of an Oxalis pes-caprae L. leaf extract and on the evaluation of its bioactivity with particular interest on its vascular activity and antioxidant potential. The polyphenolic content was characterised by HPLC-DAD and LC-MS/MS. The vascular activity was evaluated according to the influence on the serotonergic and adrenergic systems of the human internal mammary artery (HIMA). Antioxidant and neuroprotective studies were also conducted. Several luteolin and apigenin derivatives were identified as main constituents of the extract, which did not present any contractile effect nor had any effect on the serotonergic system of HIMA. However, it showed antagonistic effect on the adrenergic system, inhibiting the contraction to noradrenaline (reduction of 58.44% of maximum contraction). The extract showed antioxidant activity and standardised luteolin and apigenin derivatives showed neuroprotective potential, particularly homoorientin.
Biological and life table parameters of Typhlodromus laurentii and Iphiseius degenerans (Acari, Phytoseiidae) fed on Panonychus citri and pollen of Oxalis pes-caprae under laboratory conditions.[Pubmed: 27497592]
Typhlodromus laurentii and Iphiseius degenerans are two generalist phytoseiid mites, broadly spread in the Mediterranean area, especially in citrus orchards. In the present work we report results on various biological and life table parameters of the two phytoseiids, fed on pollen of Oxalis pes-caprae and various stages of the tetranychid Panonychus citri. Iphiseius degenerans had the shortest post embryonic development (6.53 days), the highest oviposition rate (1.83 eggs/female/day) and the shortest mean time between eggs laid (0.55 day) on Oxalis pollen, whereas the two food types did not influence these parameters in T. laurentii. However, Oxalis pollen showed a positive effect on the survivorship of the latter phytoseiid, with a median life time (LT50) of 44.51 days, which was two times longer than that registered on prey with the same phytoseiid, and on both food types with I. degenerans. This latter species had a better performance on the pollen (rm = 0.243, λ = 1.275, Ro = 22.88, DT = 2.85) than on prey (rm = 0.182, λ = 1.199, Ro = 17.43, DT = 3.81). On the other hand, the pollen influenced the net reproductive rate (25.43 females/female) of T. laurentii positively but showed the same effect as the prey on the other demographic parameters. Our results improve knowledge on the feeding behaviour of the above mentioned phytoseiids on two food sources that could represent the main possibility to maintain a consistent population of these predators during winter. Moreover, both phytoseiids were shown to be good biocontrol candidates of P. citri populations.
Invasion Fosters Change: Independent Evolutionary Shifts in Reproductive Traits after Oxalis pes-caprae L. Introduction.[Pubmed: 27446109]
Biological invasions offer optimal scenarios to study evolutionary changes under contemporary timescales. After long-distance dispersal, exotic species have to cope with strong mate limitation, and shifts toward uniparental reproduction have been hypothesized to be selectively advantageous. Oxalis pes-caprae is a clonal tristylous species native to South Africa, and invasive in Mediterranean regions worldwide. It reproduces sexually and asexually but the importance of each strategy differs between ranges. Native populations reproduce mostly sexually while in invasive ones asexual reproduction is the prevailing strategy due to the dominance of pentaploid monomorphic populations. Nevertheless, two contrasting scenarios have been observed after introduction: transition toward clonality, and re-acquisition of sexuality fueled by multiple introductions of compatible mates. Here, we aimed to assess evolutionary changes of reproductive traits in O. pes-caprae invasive populations and evaluate whether these traits could be related with invasion success and prevalence of certain forms in the western Mediterranean basin. Sexual and asexual reproduction traits were quantified under optimal conditions in a common garden experiment including native and invasive sexual, predominately asexual, and obligated asexual individuals. Different reproductive, ecological, and genetic constraints created by long-distance dispersal seem to have generated different selective pressures in sexual and asexual traits, with our results supporting evolutionary changes in invasive populations of O. pes-caprae. Native plants had higher sexual fitness, while a transition toward clonality was clear for invasive forms, supporting clonal reproduction as a major trait driving invasion. Differences were also observed among invasive plants, with sexual forms having increased dispersal potential; thus, they are expected to be in advantage in comparison with predominantly asexual and obligated asexual plants, and may become widespread in the future. Historical processes, like the initial introduction of predominantly asexual forms followed by sexual forms more recently, could be in the origin of current distribution patterns of O. pes-caprae in the western Mediterranean. This study shows that invasion processes are very dynamic and that ecological and genetic constraints determined by the invasion process may originate different reproductive strategies that are likely to determine invasion success.
Invasion genetics of the Bermuda buttercup (Oxalis pes-caprae): complex intercontinental patterns of genetic diversity, polyploidy and heterostyly characterize both native and introduced populations.[Pubmed: 25604701]
Genetic diversity in populations of invasive species is influenced by a variety of factors including reproductive systems, ploidy level, stochastic forces associated with colonization and multiple introductions followed by admixture. Here, we compare genetic variation in native and introduced populations of the clonal plant Oxalis pes-caprae to investigate the influence of reproductive mode and ploidy on levels of diversity. This species is a tristylous geophyte native to South Africa. Invasive populations throughout much of the introduced range are composed of a sterile clonal pentaploid short-styled form. We examined morph ratios, ploidy level, reproductive mode and genetic diversity at nuclear microsatellite loci in 10 and 12 populations from South Africa and the Western Mediterranean region, respectively. Flow cytometry confirmed earlier reports of diploids and tetraploids in the native range, with a single population containing pentaploid individuals. Introduced populations were composed mainly of pentaploids, but sexual tetraploids were also found. There was clear genetic differentiation between ploidy levels, but sexual populations from both regions were not significantly different in levels of diversity. Invasive populations of the pentaploid exhibited dramatically reduced levels of diversity but were not genetically uniform. The occurrence of mixed ploidy levels and stylar polymorphism in the introduced range is consistent with multiple introductions to the Western Mediterranean. This inference was supported by variation patterns at microsatellite loci. Our study indicates that some invasive populations of Oxalis pes-caprae are not entirely clonal, as often assumed, and multiple introductions and recombination have the potential to increase genetic variation in the introduced range.
Alien plant monitoring with ultralight airborne imaging spectroscopy.[Pubmed: 25010601]
Effective management of invasive plants requires a precise determination of their distribution. Remote sensing techniques constitute a promising alternative to field surveys and hyperspectral sensors (also known as imaging spectrometers, with a large number of spectral bands and high spectral resolution) are especially suitable when very similar categories are to be distinguished (e.g. plant species). A main priority in the development of this technology is to lower its cost and simplify its use, so that its demonstrated aptitude for many environmental applications can be truly realized. With this aim, we have developed a system for hyperspectral imaging (200 spectral bands in the 380-1000 nm range and circa 3 nm spectral resolution) operated on board ultralight aircraft (namely a gyrocopter), which allows a drastic reduction of the running costs and operational complexity of image acquisition, and also increases the spatial resolution of the images (circa 5-8 pixels/m(2) at circa 65 km/h and 300 m height). The detection system proved useful for the species tested (Acacia melanoxylon, Oxalis pes-caprae, and Carpobrotus aff. edulis and acinaciformis), with user's and producer's accuracy always exceeding 90%. The detection accuracy reported corresponds to patches down to 0.125 m(2) (50% of pixels 0.5 × 0.5 m in size), a very small size for many plant species, making it very effective for initial stages of invasive plant spread. In addition, its low operating costs, similar to those of a 4WD ground vehicle, facilitate frequent image acquisition. Acquired images constitute a permanent record of the status of the study area, with great amount of information that can be analyzed in the future for other purposes, thus greatly facilitating the monitoring of natural areas at detailed spatial and temporal scales for improved management.
Nutritional and antioxidant properties of wild edible plants and their use as potential ingredients in the modern diet.[Pubmed: 23944868]
Thirteen species of wild edible plants belonging to 11 botanical families consumed in the traditional Mediterranean diet were evaluated. Sanguisorba minor, Quercus ballota and Sedum sediforme showed the highest hydrophilic total antioxidant activity (H-TAA) and total phenols. Asparagus acutifolius, Allium ampeloprasum, Foeniculum vulgare and Malva sylvestris presented high levels of potassium, Malva and Asparagus are interesting due to their zinc content, and Urtica urens contains a high content of calcium. Sensory analysis indicated that fruits from Q. ballota could be considered very sweet and plants of Crithmum maritimum and Oxalis pes-caprae are very acidic. Moreover, testers highlighted the salty taste of C. maritimum. Mesembryanthemum nodiflorum and Mesembryanthemum cristalinum, the spicy taste of A. ampeloprasum, and the aroma of F. vulgare. Our results indicate that increased consumption of the investigated plant species could provide health benefits. Moreover, due to their sensorial properties, they could be used as new ingredients to improve the diversity in modern diet and highly creative cuisine.
Sexual reproduction of the pentaploid, short-styled Oxalis pes-caprae allows the production of viable offspring.[Pubmed: 23594049]
Reproduction is a key factor for the successful establishment and spread of introduced species. Oxalis pes-caprae is a tristylous species with a self- and morph-incompatibility sexual system that, in the invaded range of the western Mediterranean Basin, has been found to reproduce asexually because only the pentaploid, short-styled morph (5x S-morph) was introduced. The objective of this study was to test the ability of the 5x S-morph of O. pes-caprae to produce viable offspring in the absence of compatible mates, exploring the hypothesis that new morphs could have emerged by sexual reproduction events of the initially introduced morph. Pollen germination, pollen tube development, fruit and seed production, seed germination and offspring ploidy levels were analysed after controlled hand-pollinations to assess self- and morph-incompatibility and production of viable gametes by the 5x S-morph. The self-incompatibility system is still operating, but a partial breakdown in the morph-incompatibility system combined with the production of viable gametes was observed, allowing sexual reproduction of the 5x S-morph in the invaded range. The ability of the 5x S-morph to reproduce sexually may have major consequences for the dynamics of invasive populations of O. pes-caprae and could be one of the factors involved in the occurrence of new floral morphs in this invaded range.
Evaluation of anti-oxidant activity and identification of major polyphenolics of the invasive weed Oxalis pes-caprae.[Pubmed: 22552843]
Phytochemical analyses of weeds, many of which have been used in traditional medicine worldwide, could lead to the identification of secondary metabolites with significant biological activity.
A new aromatic component from Oxalis pes-caprae.[Pubmed: 20496235]
The fresh leaves and twigs of Oxalis pes-caprae were crumbled and extracted with ethyl acetate and methanol. The extracts were fractionated by chromatographic procedures, followed by structure elucidation using mass spectrometry and (1)H- and (13)C-NMR spectroscopy and a new phenyl cinnamate derivative was identified, along with some known compounds.


