Oxyria digyna
Oxyria digyna
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Oxyria digyna
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
BCN5330
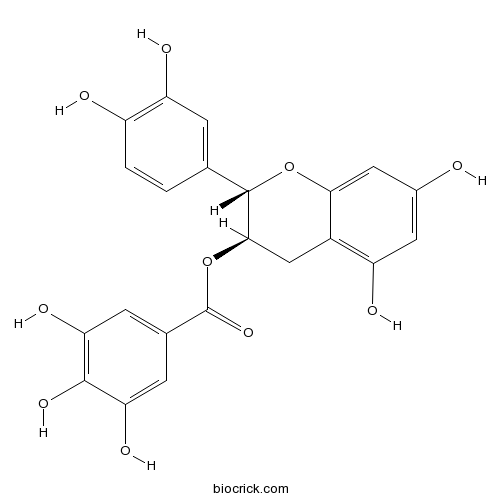
(-)-Catechin gallate(CG)130405-40-2
Instructions
Climate adaptation is not enough: warming does not facilitate success of southern tundra plant populations in the high Arctic.[Pubmed: 27391174]
Rapidly rising temperatures are expected to cause latitudinal and elevational range shifts as species track their optimal climate north and upward. However, a lack of adaptation to environmental conditions other than climate - for example photoperiod, biotic interactions, or edaphic conditions - might limit the success of immigrants in a new location despite hospitable climatic conditions. Here, we present one of the first direct experimental tests of the hypothesis that warmer temperatures at northern latitudes will confer a fitness advantage to southern immigrants relative to native populations. As rates of warming in the Arctic are more than double the global average, understanding the impacts of warming in Arctic ecosystems is especially urgent. We established experimentally warmed and nonwarmed common garden plots at Alexandra Fiord, Ellesmere Island in the Canadian High Arctic with seeds of two forb species (Oxyria digyna and Papaver radicatum) originating from three to five populations at different latitudes across the Arctic. We found that plants from the local populations generally had higher survival and obtained a greater maximum size than foreign individuals, regardless of warming treatment. Phenological traits varied with latitude of the source population, such that southern populations demonstrated substantially delayed leaf-out and senescence relative to northern populations. Our results suggest that environmental conditions other than temperature may influence the ability of foreign populations and species to establish at more northerly latitudes as the climate warms, potentially leading to lags in northward range shifts for some species.
Arctic plant origins and early formation of circumarctic distributions: a case study of the mountain sorrel, Oxyria digyna.[Pubmed: 26197783]
Many plant species comprising the present-day Arctic flora are thought to have originated in the high mountains of North America and Eurasia, migrated northwards as global temperatures fell during the late Tertiary period, and thereafter attained a circumarctic distribution. However, supporting evidence for this hypothesis that provides a temporal framework for the origin, spread and initial attainment of a circumarctic distribution by an arctic plant is currently lacking. Here we examined the origin and initial formation of a circumarctic distribution of the arctic mountain sorrel (Oxyria digyna) by conducting a phylogeographic analysis of plastid and nuclear gene DNA variation. We provide evidence for an origin of this species in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau of southwestern China, followed by migration into Russia c. 11 million yr ago (Ma), eastwards into North America by c. 4 Ma, and westwards into Western Europe by c. 1.96 Ma. Thereafter, the species attained a circumarctic distribution by colonizing Greenland from both sides of the Atlantic Ocean. Following the arrival of the species in North America and Europe, population sizes appear to have increased and then stabilized there over the last 1 million yr. However, in Greenland a marked reduction followed by an expansion in population size is indicated to have occurred during the Pleistocene.
Cytomorphological investigations in Oxyria digyna Hill. from the Kashmir Himalaya, India.[Pubmed: 24791473]
In the present paper, detailed cytomorphological investigations in Oxyria digyna Hill. from Kashmir Himalaya-India have been reported for the first time. All the of 14 investigated populations of O. digyna are diploid based on x = 7. Out of these in two populations 0-2B chromosomes have been recorded for the first time while 6 populations differed significantly in their meiotic characteristics. Meiotic abnormalities during male meiosis observed include inter PMC chromatin transfer (cytomixis). Non-synchronous disjunction of some bivalents, laggards and bridges at anaphases and telophases. Consequent to these meiotic anomalies, microsporogenesis in meiocytes is abnormal resulting in to dyads, triads and polyads with or without micronuclei. The overall effect is seen in reduced pollen fertility. Unreduced pollen grains were observed in some populations, which differed significantly in their size compared to the normal (reduced) pollen grains. It is observed that a smaller frequency of pollen grains differed morphologically in Aharbal and Yosmarg populations. The remaining eight populations showed regular meiotic course, normal microsporogenesis and high percentage of pollen fertility (95.09-99.09%).
Endophytic bacterial communities in three arctic plants from low arctic fell tundra are cold-adapted and host-plant specific.[Pubmed: 22861658]
Endophytic bacteria inhabit internal plant tissues, and have been isolated from a large diversity of plants, where they form nonpathogenic relationships with their hosts. This study combines molecular and culture-dependent approaches to characterize endophytic bacterial communities of three arcto-alpine plant species (Oxyria digyna, Diapensia lapponica and Juncus trifidus) sampled in the low Arctic (69°03'N). Analyses of a 325 bacterial endophyte isolates, as well as seven clone libraries, revealed a high diversity. In particular, members of the Actinobacteria, Bacteroidetes, Firmicutes, Acidobacteria, and Proteobacteria were found. The compositions of the endophytic bacterial communities were dependent on host-plant species as well as on snow cover at sampling sites. Several bacterial genera were found to be associated tightly with specific host-plant species. In particular, Sphingomonas spp. were characteristic for D. lapponica and O. digyna, and their phylogenetic grouping corresponded to the host plant. Most of the endophyte isolates grew well and retained activity at +4 °C, and isolate as well as clone library sequences were often highly similar to sequences from bacteria from cold environments. Taken together, this study shows that arctic plants harbour a diverse community of bacterial endophytes, a portion of which seems to be tightly associated with specific plant species.
The impact of Pleistocene climate change on an ancient arctic-alpine plant: multiple lineages of disparate history in Oxyria digyna.[Pubmed: 22822441]
The ranges of arctic-alpine species have shifted extensively with Pleistocene climate changes and glaciations. Using sequence data from the trnH-psbA and trnT-trnL chloroplast DNA spacer regions, we investigated the phylogeography of the widespread, ancient (>3 million years) arctic-alpine plant Oxyria digyna (Polygonaceae). We identified 45 haplotypes and six highly divergent major lineages; estimated ages of these lineages (time to most recent common ancestor, T(MRCA)) ranged from ∼0.5 to 2.5 million years. One lineage is widespread in the arctic, a second is restricted to the southern Rocky Mountains of the western United States, and a third was found only in the Himalayan and Altai regions of Asia. Three other lineages are widespread in western North America, where they overlap extensively. The high genetic diversity and the presence of divergent major cpDNA lineages within Oxyria digyna reflect its age and suggest that it was widespread during much of its history. The distributions of individual lineages indicate repeated spread of Oxyria digyna through North America over multiple glacial cycles. During the Last Glacial Maximum it persisted in multiple refugia in western North America, including Beringia, south of the continental ice, and within the northern limits of the Cordilleran ice sheet. Our data contribute to a growing body of evidence that arctic-alpine species have migrated from different source regions over multiple glacial cycles and that cryptic refugia contributed to persistence through the Last Glacial Maximum.
Mining of unexplored habitats for novel chitinases--chiA as a helper gene proxy in metagenomics.[Pubmed: 22526805]
The main objective of this study was to assess the abundance and diversity of chitin-degrading microbial communities in ten terrestrial and aquatic habitats in order to provide guidance to the subsequent exploration of such environments for novel chitinolytic enzymes. A combined protocol which encompassed (1) classical overall enzymatic assays, (2) chiA gene abundance measurement by qPCR, (3) chiA gene pyrosequencing, and (4) chiA gene-based PCR-DGGE was used. The chiA gene pyrosequencing is unprecedented, as it is the first massive parallel sequencing of this gene. The data obtained showed the existence across habitats of core bacterial communities responsible for chitin assimilation irrespective of ecosystem origin. Conversely, there were habitat-specific differences. In addition, a suite of sequences were obtained that are as yet unregistered in the chitinase database. In terms of chiA gene abundance and diversity, typical low-abundance/diversity versus high-abundance/diversity habitats was distinguished. From the combined data, we selected chitin-amended agricultural soil, the rhizosphere of the Arctic plant Oxyria digyna and the freshwater sponge Ephydatia fluviatilis as the most promising habitats for subsequent bioexploration. Thus, the screening strategy used is proposed as a guide for further metagenomics-based exploration of the selected habitats.


