Parthenocissus quinquefolia
Parthenocissus quinquefolia
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Parthenocissus quinquefolia
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
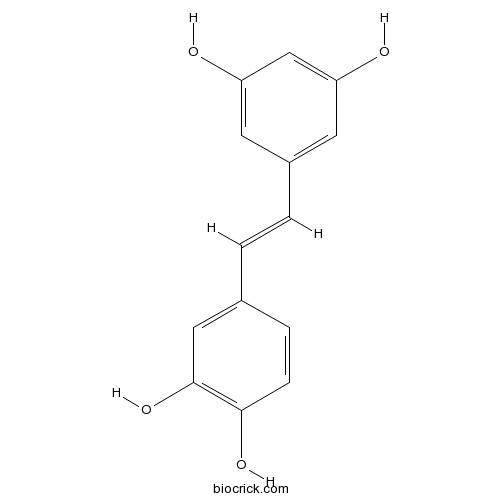
BCN5824
Piceatannol10083-24-6
Instructions
-
BCN5607
Resveratrol501-36-0
Instructions

Geographic distribution of cryptic species of Plasmopara viticola causing downy mildew on wild and cultivated grape in eastern North America.[Pubmed: 24915427]
The putative center of origin of Plasmopara viticola, the causal agent of grape downy mildew, is eastern North America, where it has been described on several members of the family Vitaceae (e.g., Vitis spp., Parthenocissus spp., and Ampelopsis spp.). We have completed the first large-scale sampling of P. viticola isolates across a range of wild and cultivated host species distributed throughout the above region. Sequencing results of four partial genes indicated the presence of a new P. viticola species on Vitis vulpina in Virginia, adding to the four cryptic species of P. viticola recently recorded. The phylogenetic analysis also indicated that the P. viticola species found on Parthenocissus quinquefolia in North America is identical to Plasmopara muralis in Europe. The geographic distribution and host range of five pathogen species was determined through analysis of the internal transcribed spacer polymorphism of 896 isolates of P. viticola. Among three P. viticola species found on cultivated grape, one was restricted to Vitis interspecific hybrids within the northern part of eastern North America. A second species was recovered from V. vinifera and V. labrusca, and was distributed across most of the sampled region. A third species, although less abundant, was distributed across a larger geographical range, including the southern part of eastern North America. P. viticola clade aestivalis predominated (83% of isolates) in vineyards of the European winegrape V. vinifera within the sampled area, indicating that a single pathogen species may represent the primary threat to the European host species within eastern North America.
Two new oligostilbenes from the stem of Parthenocissus quinquefolia.[Pubmed: 24456249]
Two new oligostilbenes, parthenocissins M (1) and N (2), together with two known compounds, miyabenol C (3) and ϵ-viniferin (4), were isolated from the stem of Parthenocissus quinquefolia. Their structures were elucidated by means of NMR, UV, IR, and MS data.
Phylogenetic and experimental evidence for host-specialized cryptic species in a biotrophic oomycete.[Pubmed: 23153246]
Assortative mating resulting from host plant specialization has been proposed to facilitate rapid ecological divergence in biotrophic plant pathogens. Downy mildews, a major group of biotrophic oomycetes, are prime candidates for testing speciation by host plant specialization. Here, we combined a phylogenetic and morphological approach with cross-pathogenicity tests to investigate host plant specialization and host range expansion in grapevine downy mildew. This destructive disease is caused by Plasmopara viticola, an oomycete endemic to North America on wild species and cultivated grapevines. Multiple genealogies and sporangia morphology provide evidence that P. viticola is a complex of four cryptic species, each associated with different host plants. Cross-inoculation experiments showed complete host plant specialization on Parthenocissus quinquefolia and on Vitis riparia, whereas cryptic species found on V. aestivalis, V. labrusca and V. vinifera were revealed to be less specific. We reconstructed the recent host range expansion of P. viticola from wild to cultivated grapevines, and showed that it was accompanied by an increase in aggressiveness of the pathogen. This case study on grapevine downy mildew illustrates how biotrophic plant pathogens can diversify by host plant specialization and emerge in agrosystems by shifting to cultivated hosts. These results might have important implications for viticulture, including breeding for resistance and disease management.
Antispila oinophylla new species (Lepidoptera, Heliozelidae), a new North American grapevine leafminer invading Italian vineyards: taxonomy, DNA barcodes and life cycle.[Pubmed: 22408380]
A grapevine leafminer Antispila oinophylla van Nieukerken & Wagner, sp. n., is described both from eastern North America (type locality: Georgia) and as a new important invader in North Italian vineyards (Trentino and Veneto Region) since 2006. The species is closely related to, and previously confused with Antispila ampelopsifoliella Chambers, 1874, a species feeding on Virginia creeper Parthenocissus quinquefolia (L.) Planchon., and both are placed in an informal Antispila ampelopsifoliella group. Wing pattern, genitalia, and DNA barcode data all confirm the conspecificity of native North American populations and Italian populations. COI barcodes differ by only 0-1.23%, indicating that the Italian populations are recently established from eastern North America. The new species feeds on various wild Vitis species in North America, on cultivated Vitis vinifera L. in Italy, and also on Parthenocissus quinquefolia in Italy. North American Antispila feeding on Parthenocissus include at least two other species, one of which is Antispila ampelopsifoliella. Morphology and biology of the new species are contrasted with those of North American Antispila Hübner, 1825 species and European Holocacista rivillei (Stainton, 1855). The source population of the introduction is unknown, but cases with larvae or pupae, attached to imported plants, are a likely possibility. DNA barcodes of the three European grapevine leafminers and those of all examined Heliozelidae are highly diagnostic. North American Vitaceae-feeding Antispila form two species complexes and include several as yet unnamed taxa. The identity of three out of the four previously described North American Vitaceae-feeding species cannot be unequivocally determined without further revision, but these are held to be different from Antispila oinophylla. In Italy the biology of Antispila oinophylla was studied in a vineyard in the Trento Province (Trentino-Alto Adige Region) in 2008 and 2009. Mature larvae overwinter inside their cases, fixed to vine trunks or training stakes. The first generation flies in June. An additional generation occurs from mid-August onwards. The impact of the pest in this vineyard was significant with more than 90% of leaves infested in mid-summer. Since the initial discovery in 2006, the pest spread to several additional Italian provinces, in 2010 the incidence of infestation was locally high in commercial vineyards. Preliminary phylogenetic analyses suggest that Antispila is paraphyletic, and that the Antispila ampelopsifoliella group is related to Coptodisca Walsingham, 1895, Holocacista Walsingham & Durrant, 1909 and Antispilina Hering, 1941, all of which possess reduced wing venation. Vitaceae may be the ancestral hostplant family for modern Heliozelidae.
Response of grape root borer (Lepidoptera: Sesiidae) neonates to root extracts from Vitaceae species and rootstocks.[Pubmed: 22251689]
Observations at regular intervals of the location of newly hatched grape root borer, Vitacea polistiformis (Harris), larvae moving freely within circular petri dish bioassays were used to measure and compare their response to dry filter paper discs treated with ethanol- or hexane-based extracts of roots from known and potential Vitaceae hosts and a nonhost. Larvae responded most strongly to discs treated with ethanol extracts, suggesting the presence of behaviorally active, polar compounds associated with roots. In single extract bioassays comparing extract versus solvent treated discs, larvae responded positively to ethanol extracts from all Vitis species and rootstocks and Virginia creeper [Parthenocissus quinquefolia (L.) Planch.], but not to apple (Malus domestica Borkh). Paired extract bioassays, in which an extract from the commercially important 3309 rootstock was used as the standard and presented simultaneously with extracts from other root sources, revealed examples of equal, significantly weaker and significantly stronger responses to the 3309 extract. Extracts of the 420 A and V. riparia 'Gloire' rootstocks appeared to possess qualities that elicited a consistently greater response than to 3309 extract in these pair-wise comparisons. The active compounds were eluted in ethanol during a 30-min extraction; larvae responded equally to 30- and 60-min 3309 root extracts in paired extract bioassays. Larvae responded equally to extracts of 3309 roots from three spatially separate vineyards in northern Virginia. These results are discussed in relation to the subterranean, plant-insect interactions of grape root borer neonates with the numerous native and non-native Vitis species that may serve as hosts in the eastern United States.
Screening of plant species for phytoremediation of uranium, thorium, barium, nickel, strontium and lead contaminated soils from a uranium mill tailings repository in South China.[Pubmed: 21523506]
The concentrations of uranium, thorium, barium, nickel, strontium and lead in the samples of the tailings and plant species collected from a uranium mill tailings repository in South China were analyzed. Then, the removal capability of a plant for a target element was assessed. It was found that Phragmites australis had the greatest removal capabilities for uranium (820 μg), thorium (103 μg) and lead (1,870 μg). Miscanthus floridulus had the greatest removal capabilities for barium (3,730 μg) and nickel (667 μg), and Parthenocissus quinquefolia had the greatest removal capability for strontium (3,920 μg). In this study, a novel coefficient, termed as phytoremediation factor (PF), was proposed, for the first time, to assess the potential of a plant to be used in phytoremediation of a target element contaminated soil. Phragmites australis has the highest PFs for uranium (16.6), thorium (8.68), barium (10.0) and lead (10.5). Miscanthus floridulus has the highest PF for Ni (25.0). Broussonetia papyrifera and Parthenocissus quinquefolia have the relatively high PFs for strontium (28.1 and 25.4, respectively). On the basis of the definition for a hyperaccumulator, only Cyperus iria and Parthenocissus quinquefolia satisfied the criteria for hyperaccumulator of uranium (36.4 μg/g) and strontium (190 μg/g), and could be the candidates for phytoremediation of uranium and strontium contaminated soils. The results show that the PF has advantage over the hyperaccumulator in reflecting the removal capabilities of a plant for a target element, and is more adequate for assessing the potential of a plant to be used in phytoremediation than conventional method.
Effect of Wrightia tinctoria and Parthenocissus quinquefolia on blood glucose and insulin levels in the Zucker diabetic rat model.[Pubmed: 22754929]
The aim of this study is to evaluate the antidiabetic activity of two Indian Ayurvedic herbs using an oral glucose tolerance test and blood insulin levels to understand the mechanism of action using the Zucker diabetic rat model. Herbal extracts of Wrightia tinctoria and Parthenocissus quinquefolia at a dose of (250 mg/kg body weight) were used throughout the study. Following a glucose challenge of 2 gm/kg using oral gavage, a timed glucose tolerance test was used to determine the ability of these extracts to alter glucose levels in diabetic animal model. The glucose lowering activities of these extracts were then compared to the controls. Both tested herbal extracts have shown to exhibit significant (P < 0.05) hypoglycemic activity compared to the control. W. tinctoria and P. quinquefolia have an antidiabetic activity which reduced the blood glucose level in oral glucose tolerance test significantly compared with the control. To further understand their mechanism of action, blood insulin levels were also studied using an insulin Elisa assay. These studies revealed that the herbal extract of P. quinquefolia has direct correlation between glucose and insulin levels. However, W. tinctoria significantly lowered blood glucose levels (P< 0.05), while it did not show any correlation between blood glucose and insulin levels. Based on these findings, it can be concluded that hypoglycemic effects of W. tinctoria are more complicated than P. quinquefolia, and may involve other possible mechanism of action.
[Chemical constituents from Parthenocissus quinquefolia].[Pubmed: 20815210]
The chemical constituents of Parthenocissus quinque were investigated. The chemical constituents were isolated by column chromatography on silical gel and sephadex LH-20. Their structures were elucidated on the basis of spectral analysis and of comparison of physical constant. Nine compounds were isolated from this plant and the structures of them were identified as 3,4,5-trihydroxy- benzoic acid (1), piceatannol (2), resveratrol (3), resveratrol trans-dehydrodimer (4), cyphoste mmin B (5), pallidol (6), cyphostemmin A (7), quercetin-3-O-alpha-L-rhamnoside (8), myricetin-3-O-alpha-L-rhamnoside (9), respectively. Compounds 1, 4-9 were isolated from this plant for the first time.
Spatiotemporal dynamics of lianas during 50 years of succession to temperate forest.[Pubmed: 20426327]
Although they are important components of forest communities, the general ecology and spatiotemporal patterns of temperate lianas during forest regeneration are largely unknown. The dependence of lianas on other plants for physical support makes them a potentially important driver of community dynamics. We examined 50 years of vegetation data from an old-field succession study to determine the dynamics and community controls on liana expansion within the Piedmont region of New Jersey, USA. Four lianas, Lonicera japonica, Parthenocissus quinquefolia, Toxicodendron radicans, and Vitis spp., occurred in enough abundance for detailed analyses. In general, liana cover peaked during mid-succession (20-30 years post-abandonment) when community composition was mostly herbaceous with scattered trees and shrubs. Liana cover began to decrease as trees became dominant and the canopy closed. Temporal patterns of cover dynamics of abundant species indicated three early- and one late-successional liana species within the community. In contrast to cover, frequency of lianas increased throughout succession, indicating that liana populations persisted despite dramatic declines in cover for the three early-successional species. Temporal dynamics between native and nonnative lianas were similar but spatially distinct as cover of native species dispersed and expanded near the forest edge while the nonnative species preferentially grew far from the forest. These dynamics indicate that successional processes may ultimately lead to the decline of most lianas. However, the persistence of lianas as high numbers of suppressed individuals suggests that they may rebound quickly following canopy disturbance.
Nondestructive estimation of anthocyanins and chlorophylls in anthocyanic leaves.[Pubmed: 21622307]
The anthocyanin and chlorophyll contents in leaves provide valuable information about the physiological status of plants. Thus, there is a need for accurate, efficient, and practical methodologies to estimate these biochemical parameters of vegetation. In this study, we tested the performance and accuracy of several nondestructive, reflectance-based techniques for estimating anthocyanin and chlorophyll contents in leaves of four unrelated species, European hazel (Corylus avellana), Siberian dogwood (Cornus alba =Swida alba), Norway maple (Acer platanoides), and Virginia creeper (Parthenocissus quinquefolia), with widely variable pigment content and composition. An anthocyanin reflectance index, which uses reflectances in the green and red edge spectral bands, and a modified anthocyanin reflectance index, employing, in addition, the near-infrared (NIR) band, were able to accurately estimate leaf anthocyanin for all species taken together with no reparameterization of algorithms. Total chlorophyll content was accurately estimated by a red edge chlorophyll index that uses spectral bands in the red edge and the NIR. These approaches can be used to estimate anthocyanin and chlorophyll nondestructively and allow the development of simple handheld field instrumentation.


