Plantago depressa
Plantago depressa
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Plantago depressa
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
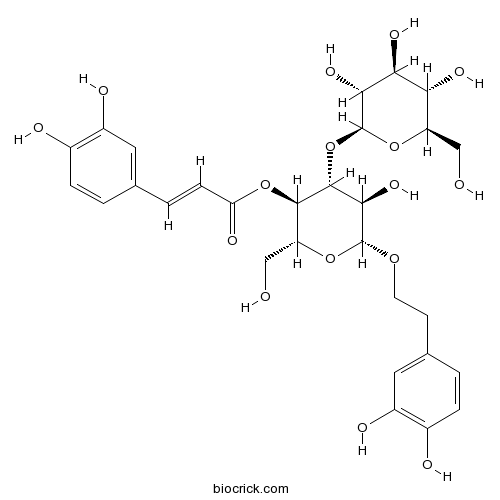
BCN6279
Plantamajoside104777-68-6
Instructions
-
BCN8614
Plantainoside D147331-98-4
Instructions

-
BCN4327
Ursolic acid77-52-1
Instructions

Optimization and antioxidant activity of polysaccharides from Plantago depressa.[Pubmed: 27616693]
None
Antioxidant-Rich Extract from Plantaginis Semen Ameliorates Diabetic Retinal Injury in a Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rat Model.[Pubmed: 27649243]
Plantaginis semen, the dried ripe seed of Plantago asiatica L. or Plantago depressa Willd. (Plantaginaceae), has been traditionally used to treat blurred vision in Asia. The aim of this work was to investigate the effect of plantaginis semen ethanol extract (PSEE) on the amelioration of diabetic retinopathy (DR) in streptozotocin (STZ)-diabetic rats. PSEE has abundant polyphenols with strong antioxidant activity. PSEE (100, 200 or 300 mg/kg) was oral administrated to the diabetic rats once daily consecutively for 8 weeks. Oral administration of PSEE resulted in significant reduction of hyperglycemia, the diameter of the retinal vessels, and retinal vascular permeability and leukostasis in diabetic rats. In addition, PSEE administration increased the activities of superoxidase dismutase (SOD) and catalase (CAT), and glutathione peroxidase (GSH) level in diabetic retinae. PSEE treatment inhibited the expression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) and the phosphorylation of Akt without altering the Akt protein expression in diabetic retinae. PSEE not only down-regulated the gene expression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (TNF-α) and interleukin-1β (IL-1β), but also reduced ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 expression in diabetic retinae. Moreover, PSEE reduced the nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) activation and corrected imbalance between histone deacetylases (HDAC) and histone acetyltransferases (HAT) activities in diabetic retinae. In conclusion, phenolic antioxidants extract from plantaginis semen has potential benefits in the prevention and/or progression of DR.
Plantadeprate A, a Tricyclic Monoterpene Zwitterionic Guanidium, and Related Derivatives from the Seeds of Plantago depressa.[Pubmed: 26562611]
Two new alkaloids, plantadeprate A (1) and 1'-(4″-hydroxybutyl)plantagoguanidinic acid (2), along with three known compounds, were isolated from the seeds of Plantago depressa. Their structures were elucidated by physical data analyses including NMR, MS, and electronic circular dichroism (ECD) methods. Plantadeprate A (1), a monoterpene zwitterionic guanidium, possesses a unique 5/5/6-tricyclic ring system. Its absolute configuration was determined by X-ray crystallography and computational methods. Compound 1, plumbagine D (3), and plantagoguanidinic acid (4) exhibited potential antihyperglycemic properties attributed to suppression of hepatic gluconeogenesis with inhibitory rates of 8.2%, 18.5%, and 12.5% at 40 μM, respectively.
Purification, characterization and immunomodulatory effects of Plantago depressa polysaccharides.[Pubmed: 25129717]
Four purified polysaccharide fractions from seeds of Plantago depressa (PDSP-1, PDSP-2, PDSP-3 and PDSP-4) were obtained by isolation and purification using DEAE-52 cellulose and Sephacryl S-400 HR chromatography. Basic physicochemical properties including molecular weight, chemical composition, FT-IR and glycosidic linkage of these fractions were investigated. They seemed to be homogeneous acidic protein-bound heteropolysaccharides with high molecular weight of over 1000 kDa and contained a lot more β-type glycosidic linkages than α-type. PDSP-3 mainly contained mannose, arabinose and fucose, and the others were rich in arabinose, fucose and galacturonic acid. The immunomodulatory effects of them were assessed by splenocyte proliferation index and production of NO and TNF-α from macrophages. They all showed significant immunomodulatory activities, and PDSP-3 presented the strongest effect. Their observed differences in biological activities were probably due to their structure differences. And monosaccharide compositions, linkage types and molecular weight may affect their immunomodulatory activities.
A new phenylethanoid glucoside from Plantago depressa Willd.[Pubmed: 22574728]
Chemical research of Plantago depressa Willd. led to one new phenylethanoid glucoside with α-L-rhamnosyl (1 → 2)-β-D-glucose structure, together with four known compounds. These five compounds (1-5) were isolated from the family Plantaginaceae for the first time; the chemotaxonomic significance of cerebrosides was also discussed.


