Rhodobryum roseum
Rhodobryum roseum
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Rhodobryum roseum
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
BCN6305
Stevioside57817-89-7
Instructions

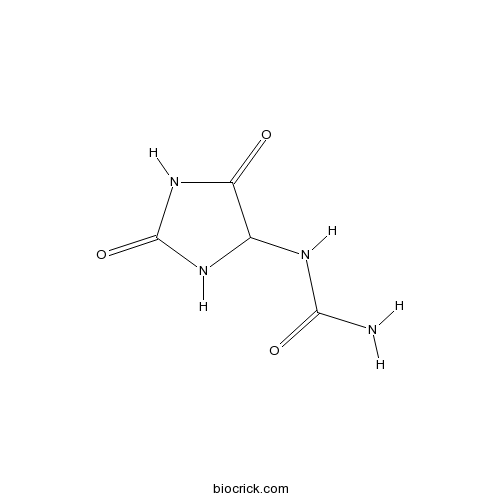
-
BCN4527
Allantoin97-59-6
Instructions
Classification and identification of Rhodobryum roseum Limpr. and its adulterants based on fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) and chemometrics.[Pubmed: 28207900]
Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) with the attenuated total reflectance technique was used to identify Rhodobryum roseum from its four adulterants. The FTIR spectra of six samples in the range from 4000 cm-1 to 600 cm-1 were obtained. The second-derivative transformation test was used to identify the small and nearby absorption peaks. A cluster analysis was performed to classify the spectra in a dendrogram based on the spectral similarity. Principal component analysis (PCA) was used to classify the species of six moss samples. A cluster analysis with PCA was used to identify different genera. However, some species of the same genus exhibited highly similar chemical components and FTIR spectra. Fourier self-deconvolution and discrete wavelet transform (DWT) were used to enhance the differences among the species with similar chemical components and FTIR spectra. Three scales were selected as the feature-extracting space in the DWT domain. The results show that FTIR spectroscopy with chemometrics is suitable for identifying Rhodobryum roseum and its adulterants.
Antioxidant effects of a Rhodobryum roseum extract and its active components in isoproterenol-induced myocardial injury in rats and cardiac myocytes against oxidative stress-triggered damage.[Pubmed: 19216232]
The aim of this study was to investigate (1) whether Rhodobryum roseum, a traditional Chinese medicine used to treat cardiac disease, can protect myocardium damage due to isoproterenol-induced injury, (2) whether the cardioprotective effect of the R. roseum extract is related to its antioxidant activity, and (3) to identify the active components of R. roseum using the oxidant-mediated injury in cardiomyocytes. R. roseum was extracted with 95% EtOH (RE-95), 50% EtOH (RE-50) and water (Re-H2O) and the rats were treated orally for 11 days at doses of 250 mg and 63 mg/kg respectively after cardiac necrosis was induced by administering ISO subcutaneously at a dose of 85 mg/kg body weight. Levels of marker enzymes (LDH, GOT and CK) were assessed in serum whilst the antioxidant parameters, superoxide dismutase (SOD), and malondialdehde (MDA) were assayed in heart homogenate. Significant myocardial necrosis, depletion of endogenous antioxidants and an increase in serum levels of marker enzymes was observed in ISO-treated animals when compared with the normal animals. The RE-50 elicited a significant cardioprotective effect by lowering the levels of serum marker enzymes, lipid peroxidation (MDA). To extend this work, we sought to investigate the antioxidant effects of the components of R. roseum, using the neonatal rat cardiomyocytes model of H2O2-induced oxidant injury. Among the four major components, piperine and methyl piperate significantly reduced the medium level of CK and LDH at a variety of dosages. Moreover, piperine and methyl piperate significantly attenuated 2',7'-dichlorofluorescein (DCF) fluorescence by 63.9% and 52.6%, respectively. The present findings demonstrate that the cardioprotective effects of extracted R. roseum in ISO-induced oxidative damage may be due to an augmentation of the endogenous antioxidants and inhibition of lipid peroxidation of the membranes. Moreover, its components piperine and methyl piperate exert significant protectective effects on cardiac myocytes.
[Studies on chemical constituents from moss Rhodobryum roseum II].[Pubmed: 17048608]
To study the chemical constituents from Rhodobryum roseum.
[Studies on the chemical constituents from herb of Rhodobryum roseum].[Pubmed: 16124603]
To study the chemical constituents from herb of Rhodobryum roseum.
Plant mitochondrial RNA editing.[Pubmed: 10093219]
RNA editing affects messenger RNAs and transfer RNAs in plant mitochondria by site-specific exchange of cytidine and uridine bases in both seed and nonseed plants. Distribution of the phenomenon among bryophytes has been unclear since RNA editing has been detected in some but not all liverworts and mosses. A more detailed understanding of RNA editing in plants required extended data sets for taxa and sequences investigated. Toward this aim an internal region of the mitochondrial nad5 gene (1104 nt) was analyzed in a large collection of bryophytes and green algae (Charles). The genomic nad5 sequences predict editing in 30 mosses, 2 hornworts, and 7 simple thalloid and leafy liverworts (Jungermanniidae). No editing is, however, required in seven species of the complex thalloid liverworts (Marchantiidae) and the algae. RNA editing among the Jungermanniidae, on the other hand, reaches frequencies of up to 6% of codons being modified. Predictability of RNA editing from the genomic sequences was confirmed by cDNA analysis in the mosses Schistostega pennata and Rhodobryum roseum, the hornworts Anthoceros husnotii and A. punctatus, and the liverworts Metzgeria conjugata and Moerckia flotoviana. All C-to-U nucleotide exchanges predicted to reestablish conserved codons were confirmed. Editing in the hornworts includes the removal of genomic stop codons by frequent reverse U-to-C edits. Expectedly, no RNA editing events were identified by cDNA analysis in the marchantiid liverworts Ricciocarpos natans, Corsinia coriandra, and Lunularia cruciata. The findings are discussed in relation to models on the phylogeny of land plants.
[Effect of Rhodobryum roseum on hemorheology following acute coronary occlusion in dogs].[Pubmed: 8155946]
Following acute occlusion of the left anterior descending coronary artery, the significant and constant hemorheologic changes were observed in venous blood from ischemic area. 30 min after occlusion, the high shear rate (r = 230s-1), middle shear rate (r = 23s-1) and low shear rate (r = 5.75s-1), viscosity of whole blood (eta b) increased significantly, and this change occurred in viscosity of plasma (eta p) and in red cell electrophoretic time (RCET) also. These increases continued thereafter. In another group of dogs, 30 min after coronary occlusion, rapid dripping was performed with Rhodobryum roseum (Huixincao) injection from right femoral vein. After 10 min, eta b at all shear rate reduced significantly, and this reduction was observed in eta p and in RCET also. These findings suggested that the hyperviscosity syndrome developed in acute myocardial ischemic could be blocked by Hui Xin Cao.


