Rubus crataegifolius
Rubus crataegifolius
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Rubus crataegifolius
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
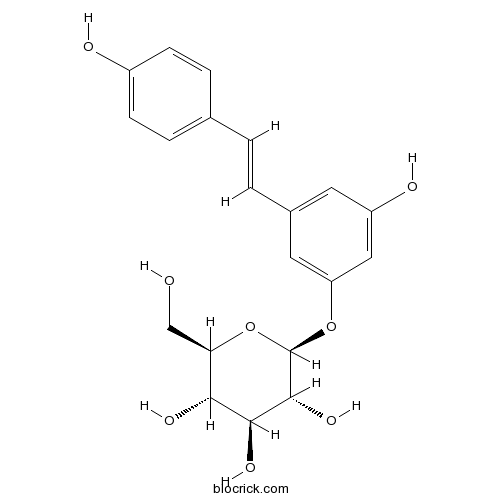
BCN5949
Polydatin27208-80-6
Instructions
-
BCN4546
4-Hydroxybenzoic acid99-96-7
Instructions

Hepatoprotective effect against CCl4-induced acute liver damage in mice and High-performance liquid chromatography mass spectrometric method for analysis of the constituents of extract of Rubus crataegifolius.[Pubmed: 28322066]
None
Rubus crataegifolius Bunge regulates adipogenesis through Akt and inhibits high-fat diet-induced obesity in rats.[Pubmed: 27123039]
Obesity is one of the greatest public health problems and major risk factors for serious metabolic diseases and significantly increases the risk of premature death. The aim of this study was to determine the inhibitory effects of Rubus crataegifolius Bunge (RCB) on adipocyte differentiation in 3 T3-L1 cells and its anti-obesity properties in high fat diet (HFD)-induced obese rats.
Novel microsatellite markers acquired from Rubus coreanus Miq. and cross-amplification in other Rubus species.[Pubmed: 25867828]
The Rubus genus consists of more than 600 species that are distributed globally. Only a few Rubus species, including raspberries and blueberries, have been domesticated. Genetic diversity within and between Rubus species is an important resource for breeding programs. We developed genomic microsatellite markers using an SSR-enriched R. coreanus library to study the diversity of the Rubus species. Microsatellite motifs were discovered in 546 of 646 unique clones, and a dinucleotide repeat was the most frequent (75.3%) type of repeat. From 97 microsatellite loci with reproducible amplicons, we acquired 29 polymorphic microsatellite markers in the Rubus coreanus collection. The transferability values ranged from 59.8% to 84% across six Rubus species, and Rubus parvifolius had the highest transferability value (84%). The average number of alleles and the polymorphism information content were 5.7 and 0.541, respectively, in the R. coreanus collection. The diversity index of R. coreanus was similar to the values reported for other Rubus species. A phylogenetic dendrogram based on SSR profiles revealed that seven Rubus species could be allocated to three groups, and that R. coreanus was genetically close to Rubus crataegifolius (mountain berry). These new microsatellite markers might prove useful in studies of the genetic diversity, population structure, and evolutionary relationships among Rubus species.
[Antioxidant activity constituents from root of Rubus crataegifolius].[Pubmed: 23477146]
To study the antioxidant constituents from the root of Rubus crataegifolius.
Preparation of a glucan from the roots of Rubus crataegifolius Bge. and its immunological activity.[Pubmed: 19853841]
A water-soluble glucan (RCP-1) was prepared from the roots of Rubus crataegifolius Bge. by extraction with hot-water, deproteination by Sevag reagent, alpha-amylase treatment and ultrafiltration. RCP-1 consisted of only glucose, and its molecular weight was determined to be approximately 7KD by high performance gel permeation chromatography (HPGPC). Fourier transform infra-red spectroscopy (FT-IR), nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (NMR), methylation and periodate oxidation analyses indicated that RCP-1 was an alpha-d-glucan. Its main chains were composed of (1-->4)- and (1-->6)-linked alpha-glucopyranosyls, and side chains were single alpha-glucopyranosyl residues attached to the O-6 of glucosyls in the main chains. RCP-1 could increase both cytotoxic activity against B16 melanoma cells and the production of nitric oxide (NO) of macrophages in vitro. Furthermore, in vivo bioassay tests indicated that RCP-1 could remarkably enhance T and B lymphocyte proliferations, augment the phagocytosis of macrophages and increase the tumour necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) levels in serum.
A triterpene glucosyl ester from the roots of Rubus crataegifolius.[Pubmed: 11693541]
Along with five known triterpene glycosides, a new triterpene glucosyl ester, named crataegioside, was isolated from the roots of Rubus crataegifolius Bunge. The structure was established as ilexosapogenin A 28-O-beta-D-glucopyranosyl ester by chemical and spectroscopic methods.
Activity of crude extract of Rubus crataegifolius roots as a potent apoptosis inducer and DNA topoisomerase I inhibitor.[Pubmed: 10976580]
The effects of methanol extract of Rubus crategifolius roots and its solvent fractions were investigated on the proliferation of MCF-7 human breast carcinoma cells. The methanol extract inhibited the proliferation of MCF-7 cells in a concentration dependent manner. Moreover, their methanol soluble (W-M) fraction had the greatest inhibitory effect on the growth of MCF-7 cells. To evaluate whether the W-M fraction affects on the cell cycle of MCF-7 cells, cells treated with this fraction were analyzed with flow cytometry. The W-M fraction increased G0/G1 phase after 24 h-treatment and induced apoptosis after 48 h-treatment. The hallmark of apoptosis, DNA fragmentation, also appeared by W-M fraction after 48 h-treatment. Furthermore, the methanol extract and its W-M fraction inhibited the activity of the topoisomerase I enzyme in the relaxation assay. From these results, their W-M fraction as well as methanol extract of R. crategifolius roots are necessary for further studies as a potent inhibitor of the growth of cancer cells.
[Anti-inflammatory effects of alcoholic extract of roots of Rubus crataegifolius Bge].[Pubmed: 9812702]
The alcoholic extract of roots of Rllbus crataegifolius can inhibited the swellfoot by albumen, and reduce the capillary permeability of pertoneum and the edematous swelling of ears in mice. The extract also facilitates the extinction of hind paw edema induced by carrageenin and inhibits the cotton pellets granuloma formation in rats.


