Rumex dentatus
Rumex dentatus
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Rumex dentatus
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
BCN1673
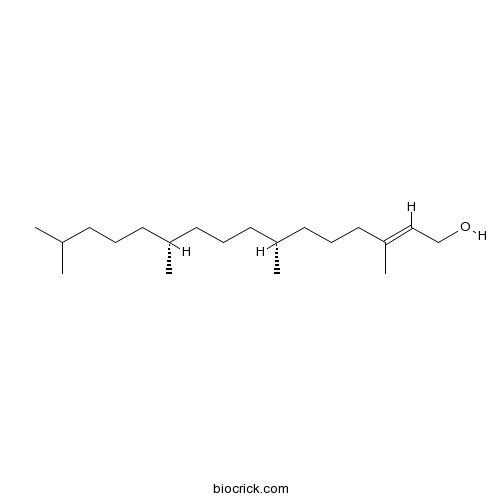
Phytol150-86-7
Instructions
Differential expression of vacuolar and defective cell wall invertase genes in roots and seeds of metalliferous and non-metalliferous populations of Rumex dentatus under copper stress.[Pubmed: 28822946]
Acid invertase activities in roots and young seeds of a metalliferous population (MP) of Rumex dentatus were previously observed to be significantly higher than those of a non-metalliferous population (NMP) under Cu stress. To date, no acid invertase gene has been cloned from R. dentatus. Here, we isolated four full-length cDNAs from the two populations of R. dentatus, presumably encoding cell wall (RdnCIN1 and RdmCIN1 from the NMP and MP, respectively) and vacuolar invertases (RdnVIN1 and RdmVIN1 from the NMP and MP, respectively). Unexpectedly, RdnCIN1 and RdmCIN1 most likely encode special defective invertases with highly attenuated sucrose-hydrolyzing capacity. The transcript levels of RdmCIN1 were significantly higher than those of RdnCIN1 in roots and young seeds under Cu stress, whereas under control conditions, the former was initially lower than the latter. Unexpected high correlations were observed between the transcript levels of RdnCIN1 and RdmCIN1 and the activity of cell wall invertase, even though RdnCIN1 and RdmCIN1 do not encode catalytically active invertases. Similarly, the transcript levels of RdmVIN1 in roots and young seeds were increased under Cu stress, whereas those of RdnVIN1 were decreased. The high correlations between the transcript levels of RdnVIN1 and RdmVIN1 and the activity of vacuolar invertase indicate that RdnVIN1 and RdmVIN1 might control distinct vacuolar invertase activities in the two populations. Moreover, a possible indirect role for acid invertases in Cu tolerance, mediated by generating a range of sugars used as nutrients and signaling molecules, is discussed.
Growth habit and leaf economics determine gas exchange responses to high elevation in an evergreen tree, a deciduous shrub and a herbaceous annual.[Pubmed: 26433706]
Plant growth at high elevations necessitates physiological and morphological plasticity to enable photosynthesis (A) under conditions of reduced temperature, increased radiation and the lower partial pressure of atmospheric gases, in particular carbon dioxide (pCO2). Previous studies have observed a wide range of responses to elevation in plant species depending on their adaptation to temperature, elevational range and growth habit. Here, we investigated the effect of an increase in elevation from 2500 to 3500 m above sea level (a.s.l.) on three montane species with contrasting growth habits and leaf economic strategies. While all of the species showed identical increases in foliar δ(13)C, dark respiration and nitrogen concentration with elevation, contrasting leaf gas exchange and photosynthetic responses were observed between species with different leaf economic strategies. The deciduous shrub Salix atopantha and annual herb Rumex dentatus exhibited increased stomatal (Gs) and mesophyll (Gm) conductance and enhanced photosynthetic capacity at the higher elevation. However, evergreen Quercus spinosa displayed reduced conductance to CO2 that coincided with lower levels of photosynthetic carbon fixation at 3500 m a.s.l. The lower Gs and Gm values of evergreen species at higher elevations currently constrains their rates of A. Future rises in the atmospheric concentration of CO2 ([CO2]) will likely predominantly affect evergreen species with lower specific leaf areas (SLAs) and levels of Gm rather than deciduous species with higher SLA and Gm values. We argue that climate change may affect plant species that compose high-elevation ecosystems differently depending on phenotypic plasticity and adaptive traits affecting leaf economics, as rising [CO2] is likely to benefit evergreen species with thick sclerophyllous leaves.
New trimethyl chitosan-based composite nanoparticles as promising antibacterial agents.[Pubmed: 26289003]
In the present study, densely dispersed silver nanoparticles (Ag NPs) were rapidly green synthesized in the presence of Rumex dentatus aqueous extract, followed by UV-irradiation reduction. The Ag NPs were characterized using UV-vis spectroscopy, FTIR, XRD, and TEM. Then, the Ag NPs were incorporated into interpenetrating polymeric networks based on cationic trimethyl chitosan (TMCS) and anionic poly(acrylamide-co-sodium acrylate) copolymer to develop a new series of composite nanoparticles as potential antibacterial agents. Both TMCS and poly(acrylamide-co-sodium acrylate) were prepared in the study, and characterized using FTIR, DSC, and SEM. The synthesized Ag NPs showed high purity and uniform particle size distribution with particle size ranged between 5 and 30 nm. The composite nanoparticles demonstrated homogeneous spherical shape with size in the range of 378-402 nm. Both Ag NPs and the composite nanoparticles showed promising bactericidal activity as compared with the control. Moreover, the antibacterial activity of the composite nanoparticles increased along with increasing the concentrations of Ag NPs and the TMCS.
New trimethyl chitosan-based composite nanoparticles as promising antibacterial agents.[Pubmed: 26266964]
In the present study, densely dispersed silver nanoparticles (Ag NPs) were rapidly green synthesized in the presence of Rumex dentatus aqueous extract, followed by UV-irradiation reduction. The Ag NPs were characterized using UV-vis spectroscopy, FTIR, XRD, and TEM. Then, the Ag NPs were incorporated into interpenetrating polymeric networks based on cationic trimethyl chitosan (TMCS) and anionic poly(acrylamide-co-sodium acrylate) copolymer to develop a new series of composite nanoparticles as potential antibacterial agents. Both TMCS and poly(acrylamide-co-sodium acrylate) were prepared in the study, and characterized using FTIR, DSC, and SEM. The synthesized Ag NPs showed high purity and uniform particle size distribution with particle size ranged between 5 and 30 nm. The composite nanoparticles demonstrated homogeneous spherical shape with size in the range of 378-402 nm. Both Ag NPs and the composite nanoparticles showed promising bactericidal activity as compared with the control. Moreover, the antibacterial activity of the composite nanoparticles increased along with increasing the concentrations of Ag NPs and the TMCS.
Differential response of terpenes and anthraquinones derivatives in Rumex dentatus and Lavandula officinalis to harsh winters across north-western Himalaya.[Pubmed: 25868521]
Herbs adapted to diverse climates exhibit distinct variability to fluctuating temperatures and demonstrate various metabolic and physiological adaptations to harsh environments. In this research, Rumex dentatus L. and Lavandula officinalis L. were collected before snowfall in September-November to evaluate variability in major phytoconstituents to diverse seasonal regime. LC-MS was used for simultaneous determination of eight anthraquinone derivatives in R. dentatus, i.e. emodin, physcion, chrysophanol, physcion glucoside, endocrocin, emodin glucoside, chrysophanol glucoside and chromone derivatives and monoterpenes in L. officinalis i.e. (Z)-β-ocimene, (E)-β-ocimene, terpene alcohol, terpin-4-ol, acetate ester-linalyl acetate and bicyclic sesquiterpene (E)-caryophyllene. The correlation analysis confirmed significant variation in anthraquinone glucoside and terpene content within Rumex and Lavender, respectively, and altitude was established as the determinant factor in secondary metabolism of both herbs. The study concludes the propagation of herbs in bioclimatic belts which favour accumulation of major constituents and validate their greater pharmacological activity.
Comparative study of root growth and sucrose-cleaving enzymes in metallicolous and non-metallicolous populations of Rumex dentatus under copper stress.[Pubmed: 24367815]
Sucrose metabolism in roots of metallophytes is very important for root growth and maintenance of heavy metal tolerance. However, rare researches have been carried out on this topic so far. We tested here a hypothesis that roots of copper-tolerant plants should manifest higher activities of sucrose-cleaving enzymes than non-tolerant plants for maintaining root growth under Cu stress. Plants of two contrasting populations of metallophyte Rumex dentatus, one from an ancient Cu mine (MP) and the other from a non-mine site (NMP), were treated with Cu in controlled experiments. Cu treatment resulted in a higher root biomass and root/shoot biomass ratio in MP compared to NMP. More complicated root system architecture was showed in MP under Cu stress. Activities and transcript levels of acid invertase as well as contents of sucrose and reducing sugar in MP were elevated under Cu treatment, while activities of neutral/alkaline invertase and sucrose synthase showed no significant differences between two populations. The results indicate important roles of acid invertase in governing root growth under Cu stress.


