Schefflera heptaphylla
Schefflera heptaphylla
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Schefflera heptaphylla
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
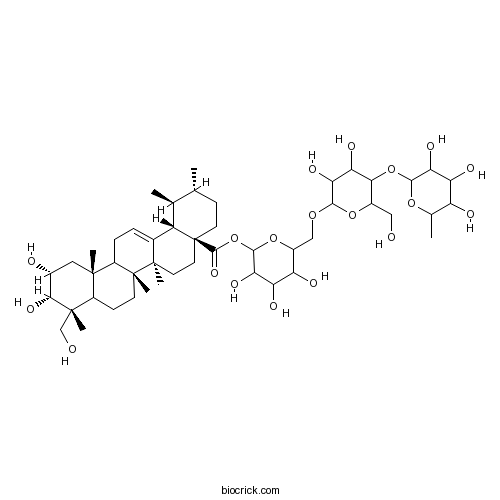
BCN1011
Asiaticoside16830-15-2
Instructions
-
BCN2502
Isovanillin621-59-0
Instructions

New ursane-type triterpenoid saponins from the stem bark of Schefflera heptaphylla.[Pubmed: 24144797]
Phytochemical investigation on the stem bark of Schefflera heptaphylla led to the isolation of five new ursane-type triterpenoid saponins (1-5). Their structures were determined on the basis of spectroscopic and chemical methods. It is noteworthy in this study that the genins of all compounds are reported for the first time. All compounds isolated from this plant were evaluated for their inhibitory activities on lipopolysaccharide-induced nitric oxide production in RAW264.7 cells, and compounds 2 and 5 showed weak anti-inflammatory activities under their non-cytotoxic concentrations.
Triterpenoid saponins from the stem barks of Schefflera heptaphylla.[Pubmed: 23925903]
Nine new triterpenoid saponins, including four ursane-type triterpenoid saponins named heptursosides A-D (1-4), four oleanane-type triterpenoid saponins named heptoleosides A-D (5-8), and one dammarane-type triterpenoid saponin, heptdamoside A (9), along with two known saponins, asiaticoside D (10) and scheffoleoside B (11), were isolated from the stem barks of Schefflera heptaphylla. Their structures were determined on the basis of spectroscopic analysis and chemical methods. It is noteworthy in this study that the aglycone of 1-6 is reported for the first time, and to the best of our knowledge, this is the first report for the presence of the tetracyclic triterpenoid saponin from Schefflera. All the saponins were evaluated for their inhibitory effects on lipopolysaccharide-induced nitric oxide production in RAW264.7 cells, and 2, 6, 7, and 10 showed anti-inflammatory activities under their noncytotoxic concentrations.
[Study on the HPLC fingerprint and simultaneous determination of three triterpene glycosides in Schefflera heptaphylla].[Pubmed: 23252267]
To establish the HPLC fingerprint and simultaneously determination three triterpene glycosides in Schefflera heptaphylla.
A new ursane-type triterpenoid from Schefflera heptaphylla (L.) Frodin.[Pubmed: 21534042]
A new ursane-type triterpenoid (1), together with 15 known compounds (2-16), was isolated from the barks of Schefflera heptaphylla (L.) Frodin. The structure of the new compound was determined on the basis of extensive spectroscopic data including IR, HR-ESI-MS, 1D and 2D NMR, and further confirmed by single-crystal X-ray diffraction. Compounds 2-6 were isolated from Schefflera genus for the first time.
Chemical composition and antiproliferative activity of essential oil from the leaves of a medicinal herb, Schefflera heptaphylla.[Pubmed: 18814213]
Schefflera heptaphylla (L.) Frodin is a medicinal herb widely used as a main ingredient of the popular health tea formulation against infections in Southern China. Twenty-seven volatile compounds were identified by GC-MS analysis from the essential oil obtained from the leaves of S. heptaphylla, and 17 of them belonged to monoterpenes or sesquiterpenes. The main volatile constituent in S. heptaphylla was found to be a monoterpene, beta-pinene, comprising about 22% of the total volatile components. The essential oil showed significant antiproliferative activity against three cancer cell lines, MCF-7, A375 and HepG2 cells, with IC50 values of 7.3 microg/mL, 7.5 microg/mL and 6.9 microg/mL, respectively. The result of the cytotoxicity assay indicates that (-)-beta-pinene and (+)-beta-pinene (commercially available from Sigma) also possessed antiproliferative activity against the cancer cells MCF-7, A375 and HepG2 with IC50 values ranging from 147.1 to 264.7 microm.
Antiviral triterpenoids from the medicinal plant Schefflera heptaphylla.[Pubmed: 17357972]
Schefflera heptaphylla (L.) Frodin is a principal ingredient of an herbal tea formulation widely used for the treatment of common cold in southern China. An extract of the long leafstalk of the compound leaf of S. heptaphylla exhibited the most potent antiviral activity against respiratory syncytial virus (RSV). Further antiviral-guided fractionation and isolation of the leafstalk extract of S. heptaphylla led to obtain two highly active pure triterpenoids, namely 3alpha-hydroxylup-20(29)-ene-23,28-dioic acid and 3-epi-betulinic acid 3-O-sulfate, together with an inactive saponin, 3alpha-hydroxylup-20(29)-ene-23,28-dioic acid 28-O-alpha-l-rhamnopyranosyl-(1-->4)-O-beta-d-glucopyranosyl-(1-->6)-beta-d-glucopyranoside. An antiviral assay using a cytopathic effect (CPE) reduction method showed that the two triterpenoids possessed broader antiviral activity against respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) with a similar 50% inhibition concentration (IC(50)) value of 6.25 microg/mL, influenza A (H1N1) virus with IC(50) values of 25 and 31.3 microg/mL, Coxsackie B3 (Cox B3) virus with IC(50) values of 12.5 and 20 microg/mL and herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) with IC(50) values of 18.8 and 25 microg/mL, respectively, whereas the saponin did not have antiviral activity against these four viruses at a concentration of 100 microg/mL.
Antiviral activity and mode of action of caffeoylquinic acids from Schefflera heptaphylla (L.) Frodin.[Pubmed: 16140400]
Schefflera heptaphylla is a popular medicinal plant in southern China. Three caffeoylquinic acid derivatives, namely 3,4-di-O-caffeoylquinic acid, 3,5-di-O-caffeoylquinic acid, and 3-O-caffeoylquinic acid, were isolated from this plant and investigated for their antiviral activity against respiratory syncytial virus (RSV). 3,4-Di-O-caffeoylquinic acid and 3,5-di-O-caffeoylquinic acid possessed potent anti-RSV activity. The median inhibitory concentrations (IC50) of 3,4-di-O-caffeoylquinic acid and 3,5-di-O-caffeoylquinic acid against RSV were 2.33 microM (1.2 microg/ml) and 1.16 microM (0.6 microg/ml), respectively, in a plaque reduction assay. The dicaffeoylquinic acids exhibited minimal cytotoxicity against HEp-2 cells with median cytotoxic concentration (CC50) higher than 1000 microM. The maximal non-cytotoxic concentration (MNCC) of the two dicaffeoylquinic acids were about 96.7 microM, which suggested their anti-RSV effect was not due to cytotoxicity. The antiviral action of 3,4-di-O-caffeoylquinic acid and 3,5-di-O-caffeoylquinic acid was specific against RSV, as they had no obvious antiviral activity against influenza A (Flu A), Coxsackie B3 (Cox B3), and Herpes simplex type one (HSV-1) viruses. Studies were performed that indicated that the dicaffeoylquinic acids could inhibit RSV directly, extracellularly, but only at much higher concentrations than seen in standard assays. Moreover, they could not inhibit RSV attachment to host cells, and could not protect HEp-2 cells from RSV infection at lower concentrations. The data suggest that the compounds exerted their anti-RSV effects via the inhibition of virus-cell fusion in the early stage, and the inhibition of cell-cell fusion at the end of the RSV replication cycle.


