Scleroderma citrinum
Scleroderma citrinum
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Scleroderma citrinum
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
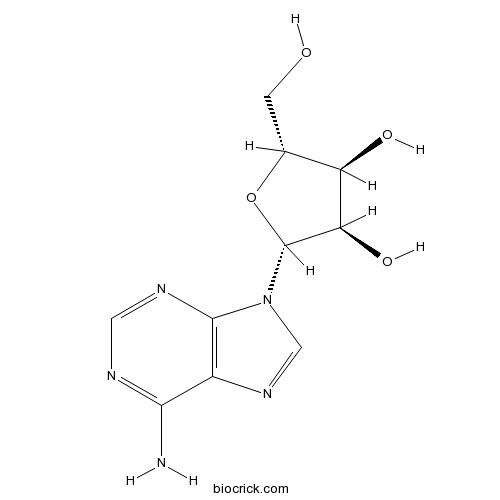
BCN5796
Adenosine58-61-7
Instructions
First record of in vitro formation of ectomycorrhizae in Psidium cattleianum Sabine, a native Myrtaceae of the Brazilian Atlantic Forest.[Pubmed: 29738553]
Like many other species of trees native to the Brazilian Mata Atlântica (Atlantic Forest), the Myrtaceae, such as the Red Araza (Psidium cattleianum Sabine), are widely cited as arbuscular mycorrhizal formers. Nevertheless, recent studies show evidence that Myrtaceae from different tropical, subtropical and neotropical ecosystems can also prompt the formation of ectomycorrhizae, indicating that this species' ectomycorrhizal status should be further explored. Because of this, this research effort studied the in vitro interaction between the Red Araza and two ectomycorrhizal fungi isolates, belonging to the Pisolithus microcarpus (D17) and Scleroderma citrinum (UFSC-Sc133) species. An analysis was performed to determine the formation of ectomycorrhizal structures, or lack thereof, and the developmental differences between the in vitro mycorrhized and non-mycorrhized plants. The analysis proved that indeed an ectomycorrhizal association was developed between the Red Araza, and the D17 and UFSC-Sc133 isolates, a fact never before registered in the existing literature. After an in vitro period of 110 days, it was confirmed that the D17 and UFSC-Sc133 isolates formed mycorrhizal colonization of 91.6% and 15.7%, respectively. Furthermore, both isolates also promoted root thickening, and the formation of a fungal mantle and a Hartig net. However, when compared to the Control plants, the fungal isolates did not contribute to an increase in the development of the subject plants, possibly due to the specific experimental conditions used, such as a high humidity environment and high availability of nutrients in the symbiotic substrate.
Caballeronia mineralivorans sp. nov., isolated from oak-Scleroderma citrinum mycorrhizosphere.[Pubmed: 28688535]
None
Scleroderma areolatum ectomycorrhiza on Fagus sylvatica L.[Pubmed: 27913893]
Despite its broad host range and distribution and its potential applications in commercial plantation forests, comprehensive descriptions of Scleroderma ectomycorrhizae are available only for Scleroderma citrinum, Scleroderma bovista and Scleroderma sinnamariense. This study provides a morphological and anatomical description of tree nursery derived ectomycorrhizae of Scleroderma areolatum on Fagus sylvatica, grown for several years in a climatized room. Ectomycorrhizae of S. areolatum were silvery white with abundant rhizomorphs; all mantle layers were plectenchymatous, rhizomorphs of type E, with prominent emanating hyphae with thick cell wall. The distal ends of emanating hyphae of rhizomorphs were inflated and often merged with other emanating hyphae. All parts of the mycorrhiza were clampless. In hyphae of the outer mantle layer, rhizomorphs and emanating hyphae, oily droplets were observed that did not stain in sulfo-vanillin and disappeared in lactic acid after a few hours. Although the phylogenetic analysis positioned the newly described ectomycorrhiza together with Scleroderma verrucosum and Scleroderma cepa in a single clade with a taxon name SH005470.07FU, the ectomycorrhizae of these three species can be morphologically well separated based on rhizomorph type.
Arsenic in Edible and Medicinal Mushrooms from Southwest China.[Pubmed: 26349517]
Many species of wild-grown mushrooms are appreciated as food and also found use in traditional medicine. As arsenic is one of the most hazardous elements due to the carcinogenic risk, the contents of total arsenic in 48 species of wild-grown edible and medicinal mushrooms in China were determined by atomic fluorescence spectrometry. The results showed that the highest content was found in Scleroderma citrinum (1.70 mg kg-1 dry weight, dw), whereas the lowest content was found in Termitomyces eurrhius (0.17 mg kg-1 dw).
Draft Genome Sequence of Burkholderia sp. Strain PML1(12), an Ectomycorrhizosphere-Inhabiting Bacterium with Effective Mineral-Weathering Ability.[Pubmed: 26205858]
We report the draft genome sequence of Burkholderia sp. PML1(12), a soil bacterium isolated from the Oak-Scleroderma citrinum ectomycorrhizosphere in the experimental forest site of Breuil-Chenue (France).
Functional profiling and distribution of the forest soil bacterial communities along the soil mycorrhizosphere continuum.[Pubmed: 23455431]
An ectomycorrhiza is a multitrophic association between a tree root, an ectomycorrhizal fungus, free-living fungi and the associated bacterial communities. Enzymatic activities of ectomycorrhizal root tips are therefore result of the contribution from different partners of the symbiotic organ. However, the functional potential of the fungus-associated bacterial communities remains unknown. In this study, a collection of 80 bacterial strains randomly selected and isolated from a soil-ectomycorrhiza continuum (oak-Scleroderma citrinum ectomycorrhizas, the ectomycorrhizosphere and the surrounding bulk soil) were characterized. All the bacterial isolates were identified by partial 16S rRNA gene sequences as members of the genera Burkholderia, Collimonas, Dyella, Mesorhizobium, Pseudomonas, Rhizobium and Sphingomonas. The bacterial strains were then assayed for β-xylosidase, β-glucosidase, N-acetyl-hexosaminidase, β-glucuronidase, cellobiohydrolase, phosphomonoesterase, leucine-aminopeptidase and laccase activities, chitin solubilization and auxin production. Using these bioassays, we demonstrated significant differences in the functional distribution of the bacterial communities living in the different compartments of the soil-ectomycorrhiza continuum. The surrounding bulk soil was significantly enriched in bacterial isolates capable of hydrolysing cellobiose and N-acetylglucosamine. In contrast, the ectomycorrhizosphere appeared significantly enriched in bacterial isolates capable of hydrolysing glucopyranoside and chitin. Notably, chitinase and laccase activities were found only in bacterial isolates belonging to the Collimonas and Pseudomonas genera. Overall, the results suggest that the ectomycorrhizal fungi favour specific bacterial communities with contrasting functional characteristics from the surrounding soil.
Distinct ectomycorrhizospheres share similar bacterial communities as revealed by pyrosequencing-based analysis of 16S rRNA genes.[Pubmed: 22307291]
Analysis of the 16S rRNA gene sequences generated from Xerocomus pruinatus and Scleroderma citrinum ectomycorrhizospheres revealed that similar bacterial communities inhabited the two ectomycorrhizospheres in terms of phyla and genera, with an enrichment of the Burkholderia genus. Compared to the bulk soil habitat, ectomycorrhizospheres hosted significantly more Alpha-, Beta-, and Gammaproteobacteria.
Tolerance to and accumulation of cadmium by the mycelium of the fungi Scleroderma citrinum and Pisolithus tinctorius.[Pubmed: 22113263]
The behavior of ectomycorrhizal (ECM) fungi on exposure to cadmium dependent upon isolation remains a poorly understood phenomenon. The in vitro growth, tolerance, and accumulation of Cd were studied in three strains of ECM fungi exposed to six Cd concentrations (0-10 mg L(-1)). The fungi studied were a strain of Scleroderma citrinum Persoon (Sc) isolated from a tailings heap containing 5 mg kg(-1) available Cd, and two strains of Pisolithus tinctorius (Pers.) Coker and Couch from unpolluted sites (Pt1 and Pt2), both common ECM fungi used for remediation. The growth kinetic (36 days) of Sc was not affected by Cd concentration. By contrast, the ED(50) in Pt1 and Pt2 occurred at 4.8 and 6.9 mg L(-1) of Cd, respectively. The biomass of the three fungi exposed to the highest Cd concentration (10 mg L(-1)) was significantly different. Sc presented the highest biomass, while this was strongly reduced for Pt1 and Pt2. The tolerance index for Sc ranged from 78% to 95% at all Cd concentrations tested, while for Pt1 it was 49% and 31%, and for Pt2 it was 62% and 35% at 5 and 10 mg of Cd L(-1), respectively. The mycelium of both Pt strains accumulated more Cd than the Sc mycelium. At the highest Cd concentration, Pt1 and Pt2 accumulated 1.9 and 1.7 times more Cd than Sc. This study suggests that regardless of the differences in tolerance to Cd by the three ECM fungi, they could have biotechnological applications for soil remediation. However, Sc has greater possibilities of being used successfully when high concentrations of Cd prevail in the environment.


