Semiaquilegia adoxoides
Semiaquilegia adoxoides
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.

Natural products/compounds from Semiaquilegia adoxoides
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
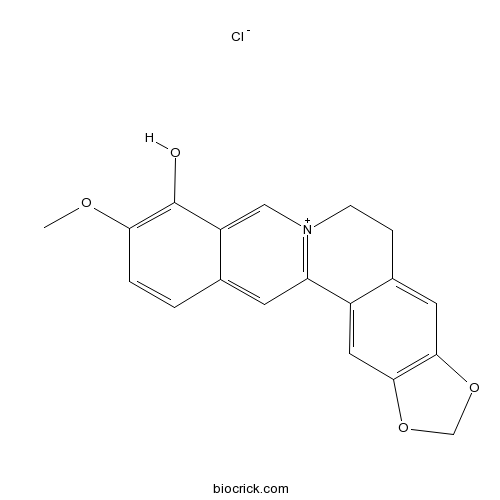
BCN2651
Berberrubine15401-69-1
Instructions
-
BCN1271
Griffonilide61371-55-9
Instructions

-
BCN1270
Lithospermoside63492-69-3
Instructions

Protective effects of Semiaquilegia adoxoides n-butanol extract against hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative stress in human lens epithelial cells.[Pubmed: 26974044]
Context Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2)-induced damage in the lens epithelium leads to cell death and cataract. Semiaquilegia adoxoides (DC.) Makino (Ranunculaceae), a folk medicine of Hmong (an ethnic group of China), has been traditionally used to treat cataract; however, the underlying molecular mechanism is yet to be uncovered. Objective This study aimed to investigate whether the n-butanol extract of S. adoxoides (nSA) is effective against the H2O2-induced oxidative stress in human lens epithelial (HLE) cells. Materials and methods Human lens epithelial (SRA 01/04) cells were stimulated by H2O2 (250 μM) in the presence or absence of nSA. The antioxidant effects of nSA were determined in terms of cell viability (MTT assay), apoptosis (AnnexinV/PI staining), radical scavenging capability (various enzymatic assays), loss of mitochondrial membrane potential (Rhodamine 123 staining), expression of apoptotic markers including caspase-3 and caspase-9 and the change of Bcl-2/Bax ratio (western blot) in the HLE cells. Results The results showed that pretreatment of nSA (250, 500 and 1000 μg/mL) markedly reduced H2O2-induced cellular apoptosis and malondialdehyde accumulation, but elevated the activities of total superoxide dismutase, catalase, glutathione peroxidase. Thus, the total antioxidative capability was enhanced upon the nSA treatment meanwhile the loss of mitochondrial membrane potential was prevented. Moreover, nSA at concentrations of 250, 500 and 1000 μg/mL also significantly suppressed the activation of caspase-3 and -9, and increased the Bcl-2/Bax ratio in the HLE cells. Discussion and conclusion Our findings suggested that nSA is a potential prophylactic agent in the prevention of cataractogeneis.
Anti-neutrophilic inflammatory secondary metabolites from the traditional Chinese medicine, Tiankuizi.[Pubmed: 23413568]
Through bioassay-guided fractionation, thirteen compounds (1-13) were isolated from the dry root of Semiaquilegia adoxoides, known as Tiankuizi in traditional Chinese medicine (TCM). Among these, four benzoic acid derivatives (1, 2, 4, 5), one 4,6-dimethoxy-5-methyl-2H-pyran-2-one (10) and one 1,2,3-propanetriol (13) were found for the first time in S. adoxoides. This is the first record of compound 10 from a natural source. 4-Hydroxybenzoic acid (1) and 3,4-dihyroxybenzoic acid (2) showed selective inhibition against elastase release and superoxide anion generation, with IC50 values of 3.20 and 6.21 microg/mL, respectively. Compound 1 had 7-fold better activity than the positive control against elastase release induced by human neutrophils. Overall, our studies demonstrated Tiankuizi (S. adoxoides) as a potential TCM and isolates 1 and 2 as promising lead compounds for neutrophilic inflammatory diseases.
[Study on the histological anatomy on medicinal parts of Semiaquilegia adoxoides in different developmental stages].[Pubmed: 23320350]
To study the structural characteristics of medicinal parts at different developmental stages of Semiaquilegia adoxoides.
[Study on correlation between the habits of growing development and the formation of morphology of Semiaquilegia adoxoides].[Pubmed: 23236814]
To study the characteristics and regular patterns in growing development of Semiaquilegia adoxoides, and their correlation with the characters medicine materials.
New diterpenoids from Semiaquilegia adoxoides.[Pubmed: 16753787]
Two new ent-kaurane-type diterpenoids, E-semiaquilegin (1) and Z-semiaquilegin (2), together with eight known compounds (3-10) were isolated from the dried roots of Semiaquilegia adoxoides (DC.) Makino. The structures of compounds 1 and 2 were elucidated mainly by 2D NMR techniques including 1H-1H COSY, HSQC, HMBC, NOESY as 16alpha-hydroxy-ent-kaurane-17,20-di-(3,4-dihydroxy-E-cinnamoyl) ester and its (Z)-isomer.
Complete assignments of 1H and 13C NMR spectral data for a novel diterpenoid from Semiaquilegia adoxoides.[Pubmed: 16607674]
Semiaquilegoside A (1), a new diterpenoid, was isolated from the roots of Semiaquilegia adoxoides. Its chemical structure was established as 3beta, 11- dihydroxy-12-O-beta-D-glucopyranosyl-8,11,13-abietatrien-6-one through spectroscopic techniques and chemical analysis.


