Sphallerocarpus gracilis
Sphallerocarpus gracilis
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Sphallerocarpus gracilis
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
BCN5905
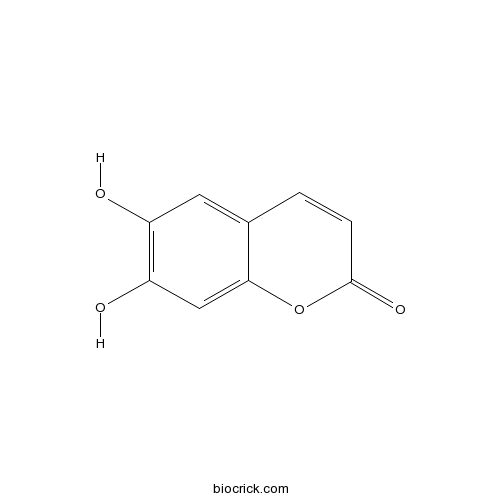
6,7-Dihydroxycoumarin305-01-1
Instructions
Sphallerocarpus gracilis polysaccharide protects pancreatic β-cells via regulation of the bax/bcl-2, caspase-3, pdx-1 and insulin signalling pathways.[Pubmed: 27645924]
None
Polysaccharide extraction from Sphallerocarpus gracilis roots by response surface methodology.[Pubmed: 27032488]
The extraction process of Sphallerocarpus gracilis root polysaccharides (SGRP) was optimized using response surface methodology with two methods [hot-water extraction (HWE) and ultrasonic-assisted extraction (UAE)]. The antioxidant activities of SGRP were determined, and the structural features of the untreated materials (HWE residue and UAE residue) and the extracted polysaccharides were compared by scanning electron microscopy. Results showed that the optimal UAE conditions were extraction temperature of 81°C, extraction time of 1.7h, liquid-solid ratio of 17ml/g, ultrasonic power of 300W and three extraction cycles. The optimal HWE conditions were 93°C extraction temperature, 3.6h extraction time, 21ml/g liquid-solid ratio and three extraction cycles. UAE offered a higher extraction yield with a shorter time, lower temperature and a lower solvent consumption compared with HWE, and the extracted polysaccharides possessed a higher antioxidant capacity. Therefore, UAE could be used as an alternative to conventional HWE for SGRP extraction.
Sulfated modification of the polysaccharide from Sphallerocarpus gracilis and its antioxidant activities.[Pubmed: 26893048]
Sphallerocarpus gracilis (S. gracilis) is a little-investigated edible plant and used as traditional Chinese medicine. In this study, polysaccharide extracted from S. gracilis,deproteined and purified. The polysaccharide (SGP) was chemically modified to obtain its sulfated derivatives (S-SGP) using the method of chlorosulfonic acid/pyridine (CSA/Pyr). In order to acquire the derivative with the highest degree of substitution (DS), the optimum conditions of the sulfation were obtained based on response surface design (RSD), and the structural characterizations and antioxidant properties of the S-SGP were comparatively investigated by Fourier transform infrared spectrometry (FT-IR), GC-MS analysis, size exclusion chromatography (SEC), and DPPH radical assay, hydroxyl radical assay, superoxide radical assay, and reducing power assay, respectively. Results showed that the modification was successful, and obtained the optimum combination of conditions. Compared with SGP, the sulfated polysaccharide with relatively the decreased degree of molecular weight (Mw) but the same composition of monosaccharides exhibited better antioxidant activities in DPPH, hydroxyl, superoxide radical and reducing power assay. These results indicated that the antioxidant activities in vitro of the S-SGP from S. gracilis may be related to combined effects of Mw, monosaccharide composition, and sulfate content.
Enrichment and Purification of Polyphenol Extract from Sphallerocarpus gracilis Stems and Leaves and in Vitro Evaluation of DNA Damage-Protective Activity and Inhibitory Effects of α-Amylase and α-Glucosidase.[Pubmed: 26633339]
An efficient preparative separation method for Sphallerocarpus gracilis stems and leaves polyphenols (SGslP) was established in this study. An X-5 macroporous adsorption resin was selected for the purification of the SGslP, and the polyphenol content of the purified SGslP (PSGslP) was increased 5.11-fold from 8.29% to 42.38% after one treatment run. The chemical composition of the PSGslP was analyzed by HPLC-MS/MS, and the predominant compounds were found to be luteolin-7-glucoside, acacetin-7-acetyglycoside and its isomers. In addition, the PSGslP was evaluated in vitro to determine the DNA damage-protective activity and inhibitory effects of α-amylase and α-glucosidase. The results indicated that the PSGslP exhibited significant protective activities against both ROO• and •OH radical-induced DNA damage. Moreover, the PSGslP exerted a dose-dependent inhibition effect on α-glucosidase but no inhibitory effect on α-amylase. These findings indicate that the Sphallerocarpus gracilis stems and leaves are good natural sources of antioxidants and are potent inhibitors of α-glucosidase activity and are potential anti-diabetic inhibitor.
Authentication of commercial processed Glehniae Radix (Beishashen) by DNA barcodes.[Pubmed: 26628908]
The radix of Glehnia littoralis Fr. Schmidt ex Miq. (Beishashen), is often misidentified and adultered in Chinese medicine. Its seven common adulterants include Chuanminshen violaceum Sheh et Shan (Chuanmingshen), Changium smyrnioides Wolff (Mingdangshen), Sphallerocarpus gracilis (Bess.) K.-Pol. (Miguoqin), Adenophora polyantha Nakai (Shishashen), Silene tatarinowii Regel (Shishengyingzicao), Adenophora tetraphylla (Thunb.) Fisch (Lunyeshashen) and Adenophora stricta Miq. (Shashen). This study aims to evaluate the feasibility of the second internal transcribed spacer (ITS2) DNA barcoding to discriminate between Glehniae Radix and its common adulterants.
Phenolic composition, DNA damage protective activity and hepatoprotective effect of free phenolic extract from Sphallerocarpus gracilis seeds.[Pubmed: 24657314]
The phenolic composition of the free phenolic extract from Sphallerocarpus gracilis seeds was analyzed by HPLC-MS and predominant compounds were chlorogenic acid, di-caffeoylquinic acid glucoside and luteolin-7-O-glucoside. The free phenolic extract was evaluated for DNA damage protective activity induced by ROO and OH radicals and hepatoprotective effect in vivo and in vitro. Results revealed that the free phenolic extract exhibited significant protective activity against both ROO and OH radical-induced DNA damage and the phenolic extract exerted more potent inhibitory activity against OH radical-induced damage than against that induced by ROO radicals. In vivo experimental results showed that the phenolic extract significantly prevented the increase of serum alanine aminotransferase, aspartate aminotransferase and alkaline phosphatase activities and hepatic malondialdehyde level caused by CCl4 in rats, and markedly increased hepatic superoxide dismutase, catalase and glutathione peroxidase levels. Histopathological examinations further confirmed that the phenolic extract could protect the liver from CCl4-induced damage. In vitro experimental results showed that the phenolic extract could reduce BRL hepatocyte apoptosis and damage induced by CCl4. These findings indicate that the S. gracilis seed could be developed as a medicinal herb for the therapy and prevention of hepatic injury.
Main nutrients, phenolics, antioxidant activity, DNA damage protective effect and microstructure of Sphallerocarpus gracilis root at different harvest time.[Pubmed: 23140708]
Sphallerocarpus gracilis roots harvested at two different times (T1: 12-10-2009 and T2: 15-04-2010) were analysed for their main nutrients, phenolics, antioxidant activity, DNA damage protective effect and microstructure. Results revealed that higher amounts of starch were detected in T1 S. gracilis root, whereas higher levels of reducing sugar, protein, amino acids and phenolic compounds were determined in T2 S. gracilis root. The antioxidant activity was assessed by DPPH, FRAP and TEAC assay and T2 S. gracilis root was found to possess higher antioxidant activity. Also, results of the correlation analysis indicated that caffeic, p-coumaric and gallic acids contributed substantially to the antioxidant property and there was significant correlation between DPPH radicals scavenging capacity and FRAP and TEAC. The highest and lowest DNA damage protective effects were found of free phenolic extracts from T2 and T1 S. gracilis roots, respectively. The microstructure of S. gracilis root varied greatly with the harvest time.
Free radical scavenging action of medicinal herbs from Mongolia.[Pubmed: 11185733]
In the present study we evaluated the free radical scavenging action of some medicinal herbs growing in Mongolia. The aqueous extract of nine herbs Chamenerion angustifolium (Ch.ang), Equisetum arvense (Eq.arv), Gentiana decumbens (Gn.dec), Geranium pratense (Gr.pra), Lomatogonium carinthiacum (L.car), Nonea poulla (N.pl), Phodococcum vitis-idaea (Ph.v), Sphallerocarpus gracilis (Sph.gr), Stellera chamaejasme (St.cha) were used in the present experiment. The free radical scavenging action was determined in vitro and ex vivo by using electron spin resonance (ESR) spectrometer and chemiluminescence (CL) analyzer. The results showed that extracts of Ch.ang, Gn.dec, Gr.pra, L.car, N.pl, Ph.v, Sph.gr and St. cha possess strong scavenging action of 1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl, superoxide and hydroxyl radicals. On the other hand, the radical scavenging action of Eq.arv was low. Extracts of N.pl and Ph.v markedly inhibited the CL generated from rat liver microsomal cytochrome P450 system whereas the CL was moderately inhibited by Eq.arv, Gn.dec, Gr.pra, L.car and St.cha. The extracts of Ch.ang and Sph.gr did not decrease the CL generation. Ch.ang, Gr.pra, L.car, N.pl, Ph.v and St.cha also depressed reactive oxygen production from polymorphonuclear leukocytes stimulated by phorbol-12-myristate acetate ex vivo. Thus it was confirmed that the medicinal herbs from Mongolia possess high antioxidant potency in vitro and ex vivo.


