Stephania japonica
Stephania japonica
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Stephania japonica
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
BCN5393
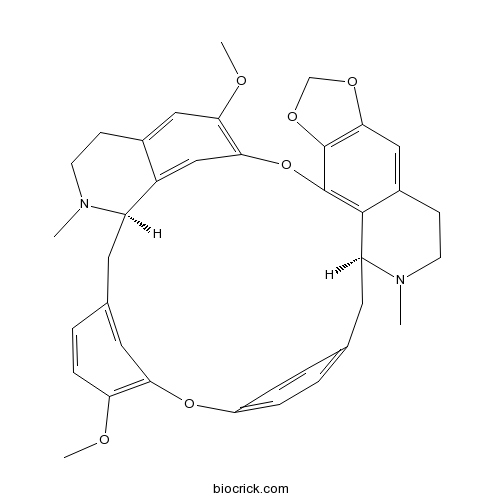
Cepharanthine481-49-2
Instructions
-
BCN1238
(+)-Bicuculline485-49-4
Instructions

Total Synthesis of the Norhasubanan Alkaloid Stephadiamine.[Pubmed: 29889502]
(+)-Stephadiamine is an unusual alkaloid isolated from the vine Stephania japonica. It features a norhasubanan skeleton, and contains two adjacent α-tertiary amines, which renders it an attractive synthetic target. Here, we present the first total synthesis of stephadiamine, which hinges on an efficient cascade reaction to implement the aza[4.3.3]propellane core of the alkaloid. The α-aminolactone moiety in a highly hindered position was installed via Tollens reaction and Curtius rearrangement. Useful building blocks for the asymmetric synthesis of morphine and (nor)hasubanan alkaloids are introduced.
Evaluation of antinociceptive activity of methanolic extract of leaves of Stephania japonica Linn.[Pubmed: 27060632]
Stephania japonica is a common plant, widely distributed in all over Bangladesh. Traditionally, this plant is considered as one of the important ingredients in treatment of a variety of ailments including inflammation, pain, rheumatism, cancer, bone fracture, fever etc. However, the scientific reports regarding the antinociceptive effect of this plant are very limited. This study evaluated the antinociceptive effect of methanolic extract of S. japonica (MESJ) leaves.
Phylogenomic and structural analyses of 18 complete plastomes across nearly all families of early-diverging eudicots, including an angiosperm-wide analysis of IR gene content evolution.[Pubmed: 26724406]
The grade of early-diverging eudicots includes five major lineages: Ranunculales, Trochodendrales, Buxales, Proteales and Sabiaceae. To examine the evolution of plastome structure in early-diverging eudicots, we determined the complete plastome sequences of eight previously unsequenced early-diverging eudicot taxa, Pachysandra terminalis (Buxaceae), Meliosma aff. cuneifolia (Sabiaceae), Sabia yunnanensis (Sabiaceae), Epimedium sagittatum (Berberidaceae), Euptelea pleiosperma (Eupteleaceae), Akebia trifoliata (Lardizabalaceae), Stephania japonica (Menispermaceae) and Papaver somniferum (Papaveraceae), and compared them to previously published plastomes of the early-diverging eudicots Buxus, Tetracentron, Trochodendron, Nelumbo, Platanus, Nandina, Megaleranthis, Ranunculus, Mahonia and Macadamia. All of the newly sequenced plastomes share the same 79 protein-coding genes, 4 rRNA genes, and 30 tRNA genes, except for that of Epimedium, in which infA is pseudogenized and clpP is highly divergent and possibly a pseudogene. The boundaries of the plastid Inverted Repeat (IR) were found to vary significantly across early-diverging eudicots; IRs ranged from 24.3 to 36.4kb in length and contained from 18 to 33 genes. Based on gene content, the IR was classified into six types, with shifts among types characterized by high levels of homoplasy. Reconstruction of ancestral IR gene content suggested that 18 genes were likely present in the IR region of the ancestor of eudicots. Maximum likelihood phylogenetic analysis of a 79-gene, 97-taxon data set that included all available early-diverging eudicots and representative sampling of remaining angiosperm diversity largely agreed with previous estimates of early-diverging eudicot relationships, but resolved Trochodendrales rather than Buxales as sister to Gunneridae, albeit with relatively weak bootstrap support, conflicting with what has been found for these three clades in most previous analyses. In addition, Proteales was resolved as sister to Sabiaceae with the highest support (bootstrap >90%) yet observed in plastome-scale phylogenetic analyses.
Molecular authentication of Cissampelos pareira L. var. hirsuta (Buch.-Ham. ex DC.) Forman, the genuine source plant of ayurvedic raw drug 'Patha', and its other source plants by ISSR markers.[Pubmed: 28324385]
Cissampelos pareira L. var. hirsuta (Buch.-Ham. ex DC.) Forman belongs to family Menispermaceae. The roots of this taxon are used in the treatment of various diseases like stomach pain, fever, skin disease, etc., in Ayurveda and is commonly known as Patha. Two other species, viz., Cyclea peltata (Lam.) Hook.f. & Thomson and Stephania japonica (Thunb.) Miers of the same family are being used as the source of this drug in various parts of India. This type of substitution or adulteration will ultimately affect the therapeutic efficacy of the medicines adversely. ISSR profiles of all the three taxa are generated and analyzed to assess the genetic relationships among these three species. The profiles of all the three species displayed a high level of polymorphism among them. ISSR markers developed can be used in authenticating and validating the exact species discrimination of the genuine raw drug of 'Patha' from its substitutes/adulterants to guarantee the quality and legitimacy of this drug in the market.
Comparative phytochemical investigation of the sources of ayurvedic drug patha: a chromatographic fingerprinting analysis.[Pubmed: 20582188]
Standardization of herbal drugs based on their chemical and biological activity profile is an important prerequisite for acquiring the herbal market. The main problem encountered in standardization of Ayurvedic drugs is proper identification of the source plant. The present study was aimed to establish identification characters, quality control parameters, chemical and biological parameters for roots of three plants Cissampelos pareira, Cyclea peltata and Stephania japonica (Fam. Menispermaceae) which are being used as source of Patha, in the market. All the three plant were subjected for evaluation of quality control parameters as per WHO guidelines and root extracts and total alkaloidal fractions were subjected for HPTLC and HPLC fingerprinting analysis using a marker compound Bebeerine isolated from roots of Cissampelos pareira. The parameters studied clearly indicated the significant differences among the three plant materials. The roots of Cissampelos pareira can be distinguished from other two plants by presence of high concentration of alkaloids especially the presence of high concentration of pharmacologically active alkaloid bebeerine, which was found to be present in very low concentration in Stephania japonica and absent in roots of Cyclea peltata. The roots of Cyclea peltata were found to contain high concentration of saponins and comparatively in low concentration in Cissampelos pareira where as it was found to be absent in roots of Stephania japonica.
Hasubanan alkaloids with delta-opioid binding affinity from the aerial parts of Stephania japonica.[Pubmed: 20426456]
Two new (1 and 2) and six known hasubanan alkaloids (3-8) and one morphinane alkaloid (9) were isolated from the leaves of the North Queensland rainforest vine Stephania japonica. The structures of 1 and 2 were determined by interpretation of their 1D and 2D NMR spectra. The hasubanan alkaloids showed affinity for the human delta-opioid receptor with IC(50) values ranging from 0.7 to 46 microM. The compounds were also tested for their affinity to micro- and kappa-opioid receptors and shown to be inactive against kappa-opioid receptors, but were of similar potency against the micro-opioid receptor.
Reproductive effects of ethnomedicinal formulation of tape-vine leaves in female rats.[Pubmed: 16946509]
Documented ethno-contraceptive use of Tape-vine or Stephania japonica (THUNB.) MIERS., Syn. Stephania hernandifolia (WILLD.) WALP. leaves is evaluated with regards to post-coital pregnancy interceptive activity of its aqueous extract (AE) and an ethnomedicinal formulation (EF) in Wistar rats. EF at 500 and 250 mg/kg doses induced 66.7% and 33.3% post-coital pregnancy interception respectively and the higher dose exhibited significant reduction in number of litters born and also anti-implantation property. In contrast, none of the dose levels of AE interfered in pregnancy but significant anti-implantation property was observed at doses of 2 and 1 g/kg, even as the higher dose produced significant reduction in number of litters born as well. EF at 500 mg/kg also exhibited significant uterotrophic activity and histological changes in uterus. Pair-wise comparison of sex hormone-levels exhibited significant increment in serum estradiol, LH and FSH but decrease in progesterone levels. Assessed blood lipid-carbohydrate profile exhibited substantial decrease in glucose, cholesterol, VLDL and triglyceride contents and significant increase in HDL. It is concluded that EF probably acts as better post-coital pregnancy interceptive agent through restriction of implantation by alteration of gonadal hormone levels and decline in blood-glucose levels that possibly disrupts oxidative energy metabolism in uterus during implantation. High surge in LH and FSH suggests negligible interference in ovulatory mechanism. This preparation also seems to be free of cardiovascular risk factors. HPTLC and HPLC analysis of both EF and AE exhibited marked chemical differences.


