Stevia rebaudiana
Stevia rebaudiana
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Stevia rebaudiana
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
BCN7860
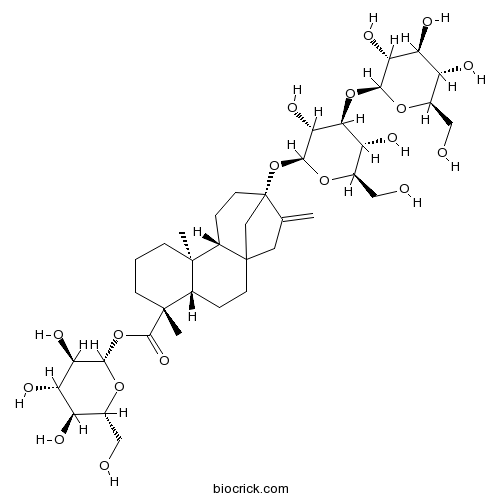
Rebaudioside G127345-21-5
Instructions
-
BCN5906
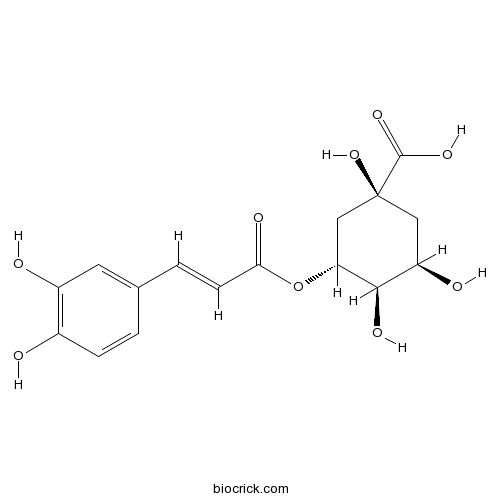
Chlorogenic acid327-97-9
Instructions
-
BCN6305
Stevioside57817-89-7
Instructions

-
BCN5900
Rebaudioside A58543-16-1
Instructions

-
BCN2404
Rebaudioside C63550-99-2
Instructions

Innovative technologies for the recovery of phytochemicals from Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni leaves: A review.[Pubmed: 30064792]
Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni has gained increased industrial and scientific interests in the last 20 years, representing a suitable nutritional alternative to sucrose and artificial sweeteners. Moreover, this plant contains polyphenols, chlorophylls, and carotenoids that may be extracted for production of nutraceuticals and functional foods. Because of nutritional and technological advantages over sucrose, innovative approaches for the extraction of highly valued compounds from Stevia leaves have been developed and optimized. In contrast to conventional alternatives, innovative extraction methods allow higher yields in a shorter time, less usage of organic solvents, and reduced energy consumption. In this paper, the use of innovative extraction techniques: MAE, UAE, HPAE, PLE, SFE, PEF, HVED, cold plasma, and RSLDE for the recovery of non-nutrients with putative health benefits from Stevia leaves is discussed.
Antihyperlipidemic efficacy of aqueous extract of Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni in albino rats.[Pubmed: 30053819]
Stevia (Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni) natural, safe, non-toxic, non-caloric sugar substitute is rich source of pharmacologically important glycoside stevioside that is linked to the pathology and complications of hyperlipidemia.
The effect of coconut jelly with natural sweeteners stevia (Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni) replacement on blood glucose, insulin, and C-peptide responses.[Pubmed: 30019656]
Coconut jelly is a popular dessert among Asian people. However, it contains high levels of sugar. The recent patents on steviol glycoside (WO2015014969A1), steviol glycoside compositions for oral ingestion or use (WO2017095932A1) and sweetener composition for preventing and improving obesity, containing glycolysis inhibitor ingredient (EP2756764B1) [3] help to select the sweetener for development of coconut jelly.
Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni and Its Effects in Human Disease: Emphasizing Its Role in Inflammation, Atherosclerosis and Metabolic Syndrome.[Pubmed: 29995279]
Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni is a perennial shrub with zero calorie content that has been increasing in popularity for its potential use as an adjuvant in the treatment of obesity. The level of evidence supporting general benefits to human health is insufficient. We conducted a review of the literature summarizing the current knowledge and role in human disease.
Stevia Leaf to Stevia Sweetener: Exploring Its Science, Benefits, and Future Potential.[Pubmed: 29982648]
Steviol glycoside sweeteners are extracted and purified from the Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni plant, a member of the Asteraceae (Compositae) family that is native to South America, where it has been used for its sweet properties for hundreds of years. With continued increasing rates of obesity, diabetes, and other related comorbidities, in conjunction with global public policies calling for reductions in sugar intake as a means to help curb these issues, low- and no-calorie sweeteners (LNCSs, also known as high-potency sweeteners) such as stevia are gaining interest among consumers and food manufacturers. This appeal is related to stevia being plant-based, zero calorie and with a sweet taste that is 50-350 times sweeter than sugar, making it an excellent choice for use in sugar- and calorie-reduced food and beverage products. Despite the fact that the safety of stevia has been affirmed by several food regulatory and safety authorities around the world, insufficient education about stevia's safety and benefits, including continuing concern with regard to the safety of LNCSs in general, deters health professionals and consumers from recommending or using stevia. Therefore, the aim of this review and the stevia symposium that preceded this review at the ASN's annual conference in 2017 was to examine, in a comprehensive manner, the state of the science for stevia, its safety and potential health benefits, and future research and application. Topics covered included metabolism, safety and acceptable intake, dietary exposure, impact on blood glucose and insulin concentrations, energy intake and weight management, blood pressure, dental caries, naturality and processing, taste and sensory properties, regulatory status, consumer insights, and market trends. Data for stevia are limited in the case of energy intake and weight management as well as for the gut microbiome; therefore, the broader literature on LNCSs was reviewed at the symposium and therefore is also included in this review.


