Taxus wallichiana var. mairei
Taxus wallichiana var. mairei
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Taxus wallichiana var. mairei
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
BCN5342
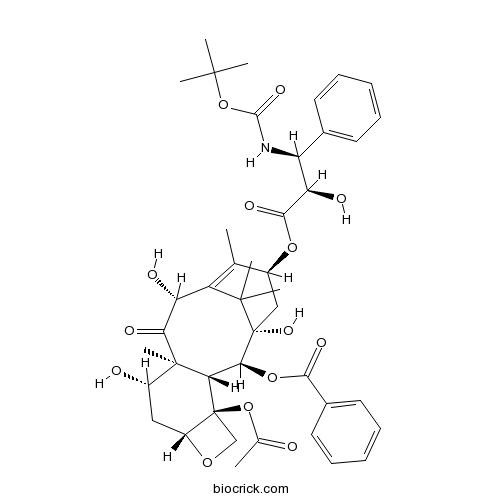
Docetaxel114977-28-5
Instructions
-
BCN4650
Paclitaxel33069-62-4
Instructions

-
BCN5343
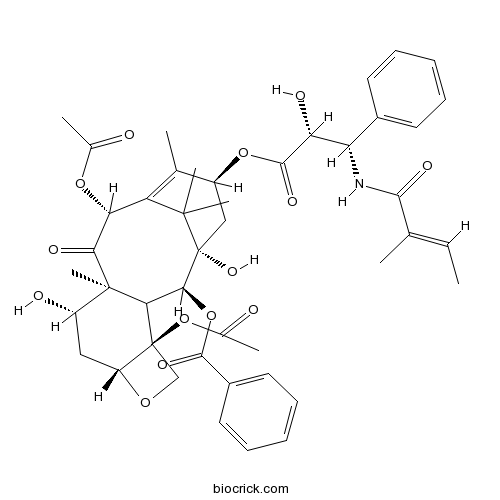
Cephalomannine71610-00-9
Instructions
An endophytic fungus efficiently producing paclitaxel isolated from Taxus wallichiana var. mairei.[Pubmed: 28682896]
Paclitaxel is a medicinal ingredient with high anticancer activity and widely used in hospitals and clinics. In this study, we isolate endophytic fungi efficiently producing paclitaxel from yew for the purpose of paclitaxel manufacture.The bark of Taxus wallichiana var. mairei was surface sterilized and then inoculated in potato dextrose agar culture medium to isolate endophytic fungi. The paclitaxel in the fungal culture was extracted with mixture of chloroform and the same amount of methanol. The content of paclitaxel in the extract was determined and identified with LC-MS. The endophytic fungus efficiently producing paclitaxel was species identified with ITS rDNA and 26S D1/D2 rDNA sequencing.There were 528 endophytic fungal strains were isolated from the bark of T wallichiana var. mairei in total. There was only a strain efficiently producing paclitaxel in these endophytic fungi. The unique strain was identified as Phoma medicaginis. The paclitaxel contents in whole potato dextrose broth (PDB) culture, spent culture medium from this strain and that in dry mycelium is 1.215 mg/L, 0.936 mg/L, and 20 mg/kg, respectively.An endophytic fungus efficiently producing paclitaxel was isolated from T wallichiana var. mairei. This isolated endophytic fungus can be used as a producing strain for paclitaxel manufacture.
Taxanes from Taxus wallichiana var. mairei cultivated in the southern area of the Yangtze River in China.[Pubmed: 28322597]
None
Seasonal Dynamics of Metabolites in Needles of Taxus wallichiana var. mairei.[Pubmed: 27775631]
None
ISOLATION AND IDENTIFICATION OF AN ENDOPHYTIC FUNGUS PRODUCING PACLITAXEL FROM TAXUS WALLICHIANA VAR MAIREI.[Pubmed: 26667755]
El objetivo de este estudio fue aislar hongos endofíticos productores de paclitaxel a partir de tejo con el propósito de fabricar paclitaxel. Se utilizó la superficie de la corteza esterilizada de Taxus wallichiana var. mairei como material de origen y dextrosa de patata en medio de cultivo de agar para el aislamiento de hongos endófitos. Los cultivos de hongos se extrajeron con una mezcla de cloroformo / metanol (1:1, v/v) y el paclitaxel en los extractos se determinó y autentificó con LC-MS. Un hongo endófito que produjo paclitaxel fue identificado por su ADNr 26S y secuenciación D1/D2 ADNr. Los resultados mostraron que un total de 435 cepas de hongos endófitos se aislaron y purificarón a partir de T. wallichiana var. mairei. Solo una de estas cepas produce paclitaxel y pertenece a Fusarium. La productividad del cultivo de paclitaxel procedente de esta cepa es 0,0153 mg/L y 0,0119 mg/L, respectivamente. El contenido de paclitaxel en micelio seco es 0,27 mg/kg. Este aislado de hongos endófitos produjo paclitaxel a un nivel considerable y muestra potencial como cepa para la fabricación de paclitaxel después de llevar a cabo una mejora de las cepas.
Isolation and cytotoxicity evaluation of taxanes from the barks of Taxus wallichiana var. mairei.[Pubmed: 25682561]
Fifteen taxanes (1-15) including a new taxane glucoside, 7β,9α,10β-triacetoxy-13α-hydroxy-5α-O-(β-d-glucopyranosyl)taxa-4(20),11-diene (1), were isolated from the barks of Taxus wallichiana var. mairei. Compounds 1-15 representing three sub-types of 6/8/6-taxane were evaluated in vitro for anti-proliferative activity against a panel of parental and drug-resistant cancer cells. Potent compounds were found while several exhibited selective cytotoxicity. Especially, 3, 8, and 10 showed selective inhibition to breast carcinoma cell line MCF-7, while 13 selectively inhibited taxol resistant human ovarian carcinoma cell line A2780/TAX (IC50=0.19μM), being more potent than the clinical drugs taxol (IC50=4.4μM) and docetaxol (IC50=0.42μM), and less cytotoxic to mouse embryonic fibroblast cell line NIH-3T3, a cell line close to normal cell line. The possible P-glycoprotein evasion mechanism of 13 against A2780/TAX and the preliminary structure-activity relationships (SARs) of this group of compounds were also discussed.
Isolation and identification of a 10-deacetyl baccatin-III-producing endophyte from Taxus wallichiana.[Pubmed: 25475888]
Endophytic fungi of inner root bark of Taxus wallichiana var. mairei were investigated in order to find endophytes producing 10-DABIII (10-deacetyl baccatin III). Purified colonies were cultured in potato dextrose broth (PDB), and then the organic extracts from fungi were analyzed with HPLC, LC-MS, and (1)H NMR. Of 102 fungal endophytes isolated from the inner root bark, only one strain named IRB54 can yield 10-DABIII but no taxol and baccatin III. In PDB culture medium, its productivity was 187.564 ug/l. Based on its morphological characteristics and molecular data, the IRB54 strain was identified as Trichoderma sp. The isolation of the fungus IRB54 yielding 10-DABIII will provide an alternative resource to manufacture taxol/taxotere via semi-synthesis and some useful clues for improving the understanding of taxane synthesis evolution.
Comparative proteomic analysis of differential responses of Pinus massoniana and Taxus wallichiana var. mairei to simulated acid rain.[Pubmed: 24625662]
Acid rain (AR), a serious environmental issue, severely affects plant growth and development. As the gymnosperms of conifer woody plants, Pinus massoniana (AR-sensitive) and Taxus wallichiana var. mairei (AR-resistant) are widely distributed in southern China. Under AR stress, significant necrosis and collapsed lesions were found in P. massoniana needles with remarkable yellowing and wilting tips, whereas T. wallichiana var. mairei did not exhibit chlorosis and visible damage. Due to the activation of a large number of stress-related genes and the synthesis of various functional proteins to counteract AR stress, it is important to study the differences in AR-tolerance mechanisms by comparative proteomic analysis of tolerant and sensitive species. This study revealed a total of 65 and 26 differentially expressed proteins that were identified in P. massoniana and T. wallichiana var. mairei, respectively. Among them, proteins involved in metabolism, photosynthesis, signal transduction and transcription were drastically down-regulated in P. massoniana, whereas most of the proteins participating in metabolism, cell structure, photosynthesis and transcription were increased in T. wallichiana var. mairei. These results suggest the distinct patterns of protein expression in the two woody species in response to AR, allowing a deeper understanding of diversity on AR tolerance in forest tree species.
Isolation of an endophytic fungus producing baccatin III from Taxus wallichiana var. mairei.[Pubmed: 23958913]
The objective of this study was to isolate endophytic fungi producing baccatin III from yew for the purpose of baccatin III and paclitaxel manufacture. Surface sterilized bark of Taxus wallichiana var. mairei was used as source material with potato dextrose agar culture medium for isolation of endophytic fungi. Fungal cultures were extracted with a mixture of chloroform/methanol (1:1, v/v) and the baccatin III in the extracts was determined and authenticated with LC-MS. An endophytic fungus that produced baccatin III was identified by ITS rDNA and 26S D1/D2 rDNA sequencing. A total of 192 endophytic fungal strains were isolated from T. wallichiana var. mairei. Only one of the 192 strains produced baccatin III and it was identified as Diaporthe phaseolorum. The productivity of this strain cultured in PDA culture medium was 0.219 mg/l. The isolated endophytic fungus produced baccatin III at a relatively high level and shows promise as a producing strain for baccatin III and paclitaxel manufacture after strain improvement.
Separation and purification of flavonoid from Taxus remainder extracts free of taxoids using polystyrene and polyamide resin.[Pubmed: 23936912]
An efficient separation process of flavonoid from Taxus wallichiana var. mairei remainder extracts free of taxoids was developed in this study. AB-8 macroporous resin and polyamide resin offered the fine adsorption capacity, and its adsorption rate at 30°C fitted well to the Langmuir and Freundich isotherms. Resin dynamic adsorption and desorption experiments were conducted to optimize the separation process of total flavonoids from T. wallichiana var. mairei remainder extracts free of taxoids. The optimum parameters for adsorption by AB-8 resin were as follows: (1) the concentration of flavonoids in a sample solution of 5.61 mg/mL with a processing volume of 2 bed volume (BV) (60 mL); (2) for desorption, ethanol-water (80:20, v/v), with 6 BV as an eluent at a flow rate of 2 BV/h. After a one-run treatment with AB-8 resin, the content of flavonoids was increased 5.10-fold from 4.05 to 20.65%. The optimum parameters for adsorption by polyamide resin were as follows: processing volume of 2 BV (30 mL); for desorption, ethanol-water (70:30, v/v), with 8 BV as an eluent at a flow rate of 2 BV/h. After one-run treatment with polyamide resin, the content of total flavonoids increased from 20.65 to 65.21%. The method will provide a potential approach for large-scale separation and purification of flavonoid for its wide pharmaceutical use.
Microsatellite loci for an old rare species, Pseudotaxus chienii, and transferability in Taxus wallichiana var. mairei (Taxaceae).[Pubmed: 25202547]
None


