Zanthoxylum avicennae
Zanthoxylum avicennae
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Zanthoxylum avicennae
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
BCN8303
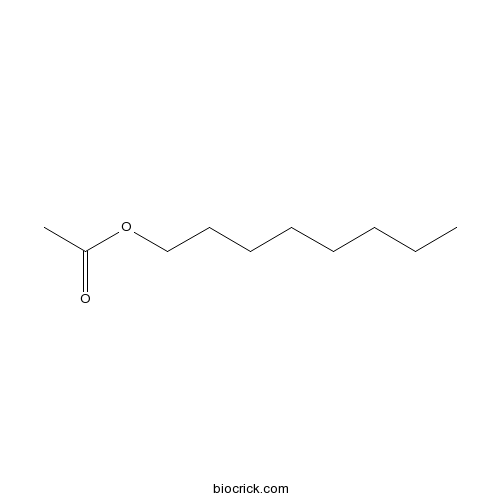
Acetic acid octyl ester112-14-1
Instructions
Zanthoxylum avicennae extract enhances GSK-3β to attenuate β-catenin via phosphatase 2A to block metastatic effects of HA22T cells and hepatocellular carcinoma xenografted nude mice.[Pubmed: 28548306]
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) metastasis is often associated with the activation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Zanthoxylum avicennae (Ying Bu Bo, YBB), a traditional herb with hepatoprotective effect, has been proven to inhibit human HCC in in vivo models however, the in vitro and in vivo effect of YBB on tumor metastasis is not clear yet. To determine whether YBB could inhibit HA22T human HCC cell by acting on β-catenin metastatic signaling in vitro and in vivo, HA22T cells were treated with different concentrations of YBB extracts (YBBE) and analyzed by Immunofluorescence staining assay, western blot analysis, siRNA mediated gene knock-down assays and co-immunoprecipitation assay. Additionally, the HA22T-implanted xenograft nude mice were used to confirm the assessed cellular effects. Mice treated with YBBEs showed a strong increasing trend in PP2Acα, GSK-3β, APC, and β-TrCP/HOS levels, however the expression of β-catenin, p-GSK-3β, TBX 3, and IL8 proteins showed a decreasing trend. YBBE significantly downregulated the nuclear and cytosolic β-catenin levels by facilitating the proteosomal degradation of β-catenin. Moreover, as observed by co-immunoprecipitation assay, YBBE directly promoted the protein interactions between GSK-3β, β-TrCP, APC, PP2A, and β-catenin. In conclusion, both in vitro and in vivo models clearly demonstrated that YBBE inhibits β-catenin involved metastatic signaling in highly metastatic HA22T cells through PP2A activation.
New Coumarin Derivatives and Other Constituents from the Stem Bark of Zanthoxylum avicennae: Effects on Neutrophil Pro-Inflammatory Responses.[Pubmed: 25938967]
Three new coumarin derivatives, 8-formylalloxanthoxyletin (1), avicennone (2), and (Z)-avicennone (3), have been isolated from the stem bark of Zanthoxylum avicennae (Z. avicennae), together with 15 known compounds (4-18). The structures of these new compounds were determined through spectroscopic and MS analyses. Compounds 1, 4, 9, 12, and 15 exhibited inhibition (half maximal inhibitory concentration (IC₅₀) values ≤7.65 µg/mL) of superoxide anion generation by human neutrophils in response to formyl-l-methionyl-l-leucyl-l-phenylalanine/cytochalasin B (fMLP/CB). Compounds 1, 2, 4, 8 and 9 inhibited fMLP/CB-induced elastase release with IC₅₀ values ≤8.17 µg/mL. This investigation reveals bioactive isolates (especially 1, 2, 4, 8, 9, 12 and 15) could be further developed as potential candidates for the treatment or prevention of various inflammatory diseases.
Chemical composition of the volatile oil from Zanthoxylum avicennae and antimicrobial activities and cytotoxicity.[Pubmed: 24914299]
Through literature retrieval, there has been no report on the research of the chemical components in Zanthoxylum avicennae (Lam.) DC. This paper extracted and determined the chemical components of the volatile oil in Z. avicennae, and at the same time, measured and evaluated the bioactivity of the volatile oil in Z. avicennae.
Suppression of plasminogen activators and the MMP-2/-9 pathway by a Zanthoxylum avicennae extract to inhibit the HA22T human hepatocellular carcinoma cell migration and invasion effects in vitro and in vivo via phosphatase 2A activation.[Pubmed: 24018669]
This study shows that the ECM degradation-associated pathway, including uPA and tPA and the downstream MMP-2/-9 protein, was significantly suppressed in HA22T cells treated with a Zanthoxylum avicennae extract (YBBE). The endogenous inhibitors, including TIMP-1/-2 and PAI-1, were enhanced in HA22T cells by the YBBE treatment. The expression of MMP-2/-9 and TIMP-1/-2 was respectively assessed by using RT-PCR and a zymography assay. The mRNA levels and enzymatic activity of MMP-2/-9 were down-regulated by the YBBE treatment in a dose-dependent manner, while the TIMP-1/-2 levels were conversely markedly increased. The PP2A siRNA or PP2A inhibitor totally reversed the YBBE effects, confirming the essential role of PP2A in YBBE inhibiting the HA22T cell migration and invasion effects. Xenografted animal experiments on nude mice demonstrated similiar results to the in vitro system. Both the in vitro and in vivo models clearly demonstrate that YBBE inhibited the highly metastatic HA22T liver cancer cell migration and invasion effects through PP2A activation.
[Study on the chemical components, antimicrobial and antitumor activities of the essential oil from the leaves of Zanthoxylum avicennae].[Pubmed: 23320360]
To study the chemical constituents, antimicrobial activity and antitumor activity of the essential oil from Zanthoxylum avicennae.
Zanthoxylum avicennae extracts inhibit cell proliferation through protein phosphatase 2A activation in HA22T human hepatocellular carcinoma cells in vitro and in vivo.[Pubmed: 22426520]
Hepatocellular carcinoma is a common type of cancer that is usually associated with poor prognosis. In this study, we examined the in vitro and in vivo mechanisms of the traditional Vietnamese herb Zanthoxylum avicennae on the inhibition of HA22T human hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation. HA22T cells were treated with different concentrations of Zanthoxylum avicennae extracts (YBBEs) and analyzed with the MTT assay, western blot analysis, flow cytometry, siRNA transfection assays and co-immunoprecipitation assay. Additionally, the HA22T-implanted xenograft nude mouse model was applied to confirm the cellular effects. YBBEs showed a strong inhibition of HA22T cell viability in a dose-dependent manner and significantly reduced cell proliferation-related proteins as well as induced cell cycle arrest in the G2/M phase. Protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A) siRNA or okadaic acid totally blocked YBBE-mediated cell proliferation inhibition. In addition, an HA22T-implanted nude mouse model further confirmed that YBBEs inhibit HA22T tumor cell growth and downregulate the survival and cell cycle regulating proteins, as well as activate the PP2A protein. Our findings indicate that the inhibition of HA22T cell proliferation by YBBEs is mediated through PP2A activation.
Zanthoxylum avicennae extracts induce cell apoptosis through protein phosphatase 2A activation in HA22T human hepatocellular carcinoma cells and block tumor growth in xenografted nude mice.[Pubmed: 21874223]
The use of herbs as alternative cancer therapies has attracted a great deal of attention owing to their lower toxicity. Whether Zanthoxylum avicennae (Ying Bu Bo, YBB) induces liver cancer cell apoptosis remains unclear. In this study, we investigated the effect of YBB extracts (YBBEs) on HA22T human hepatocellular carcinoma cells in vitro and in an in vivo mouse xenograft model. HA22T cells were treated with different concentrations of YBBEs and analyzed with Western blot analysis, TUNEL, JC-1 staining and siRNA transfection assays. Additionally, the HA22T-implanted xenograft nude mice model was applied to confirm the cellular effects. YBBEs-induced apoptosis, up-regulated death receptor apoptotic pathway markers as well as mitochondrial proteins, and suppressed the survival proteins in a dose-dependent manner. Pro-survival Bcl-2 family proteins were inhibited and the pro-apoptotic ones were increased. Protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A) siRNA or okadaic acid reversed the YBBEs effects, confirming the role of PP2A in YBBEs-induced HA22T apoptosis. All our experimental evidence indicates that YBBEs significantly promote HA22T apoptosis and reduce tumor sizes in xenograft nude mice via PP2A in a dose-dependent manner.
Neolignans, a coumarinolignan, lignan derivatives, and a chromene: anti-inflammatory constituents from Zanthoxylum avicennae.[Pubmed: 18211005]
Eight new compounds, including four new neolignans, (7' S,8' S)-bilagrewin ( 1), (7' S,8' S)-5-demethoxybilagrewin ( 2), (7' S,8' S)-5- O-demethyl-4'- O-methylbilagrewin ( 3), and (7' S,8' S)-nocomtal ( 4), a new coumarinolignan, (7' S,8' S)-4'- O-methylcleomiscosin D ( 5), two new lignan derivatives, (+)-9'- O-( Z)-feruloyl-5,5'-dimethoxylariciresinol ( 6) and (+)-9'- O-( E)-feruloyl-5,5'-dimethoxylariciresinol ( 7), and a new chromene, ( E)-3-(2,2-dimethyl-2 H-chromen-6-yl)prop-2-enal ( 8), have been isolated from the stem wood of Zanthoxylum avicennae, together with 18 known compounds ( 9- 26). The structures of these new compounds were determined through spectroscopic and MS analyses. (7' S,8' S)-4'- O-Methylcleomiscosin D ( 5), cleomiscosin D ( 9), skimmianine ( 18), robustine ( 19), and integrifoliolin ( 23) exhibited inhibition (IC 50 < or = 18.19 microM) of superoxide anion generation by human neutrophils in response to formyl- l-methionyl- l-leucyl- l-phenylalanine/cytochalasin B (FMLP/CB). In addition, skimmianine ( 18) inhibited FMLP/CB-induced elastase release with an IC 50 value of 19.15 +/- 0.66 microM.


