| Catalog No. | BCN3260 | 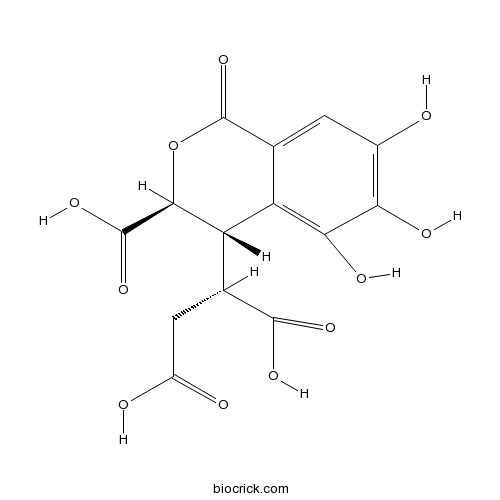 |
|
| CAS RN | 23725-05-5 | ||
| Molecular Weight | 356.2 | ||
| Molecular Formula | C14H12O11 | ||
| Database | [PubChem]:382158861 [ChEBI]: [PCIDB]: |
||
InChI=1S/C14H12O11/c15-5-1-4-7(10(19)9(5)18)8(3(12(20)21)2-6(16)17)11(13(22)23)25-14(4)24/h1,3,8,11,15,18-19H,2H2,(H,16,17)(H,20,21)(H,22,23)/t3-,8-,11-/m0/s1
Chebulic acid was selected, as tannins from Terminalia chebula are used as antidiabetic, renoprotective, antioxidant, hypotensive and an α-glucosidase inhibitor; chebulic acid at both doses (25 and 50mg/kg) improves biochemical alterations caused by renal ischemia in diabetic rats.[1]
Chebulic acid has preventive effects on advanced glycation endproduct-induced endothelial cell dysfunction, suggests that it may constitute a promising intervention agent against diabetic vascular complications.[2]
Chebulic acid exhibits in vitro a free radical-scavenging activity and ferric-reducing antioxidant activity, significantly reduces the tert-butyl hydroperoxide (t-BHP)-induced cell cytotoxicity, intracellular reactive oxygen species level, and the ratio of GSSH.[3]
Chebulic acid prevents the glycer-AGEs-induced ROS formation of LX-2 cells and collagen accumulation by ERK-phosphorylation-mediated Nrf2 nuclear translocation, which causes upregulation of antioxidant protein production.[4]
English website: Chebulic acid
Japanese website: Chebulic acid
Chinese website: Chebulic acid
[1] Gupta V B. Pharm Biol, 2012, 51(1):23-9.
[2] Lee H S, Koo Y C, Suh H J, et al. J Ethnopharmacol, 2010, 131(3):567-74.
[3] Lee H S, Jung S H, Yun B S, et al. Archive Für Toxikologie, 2007, 81(3):211-8.
[4] Koo Y C, Min C P, Nam M H, et al. Toxicol Vitro, 2016, 34:8-15.
[5] Han Q, Song J, Qiao C, et al. J Sep Sci, 2006, 29(11):1653-7.


