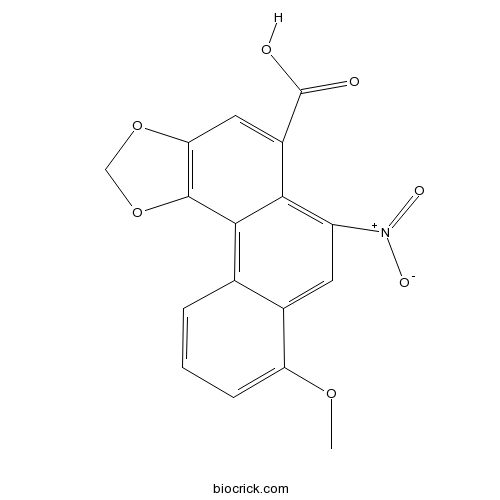
A monocarboxylic acid that is phenanthrene-1-carboxylic acid that is substituted by a methylenedioxy group at the 3,4 positions, by a methoxy group at position 8, and by a nitro group at position 10. It is the most abundant of the aristolochic acids and is found in almost all Aristolochia (birthworts or pipevines) species. It has been tried in a number of treatments for inflammatory disorders, mainly in Chinese and folk medicine. However, there is concern over their use as aristolochic acid is both carcinogenic and nephrotoxic.
Aristolochic acid, a potent human carcinogen produced by Aristolochia plants, is associated with urothelial carcinoma of the upper urinary tract (UUC), exposure to aristolochic acid contributes significantly to the incidence of UUC in Taiwan and endemic (Balkan) nephropathy .[1]
DNA damage by aristolochic acid (AA) is not only responsible for the tumour development but also for the destructive fibrotic process in the kidney; AA is a powerful nephrotoxic and carcinogenic substance with an extremely short latency period, not only in animals but also in humans, therefore, all products containing botanicals known to or suspected of containing AA should be banned from the market world wide.[2,3]
Aristolochic acid can induce proximal tubule apoptosis and epithelial to mesenchymal transformation.[4]
Aristolochic acid induces tumors in rats and mice, activates mutations at codon 61 of the c-Ha- ras gene in thin-tissue sections of tumors. [5]
English website: Aristolochic acid A
Japanese website: Aristolochic acid A
Chinese website: Aristolochic acid A
[1] Chen C H, Dickman K G, Moriya M, et al. P Nat Acad Sci US A, 2012, 109(21):8241-6.
[2] Grollman A P, Shibutani S, Moriya M, et al. P Nat Acad Sci US A, 2007, 104(29):12129-34.
[3] Arlt V M, Stiborova M, Schmeiser H H. Mutagenesis, 2002, 17(4):265-77.
[4] Pozdzik A A, Salmon I J, Debelle F D, et al. Kidney International, 2008, 73(5):595-607.
[5] Schmeiser H H, Scherf H R, Wiessler M. Cancer Letters, 1991, 59(2):139-43.
[6] Zhu G, Wang Z, Wang Q, et al. China Pharmacy, 2006, 17(18):21-4.