5-O-MethyllatifolinCAS# 18525-14-9 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 18525-14-9 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 3954893 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C18H20O4 | M.Wt | 300.3 |
| Type of Compound | Phenols | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
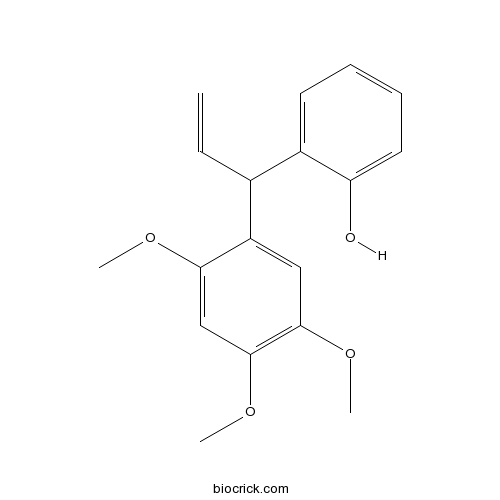
| Chemical Name | 2-[1-(2,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)prop-2-enyl]phenol | ||
| SMILES | COC1=CC(=C(C=C1C(C=C)C2=CC=CC=C2O)OC)OC | ||
| Standard InChIKey | NKFNPUQSPATHPN-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C18H20O4/c1-5-12(13-8-6-7-9-15(13)19)14-10-17(21-3)18(22-4)11-16(14)20-2/h5-12,19H,1H2,2-4H3 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

5-O-Methyllatifolin Dilution Calculator

5-O-Methyllatifolin Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.33 mL | 16.65 mL | 33.3 mL | 66.6001 mL | 83.2501 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.666 mL | 3.33 mL | 6.66 mL | 13.32 mL | 16.65 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.333 mL | 1.665 mL | 3.33 mL | 6.66 mL | 8.325 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0666 mL | 0.333 mL | 0.666 mL | 1.332 mL | 1.665 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0333 mL | 0.1665 mL | 0.333 mL | 0.666 mL | 0.8325 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Cinchonain Ib
Catalog No.:BCN9255
CAS No.:85022-69-1
- 16,23-Oxidoalisol B
Catalog No.:BCN9254
CAS No.:169326-06-1
- 2-Methoxy-1,6-dimethyl-5-vinyl-9,10-dihydrophenanthren-7-ol
Catalog No.:BCN9253
CAS No.:2266586-31-4
- Jinflexin A
Catalog No.:BCN9252
CAS No.:2055155-75-2
- 1,6-Dimethyl-5-vinyl-9,10-dihydrophenanthren-2-ol
Catalog No.:BCN9251
CAS No.:745056-83-1
- Dauricumine
Catalog No.:BCN9250
CAS No.:345641-00-1
- Murrayanine
Catalog No.:BCN9249
CAS No.:723-97-7
- Dictysine
Catalog No.:BCN9248
CAS No.:67256-05-7
- Qingyangshengenin 3-O-β-D-cymaropyranosyl-(1→4)-β-D-digitoxopyranoside
Catalog No.:BCN9247
CAS No.:1186628-87-4
- Periplocoside O
Catalog No.:BCN9246
CAS No.:116709-67-2
- Dehydrojuncuenin A
Catalog No.:BCN9245
CAS No.:1161681-26-0
- Lehmbachol D
Catalog No.:BCN9244
CAS No.:913556-40-8
- Matairesinol monoglucoside
Catalog No.:BCN9257
CAS No.:34446-06-5
- threo-Guaiacylglycerol β-coniferyl ether
Catalog No.:BCN9258
CAS No.:168393-18-8
- Jasminoside
Catalog No.:BCN9259
CAS No.:82451-18-1
- Gancaonin O
Catalog No.:BCN9260
CAS No.:129145-53-5
- 9-Oxooctadeca-10,12-dienoic acid
Catalog No.:BCN9261
CAS No.:54232-58-5
- (+)-Dalbergiphenol
Catalog No.:BCN9262
CAS No.:82358-44-9
- Juncuenin B
Catalog No.:BCN9263
CAS No.:1161681-20-4
- Juncuenin A
Catalog No.:BCN9264
CAS No.:1161681-18-0
- Sepiumol E
Catalog No.:BCN9265
CAS No.:2412027-09-7
- 4-Demethyltraxillaside
Catalog No.:BCN9266
CAS No.:1691201-82-7
- Tatsinine
Catalog No.:BCN9267
CAS No.:90038-21-4
- Platyphyllonol 5-O-β-D-xylopyranoside
Catalog No.:BCN9268
CAS No.:288141-04-8
Bioactivity of latifolin and its derivatives against termites and fungi.[Pubmed:19499920]
J Agric Food Chem. 2009 Jul 8;57(13):5707-12.
Latifolin (1) and its derivatives were investigated with the aim of confirming the correlation between bioactivity (antitermite and antifungal activity) and chemical structure. Termite mortality in response to the derivatives 2'-O-methyllatifolin (2), latifolin dimethyl ether (4), and latifolin diacetate (5) increased 2-fold compared to compound 1. The mortality rate from 5-O-Methyllatifolin (3) was not different from 1. The mass loss (feed consumption by termite) in response to compounds 3-5 was 3 times greater than compound 1, and the mass loss from compound 2 was twice as great as compound 1. The mortality rate from compounds 4 and 5 increased sharply 7 days after initial exposure. In assessing the antifungal activity of these compounds, it was found that the inhibition rates of white- and brown-rot fungi in response to all derivatives were less than that for compound 1. Our findings indicate that the phenolic hydroxyl group at C-5 of the A ring provides antitermite activities (mortality and mass loss). In addition, both C-5 and C-2' phenolic hydroxyl groups in the A and B rings have antifungal activity against white- and brown-rot fungi. In conclusion, the bioactivity of compound 1 depends upon the position of phenolic hydroxyl groups.


