Bisphenol PCAS# 2167-51-3 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 2167-51-3 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 630355 | Appearance | Powder |
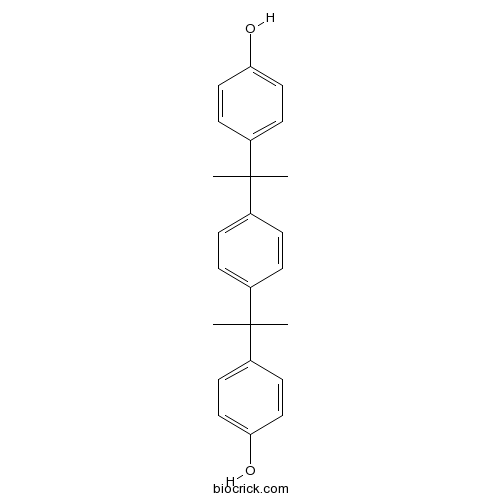
| Formula | C24H26O2 | M.Wt | 346.5 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | 4-[2-[4-[2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propan-2-yl]phenyl]propan-2-yl]phenol | ||
| SMILES | CC(C)(C1=CC=C(C=C1)C(C)(C)C2=CC=C(C=C2)O)C3=CC=C(C=C3)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | GIXXQTYGFOHYPT-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C24H26O2/c1-23(2,19-9-13-21(25)14-10-19)17-5-7-18(8-6-17)24(3,4)20-11-15-22(26)16-12-20/h5-16,25-26H,1-4H3 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

Bisphenol P Dilution Calculator

Bisphenol P Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.886 mL | 14.43 mL | 28.86 mL | 57.7201 mL | 72.1501 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5772 mL | 2.886 mL | 5.772 mL | 11.544 mL | 14.43 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2886 mL | 1.443 mL | 2.886 mL | 5.772 mL | 7.215 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0577 mL | 0.2886 mL | 0.5772 mL | 1.1544 mL | 1.443 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0289 mL | 0.1443 mL | 0.2886 mL | 0.5772 mL | 0.7215 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Sophoflavescenol
Catalog No.:BCN2891
CAS No.:216450-65-6
- N-Demethylricinine
Catalog No.:BCC9098
CAS No.:21642-98-8
- Isoquerglanin
Catalog No.:BCC8189
CAS No.:143519-53-3
- 3',4',5',3,5,7,8-Heptamethoxyflavone
Catalog No.:BCN4927
CAS No.:21634-52-6
- α-Conotoxin AuIB
Catalog No.:BCC5975
CAS No.:216299-21-7
- 1alpha, 25-Dihydroxy VD2-D6
Catalog No.:BCC1299
CAS No.:216244-04-1
- Bis(2,6-diisopropylphenyl)carbodiimide
Catalog No.:BCC8879
CAS No.:2162-74-5
- β-Pompilidotoxin
Catalog No.:BCC1048
CAS No.:216064-36-7
- 1-Methyl-3-nitrophthalate
Catalog No.:BCC8468
CAS No.:21606-04-2
- 15,16-Epoxy-12S-hydroxylabda-8(17),13(16),14-triene
Catalog No.:BCN1491
CAS No.:216011-55-1
- 7-Hydroxy-beta-carboline-1-propionic acid
Catalog No.:BCN1492
CAS No.:215934-15-9
- CX 546
Catalog No.:BCC7532
CAS No.:215923-54-9
- Shoreic acid
Catalog No.:BCN4928
CAS No.:21671-00-1
- Fludarabine
Catalog No.:BCC2518
CAS No.:21679-14-1
- Kulinone
Catalog No.:BCN7954
CAS No.:21688-61-9
- Lauroscholtzine
Catalog No.:BCN4929
CAS No.:2169-44-0
- Z-N-Me-Ala-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3344
CAS No.:21691-41-8
- Z-DL-Nva-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3304
CAS No.:21691-44-1
- Procurcumenol
Catalog No.:BCN3555
CAS No.:21698-40-8
- Shyobunone
Catalog No.:BCN4930
CAS No.:21698-44-2
- 15-Epi-Danshenol-A
Catalog No.:BCN3146
CAS No.:216987-13-2
- WB 4101 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6858
CAS No.:2170-58-3
- Apelin-17 (human, bovine)
Catalog No.:BCC5959
CAS No.:217082-57-0
- [Pyr1]-Apelin-13
Catalog No.:BCC7358
CAS No.:217082-60-5
Bisphenol P activates hormonal genes and introduces developmental outcomes in Chironomus tentans.[Pubmed:30878007]
Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2019 Jun 15;174:675-682.
The endocrine disrupting properties of bisphenol A (BPA) discharged to the environment have been newly identified by the European Chemicals Agency, increasing the need to assess the environmental endocrine disrupting potentials of its alternatives with which it shares close structural features. However, few investigations of the environmental endocrine disrupting functions of BPA analogs have been conducted to date. In this study, the endocrine disrupting effects of a BPA analog of Bisphenol P (BPP) were investigated in the nonbiting midge (Chironomus tentans), a model organism in ecotoxicology. An initial ex vivo test using salivary gland cells explanted from the larvae and a subsequent in vivo test using embryos and larvae revealed the upregulatory effects of BPP on ecdysone receptor genes encoding the ecdysone receptor (EcR) and the early responsive gene E74, with a similar temporal pattern of gene activation. Partial life cycle and full life cycle toxicity tests demonstrated BPP altered embryo hatching, larval emergence, and adult sex ratio at concentrations close to the effective concentrations for hormonal genetic endpoints in embryos and larvae after 48h of exposure. Although embryos appeared to be more sensitive to BPP than the fourth instar larvae, the impact on neither life stage seemed enough to estimate the developmental impairment of the insects. These results demonstrate the ecdysone pathway is a target of BPP, and that long-term exposure could cause apical effects on the development of C. tentans. The endocrine disrupting effects towards aquatic organisms, as well as the high persistence and bioconcentration potential, indicate an urgent need to assess the environmental risks associated with BPP.


