Eschweilenol CCAS# 211371-02-7 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 211371-02-7 | SDF | File under preparation. |
| PubChem ID | 10026656 | Appearance | Powder |
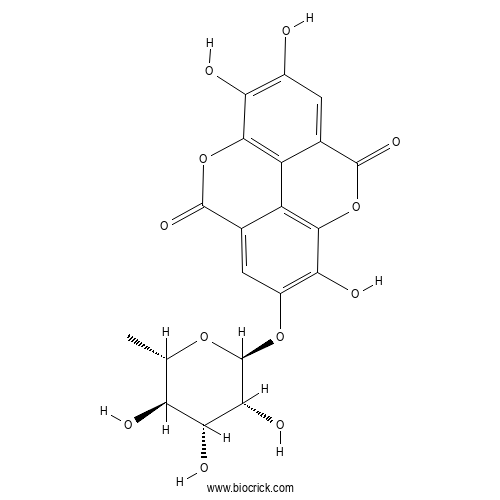
| Formula | C20H16O12 | M.Wt | 448.3 |
| Type of Compound | Phenols | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | 4-(alpha-Rhamnopyranosyl)ellagic acid;Ellagic acid deoxyhexoside | ||
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | 6,7,14-trihydroxy-13-[(2S,3R,4R,5R,6S)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-methyloxan-2-yl]oxy-2,9-dioxatetracyclo[6.6.2.04,16.011,15]hexadeca-1(15),4,6,8(16),11,13-hexaene-3,10-dione | ||
| SMILES | CC1C(C(C(C(O1)OC2=C(C3=C4C(=C2)C(=O)OC5=C4C(=CC(=C5O)O)C(=O)O3)O)O)O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | NLOYJHDXNPMFKW-RGYXEVLJSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C20H16O12/c1-4-11(22)14(25)15(26)20(29-4)30-8-3-6-10-9-5(18(27)32-17(10)13(8)24)2-7(21)12(23)16(9)31-19(6)28/h2-4,11,14-15,20-26H,1H3/t4-,11-,14+,15+,20-/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

Eschweilenol C Dilution Calculator

Eschweilenol C Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.2306 mL | 11.1532 mL | 22.3065 mL | 44.613 mL | 55.7662 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4461 mL | 2.2306 mL | 4.4613 mL | 8.9226 mL | 11.1532 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2231 mL | 1.1153 mL | 2.2306 mL | 4.4613 mL | 5.5766 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0446 mL | 0.2231 mL | 0.4461 mL | 0.8923 mL | 1.1153 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0223 mL | 0.1115 mL | 0.2231 mL | 0.4461 mL | 0.5577 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Foliachinenoside C
Catalog No.:BCN0378
CAS No.:1041180-87-3
- Apigenin 6,8-di-C-alpha-L-arabinopyranoside
Catalog No.:BCN0377
CAS No.:73140-47-3
- Isospinosin
Catalog No.:BCN0376
CAS No.:89701-83-7
- Apigenin 7-[rhamnosyl-(1->2)-galacturonide]
Catalog No.:BCN0375
CAS No.:124167-97-1
- Japondipsaponin E1
Catalog No.:BCN0374
CAS No.:175586-66-0
- Hederagenin 3-O-(2-O-acetyl-alpha-L-arabinopyranoside)
Catalog No.:BCN0373
CAS No.:87562-05-8
- 8-Hydroxypinoresinol 4'-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN0372
CAS No.:102582-69-4
- Kaempferol 3,4'-di-O-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN0371
CAS No.:71939-16-7
- Acacetin 7-[rhamnosyl-(1->2)-galacturonide]
Catalog No.:BCN0370
CAS No.:38722-95-1
- Dipsacus saponin C
Catalog No.:BCN0369
CAS No.:152406-43-4
- Dipsacus saponin B
Catalog No.:BCN0368
CAS No.:152406-42-3
- Dipsacus saponin A
Catalog No.:BCN0367
CAS No.:99624-66-5
- (7'E,8S)-2',4,8-Trihydroxy-3-methoxy-2,4'-epoxy-8,5'-neolign-7'-en-7-one
Catalog No.:BCN0380
CAS No.:2292113-33-6
- 4'-O-Methyl-8-prenylnaringenin
Catalog No.:BCN0381
CAS No.:120727-36-8
- 6α,7α-Epoxy-5β-hydroxy-12-deoxyphorbol 13-decanoate
Catalog No.:BCN0382
CAS No.:1256844-45-7
- 7-Oxodehydroabietic acid
Catalog No.:BCN0383
CAS No.:18684-55-4
- Taraxasteryl palmitate
Catalog No.:BCN0384
CAS No.:29803-90-5
- Robipseudin A
Catalog No.:BCN0385
CAS No.:1460737-79-4
- 2',4',6'-Trihydroxydihydrochalcone 4'-O-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN0386
CAS No.:73519-16-1
- Wikstroelide E
Catalog No.:BCN0387
CAS No.:66107-38-8
- 3'-O-Methylgnetifolin M
Catalog No.:BCN0388
CAS No.:2411994-31-3
- (+)-Phyllocladene
Catalog No.:BCN0389
CAS No.:469-86-3
- Hypoglaucin A
Catalog No.:BCN0390
CAS No.:93528-39-3
- 27-Epichantrieroside A
Catalog No.:BCN0391
CAS No.:290809-72-2
Antifungal and anti-inflammatory potential of eschweilenol C-rich fraction derived from Terminalia fagifolia Mart.[Pubmed:31100435]
J Ethnopharmacol. 2019 Aug 10;240:111941.
ETHNOPHARMACOLOGICAL RELEVANCE: Folk knowledge transmitted between generations allows traditional populations to maintain the use of medicinal plants for the treatment of several diseases. In this context, the species Terminalia fagifolia Mart., native to Brazil, is used for the treatment of chronic and infectious diseases. Plants rich in secondary metabolites, such as this species and their derivatives, may represent therapeutic alternatives for the treatment of diseases that reduce the quality of life of people. AIM OF THE STUDY: The aim of this study was to evaluate the antifungal and anti-inflammatory potential of aqueous fraction from ethanolic extract of T. fagifolia, with in silico study of the major compound of the fraction. MATERIAL AND METHODS: The phytochemical study of the aqueous fraction was performed by HPLC, LC/MS and NMR. The antifungal activity was evaluated against yeasts, by determination of the minimum inhibitory concentration and minimum fungicidal concentration. The effect on Candida albicans was analyzed by AFM. The antibiofilm potential against biofilms of C. albicans was also tested. The anti-inflammatory potential of the aqueous fraction was evaluated in vivo by the carrageenan-induced paw edema and peritonitis. A microglial model of LPS-induced neuroinflammation was also studied. Further insights on the activation mechanism were studied using quantum chemistry computer simulations. Toxicity was evaluated in the Galleria mellonella and human erythrocytes models. RESULTS: Eschweilenol C was identified as the major constituent of the aqueous fraction of the ethanolic extract of T. fagifolia. The aqueous fraction was active against all Candida strains used (sensitive and resistant to Fluconazole) with MICs ranging from 1000 to 0.4mug/mL. By AFM it was possible to observe morphological alterations in treated Candida cells. The fraction significantly (p<0.05) inhibited paw edema and decreased levels of malondialdehyde induced by carrageenan. In a microglial cell model, aqueous fraction demonstrated the ability to inhibit NF-kappaB after induction with lipopolysaccharide. The theoretical studies showed structural similarity between Eschweilenol C and indomethacin and an excellent antioxidant potential. The aqueous fraction did not present toxicity in the studied models. CONCLUSION: The results indicate that the aqueous fraction of T. fagifolia has potential for biomedical applications with low toxicity. This finding can be attributed to the predominance of Eschweilenol C in the aqueous fraction.
N-myristoyltransferases inhibitory activity of ellagitannins from Terminalia bentzoe (L.) L. f. subsp. bentzoe.[Pubmed:30342177]
Fitoterapia. 2018 Nov;131:91-95.
N-myristoylation (Myr) is an eukaryotic N-terminal co- or post-translational protein modification in which the enzyme N-myristoyltransferase (NMT) transfers a fatty acid (C14:0) to the N-terminal glycine residues of several cellular key proteins. Depending on the cellular context, NMT may serve as a molecular target in anticancer or anti-infectious therapy, and drugs that inhibit this enzyme may be useful in the treatment of cancer or infectious diseases. As part of an on-going project to identify natural Homo sapiens N-myristoyltransferase 1 inhibitors (HsNMT1), two ellagitannins, punicalagin (1) and isoterchebulin (2), along with Eschweilenol C (3) and ellagic acid (4) were isolated from the bark of Terminalia bentzoe (L.) L. f. subsp. bentzoe. Their structures were determined by means of spectroscopic analyses and comparison with literature data. Punicalagin (1) and isoterchebulin (2) showed significant inhibitory activity towards HsNMT1, and also against Plasmodium falciparum NMT (PfNMT) both in vitro and in cellulo, opening alternative paths for new NMT inhibitors development. This is the first report identifying natural products from a botanical source as inhibitors of HsNMT and PfNMT.
Three new ellagic acid derivatives from the bark of Eschweilera coriacea from the Suriname rainforest.[Pubmed:9677272]
J Nat Prod. 1998 Jul;61(7):901-6.
Bioassay-guided fractionation of Eschweilera coriacea collected in the lowland wet forest of Suriname yielded the new but only weakly active ellagic acid derivative eschweilenol A (1) and the two new but inactive ellagic acid derivatives eschweilenol B (2) and Eschweilenol C (3). The four known compounds, sucrose, ellagic acid, 3-O-galloylepigallocatechin, and epigallocatechin, were also isolated. The structures of the three new compounds were determined by spectrometric methods, primarily from the HMQC, HMBC, NOESY, and ROESY NMR techniques, and chemical methods, including methylation and triethylsilylation. The location of a hydroxyl group in one ellagic acid derivative was determined by a new technique involving an NOE correlation of the protons of a triethylsilyl derivative with a proton on a neighboring aromatic ring.


