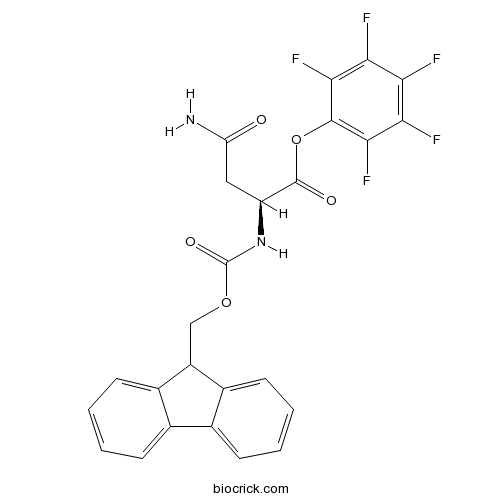
Fmoc-Asn-OPfpCAS# 86060-99-3 |
- PF-4708671
Catalog No.:BCC5031
CAS No.:1255517-76-0
- BIX 02565
Catalog No.:BCC4303
CAS No.:1311367-27-7
- BI-D1870
Catalog No.:BCC5030
CAS No.:501437-28-1
- CMK
Catalog No.:BCC1489
CAS No.:821794-90-5
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 86060-99-3 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 10875019 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C25H17N2O5F5 | M.Wt | 520.5 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in water or 1% acetic acid | ||
| Chemical Name | (2,3,4,5,6-pentafluorophenyl) (2S)-4-amino-2-(9H-fluoren-9-ylmethoxycarbonylamino)-4-oxobutanoate | ||
| SMILES | C1=CC=C2C(=C1)C(C3=CC=CC=C32)COC(=O)NC(CC(=O)N)C(=O)OC4=C(C(=C(C(=C4F)F)F)F)F | ||
| Standard InChIKey | FESVUEALWMQZEP-INIZCTEOSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C25H17F5N2O5/c26-18-19(27)21(29)23(22(30)20(18)28)37-24(34)16(9-17(31)33)32-25(35)36-10-15-13-7-3-1-5-11(13)12-6-2-4-8-14(12)15/h1-8,15-16H,9-10H2,(H2,31,33)(H,32,35)/t16-/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

Fmoc-Asn-OPfp Dilution Calculator

Fmoc-Asn-OPfp Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.9212 mL | 9.6061 mL | 19.2123 mL | 38.4246 mL | 48.0307 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.3842 mL | 1.9212 mL | 3.8425 mL | 7.6849 mL | 9.6061 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.1921 mL | 0.9606 mL | 1.9212 mL | 3.8425 mL | 4.8031 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0384 mL | 0.1921 mL | 0.3842 mL | 0.7685 mL | 0.9606 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0192 mL | 0.0961 mL | 0.1921 mL | 0.3842 mL | 0.4803 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Fmoc-Asn-OPfp
- Fmoc-Lys(Boc)-OPfp
Catalog No.:BCC3517
CAS No.:86060-98-2
- Fmoc-Cys(Acm)-OPfp
Catalog No.:BCC3474
CAS No.:86060-96-0
- Fmoc-Met-OPfp
Catalog No.:BCC3529
CAS No.:86060-94-8
- Fmoc-Tyr(tBu)-OPfp
Catalog No.:BCC3568
CAS No.:86060-93-7
- Fmoc-Phe-OPfp
Catalog No.:BCC3536
CAS No.:86060-92-6
- Fmoc-Pro-OPfp
Catalog No.:BCC3539
CAS No.:86060-90-4
- Fmoc-Ile-OPfp
Catalog No.:BCC3506
CAS No.:86060-89-1
- Fmoc-Leu-OPfp
Catalog No.:BCC3510
CAS No.:86060-88-0
- Fmoc-Val-OPfp
Catalog No.:BCC3571
CAS No.:86060-87-9
- Fmoc-Ala-OPfp
Catalog No.:BCC3035
CAS No.:86060-86-8
- Fmoc-Gly-OPfp
Catalog No.:BCC3499
CAS No.:86060-85-7
- Fmoc-Asp-OBzl
Catalog No.:BCC3087
CAS No.:86060-83-5
- Fmoc-Gln-OPfp
Catalog No.:BCC3484
CAS No.:86061-00-9
- Fmoc-Asp(OtBu)-OPfp
Catalog No.:BCC3091
CAS No.:86061-01-0
- Fmoc-Glu(OtBu)-OPfp
Catalog No.:BCC3495
CAS No.:86061-04-3
- Fmoc-β-Homo-Pro-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2627
CAS No.:86069-86-5
- Fmoc-Trp-OPfp
Catalog No.:BCC3557
CAS No.:86069-87-6
- M617
Catalog No.:BCC5929
CAS No.:860790-38-1
- A 844606
Catalog No.:BCC6200
CAS No.:861119-08-6
- 5'-Fluoroindirubinoxime
Catalog No.:BCC6104
CAS No.:861214-33-7
- Fmoc-D-Phe-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3537
CAS No.:86123-10-6
- Fmoc-D-Trp-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3559
CAS No.:86123-11-7
- SKF 86466 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7795
CAS No.:86129-54-6
- A-740003
Catalog No.:BCC1322
CAS No.:861393-28-4
Asparagine coupling in Fmoc solid phase peptide synthesis.[Pubmed:2599767]
Int J Pept Protein Res. 1989 Oct;34(4):287-94.
To investigate side reactions during the activation of side chain unprotected asparagine in Fmoc-solid phase peptide synthesis the peptide Met-Lys-Asn-Val-Pro-Glu-Pro-Ser was synthesized using different coupling conditions for introduction of the asparagine residue. Asparagine was activated by DCC/HOBt, BOP (Castro's reagent) or introduced as the pentafluorophenyl ester. The resulting peptide products were analyzed by HPLC, mass spectrometry and Edman degradation. In the crude products varying amounts of beta-cyano alanine were found, which had been formed by dehydration of the side chain amide during carboxyl activation of Fmoc-asparagine. A homogeneous peptide was obtained by using either side chain protected asparagine derivatives with BOP mediated activation or by coupling of Fmoc-Asn-OPfp. Fmoc-Asn(Mbh)-OH and Fmoc-Asn(Tmob)-OH were coupled rapidly and without side reactions with BOP. For the side chain protected derivatives the coupling was as fast as that of other Fmoc-amino acid derivatives, whereas couplings of Fmoc-Asn-OH proceed more slowly. However, during acidolytic cleavage both protection groups, Mbh and Tmob, generate carbonium ions which readily alkylate tryptophan residues in a peptide. Tryptophan modification was examined using the model peptide Asn-Trp-Asn-Val-Pro-Glu-Pro-Ser. Alkylation could be reduced by addition of scavengers to the TFA during cleavage and side chain deprotection. A homogeneous peptide containing both, asparagine and tryptophan, was obtained only by coupling of Fmoc-Asn-OPfp.


