Leonurine hydrochlorideCAS# 24697-74-3 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 24697-74-3 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 161464 | Appearance | White cryst. |
| Formula | C14H21N3O5 | M.Wt | 311.33 |
| Type of Compound | Alkaloids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | SCM-198 | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : 6 mg/mL (19.27 mM; Need ultrasonic) | ||
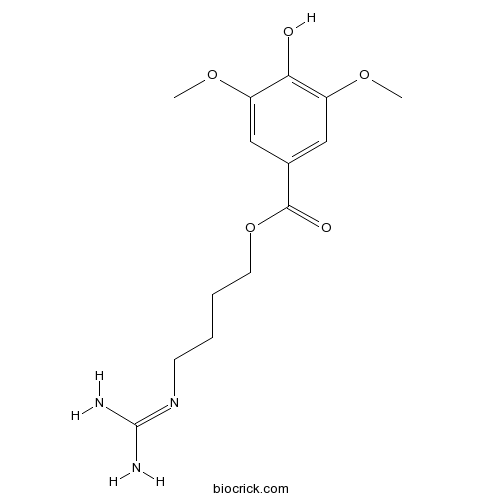
| Chemical Name | 4-(diaminomethylideneamino)butyl 4-hydroxy-3,5-dimethoxybenzoate | ||
| SMILES | COC1=CC(=CC(=C1O)OC)C(=O)OCCCCN=C(N)N | ||
| Standard InChIKey | WNGSUWLDMZFYNZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C14H21N3O5/c1-20-10-7-9(8-11(21-2)12(10)18)13(19)22-6-4-3-5-17-14(15)16/h7-8,18H,3-6H2,1-2H3,(H4,15,16,17) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Leonurine hydrochloride has anti-oxidative, anti-inflammatory, and antitumor activities, it exerts antidiabetic, cardiovascular, and bovine mastitis protection, it has an inhibitory effect on bleeding caused by incomplete abortion. Leonurine hydrochloride increases the expression levels of caspase-3, caspase-9 and Bax/Bcl-2, and it inhibits osteoclastogenesis and prevent osteoporosis associated with estrogen deficiency by inhibiting the NF-κB and PI3K/Akt signaling pathways. |
| Targets | NF-kB | PI3K | Akt | IkB | ERK | p38MAPK | AP-1 | PKC | NO | Caspase | Bcl-2/Bax | ROS | Calcium Channel | IKK |
| In vitro | Leonurine hydrochloride inhibits osteoclastogenesis and prevents osteoporosis associated with estrogen deficiency by inhibiting the NF-κB and PI3K/Akt signaling pathways.[Pubmed: 25708053]Bone. 2015 Jun;75:128-37.Osteoclasts, the primary bone resorbing cells, are responsible for destructive bone diseases such as postmenopausal osteoporosis, rheumatoid arthritis, and periodontitis. Many plant-derived traditional medicines that might suppress the formation and/or function of osteoclasts are promising treatments for osteoclast-related diseases. |
| In vivo | Effect of leonurine hydrochloride on endothelin and the endothelin receptor-mediated signal pathway in medically-induced incomplete abortion in rats.[Pubmed: 23541415]Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2013 Jul;169(2):299-303.Endothelin (ET) is involved in uterine contractions. Our previous study showed that Leonurine hydrochloride (LH) inhibits abnormal bleeding caused by incomplete abortion through an increase in uterine contractions in rats. The present study was conducted to show that LH treatment regulates the ET-mediated signal pathway in abortion in rats.
Effects of leonurine hydrochloride on medically induced incomplete abortion in early pregnancy rats.[Pubmed: 22030073]Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2011 Dec;159(2):375-80.To determine the effect of Leonurine hydrochloride (LH) on abnormal bleeding induced by medical abortion. |
| Cell Research | Leonurine hydrochloride induces apoptosis of H292 lung cancer cell by a mitochondria-dependent pathway.[Pubmed: 25856714]Pharm Biol. 2015 Apr 9:1-7.Leonurine hydrochloride (LH), a major alkaloid compound extracted from Leonurus japonicas Houtt. (Labiatae), is considered to have antitumor roles.
This study investigated its effects on human non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) H292 cells and illustrated the possible mechanism involved.
|

Leonurine hydrochloride Dilution Calculator

Leonurine hydrochloride Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.212 mL | 16.0601 mL | 32.1203 mL | 64.2405 mL | 80.3006 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.6424 mL | 3.212 mL | 6.4241 mL | 12.8481 mL | 16.0601 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3212 mL | 1.606 mL | 3.212 mL | 6.4241 mL | 8.0301 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0642 mL | 0.3212 mL | 0.6424 mL | 1.2848 mL | 1.606 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0321 mL | 0.1606 mL | 0.3212 mL | 0.6424 mL | 0.803 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Leonurine, a natural alkaloid extracted from Herba leonuri, has been proved to have anti-inflammatory effect.
In Vitro:Leonurine can obviously attenuate the spontaneous excitatory postsynaptic current amplitude and frequency on pyramidal neurons[1]. Leonurine can dose-dependently suppress PI glycation. Leonurine may inhibit PI glycation through trapping MGO and keeping it from reacting with PI[2]. Leonurine can dose-dependently suppress PI glycation[3].
In Vivo:Leonurine (60 mg/kg/day)+2-VO significantly decreases levels of glutamate and hydrogen peroxide, improves both the cognitive flexibility and the spatial learning and memory abilities. Moreover, leonurine obviously enhances long-term depression, elevates the ratio of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor 2A/2B, and decreases the expression of postsynaptic density protein-95. Interestingly, the ratio of LC3II/LC3I and beclin-1 expression are markedly down-regulated by leonurine[1]. Leonurine significantly alleviates LPS-induced histopathological changes, downregulates the levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interleukin-6 (IL-6), upregulates the level of anti-inflammatory cytokine interleukin-10 (IL-10), and inhibits the expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) and cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) in mouse mastitis model. Leonurine inhibits the expression of Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) and the activation of nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-κB) and the phosphorylation of p38, extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK), and Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK)[4].
References:
[1]. Liu C, et al. Leonurine ameliorates cognitive dysfunction via antagonizing excitotoxic glutamate insults and inhibiting autophagy. Phytomedicine. 2016 Dec 1;23(13):1638-1646.
[2]. Gao H, et al. Synthesis and biological evaluation of the codrug of Leonurine and Aspirin as cardioprotective agents. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2016 Oct 1;26(19):4650-4.
[3]. Huang L, et al. Inhibitory effect of leonurine on the formation of advanced glycation end products. Food Funct. 2015 Feb;6(2):584-9.
[4]. Song X, et al. Leonurine exerts anti-inflammatory effect by regulating inflammatory signaling pathways and cytokines in LPS-induced mouse mastitis. Inflammation. 2015 Feb;38(1):79-88.
- Chlorouvedalin
Catalog No.:BCN4664
CAS No.:24694-80-2
- Uvedalin
Catalog No.:BCN4665
CAS No.:24694-79-9
- Senegenin
Catalog No.:BCN5899
CAS No.:2469-34-3
- Derrisisoflavone B
Catalog No.:BCN3955
CAS No.:246870-75-7
- Aglinin A
Catalog No.:BCN5111
CAS No.:246868-97-3
- 1-Benzoyl-4-oxopiperidine
Catalog No.:BCC8455
CAS No.:24686-78-0
- Ro 64-5229
Catalog No.:BCC7513
CAS No.:246852-46-0
- Catharanthine
Catalog No.:BCN1255
CAS No.:2468-21-5
- 3-Amino-2,6-piperidinedione hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC8606
CAS No.:24666-56-6
- Neolitsine
Catalog No.:BCN4817
CAS No.:2466-42-4
- Stellasterol
Catalog No.:BCN5110
CAS No.:2465-11-4
- H-Isoleucinol
Catalog No.:BCC2726
CAS No.:24629-25-2
- Isomangiferin
Catalog No.:BCN2528
CAS No.:24699-16-9
- NVP DPP 728 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC2365
CAS No.:247016-69-9
- Weinreb Linker
Catalog No.:BCC2836
CAS No.:247021-90-5
- 7beta-Methoxyrosmanol
Catalog No.:BCN7965
CAS No.:24703-38-6
- 6-Deoxy-9alpha-hydroxycedrodorin
Catalog No.:BCN5112
CAS No.:247036-52-8
- Daphnezomine B
Catalog No.:BCN5113
CAS No.:247078-43-9
- Fimasartan
Catalog No.:BCC5552
CAS No.:247257-48-3
- Dihydroergocristine mesylate
Catalog No.:BCC6657
CAS No.:24730-10-7
- Leonurin monohydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCN8304
CAS No.:24735-18-0
- SB 328437
Catalog No.:BCC6056
CAS No.:247580-43-4
- Beta-Peltoboykinolic acid
Catalog No.:BCN6635
CAS No.:24778-48-1
- 1,3-Bis(4-aminophenoxy)benzene
Catalog No.:BCC8418
CAS No.:2479-46-1
Effects of leonurine hydrochloride on medically induced incomplete abortion in early pregnancy rats.[Pubmed:22030073]
Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2011 Dec;159(2):375-80.
OBJECTIVES: To determine the effect of Leonurine hydrochloride (LH) on abnormal bleeding induced by medical abortion. STUDY DESIGN: Rats had incomplete abortions induced in early pregnancy using mifepristone in combination with misoprostol. After abortion, rats were treated with LH for 7 days, and the duration and volume of uterine bleeding were observed. Approximately 30min after the last treatment, the animals were killed and the uterine shape was observed. The sinistro-uteri were suspended in organ baths to record the contraction curves, including the frequency and tension for 10min; the dextro-uteri were fixed with formaldehyde for pathologic evaluation. In addition, blood samples were collected from the femoral artery for the measurement of estradiol (E(2)) and progesterone (P) levels by radioimmunoassay. RESULTS: In in vivo experiments, compared with the model group, LH treatment markedly reduced the volume of bleeding and intrauterine residual, and significantly shortened the duration of bleeding. From the contraction curve, LH notably reinforced the frequency and tension of uterine contractions. LH remarkably elevated the serum estradiol level in rats, but had no obvious effect on progesterone level. CONCLUSIONS: LH has an inhibitory effect on bleeding caused by incomplete abortion; the mechanism may be related to up-regulation of the E(2) level, leading to an increase in uterine contractions and evacuation of intrauterine residuum.
Effect of leonurine hydrochloride on endothelin and the endothelin receptor-mediated signal pathway in medically-induced incomplete abortion in rats.[Pubmed:23541415]
Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2013 Jul;169(2):299-303.
OBJECTIVE: Endothelin (ET) is involved in uterine contractions. Our previous study showed that Leonurine hydrochloride (LH) inhibits abnormal bleeding caused by incomplete abortion through an increase in uterine contractions in rats. The present study was conducted to show that LH treatment regulates the ET-mediated signal pathway in abortion in rats. STUDY DESIGN: Early pregnancies in rats had incomplete abortions induced using mifepristone in combination with misoprostol. After the abortions, the rats were treated with LH orally for 7 days and surgery was performed. The sinistro-uterus was dissected for measurement of ET and nitric oxide (NO); the dextro-uterus was stored at -80 degrees C for ET receptor (ETA and ETB) analysis. Myometrial cells from the dextro-uterus were cultured for measurement of phospholipase C (PLC) activity, intra-cellular Ca(2+) concentration ([Ca(2+)]i), and protein kinase C (PKC) activity. RESULTS: In in vivo experiments, LH treatment elevated the ET level and ET/NO ratio in rats with induced abortions and up-regulated ETA mRNA expression (P<0.01 vs. the model group), but there was no change in ETB mRNA. LH significantly increased the [Ca(2+)]i, PLC activity, and relative production of PKC protein in myometrial cells. CONCLUSION: LH increased uterine contractions in rats with incomplete abortions by modulating the ET receptor-mediated signal pathway.
Leonurine hydrochloride inhibits osteoclastogenesis and prevents osteoporosis associated with estrogen deficiency by inhibiting the NF-kappaB and PI3K/Akt signaling pathways.[Pubmed:25708053]
Bone. 2015 Jun;75:128-37.
Osteoclasts, the primary bone resorbing cells, are responsible for destructive bone diseases such as postmenopausal osteoporosis, rheumatoid arthritis, and periodontitis. Many plant-derived traditional medicines that might suppress the formation and/or function of osteoclasts are promising treatments for osteoclast-related diseases. In this study, we investigated the effects of Leonurine hydrochloride (LH) on receptor activator NF-kappaB ligand (RANKL)-induced osteoclastogenesis and ovariectomy-induced bone loss. LH is a synthetic chemical compound based on the structure of leonurine, which is found in motherwort and has been reported to exhibit phytoestrogenic activity. In RAW 264.7 cells and mouse bone marrow monocytes (BMMs), LH suppressed RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis and actin ring formation in a dose-dependent manner. LH targeted RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis and bone resorption at an early stage. Molecular analysis demonstrated that LH attenuated RANKL-induced NF-kappaB signaling by inhibiting the phosphorylation and degradation of IkappaBalpha and NF-kappaB p65 nuclear translocation. LH inhibited the RANK-TRAF6 association triggered by RANKL binding and the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/Akt axis, without significantly affecting the extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK)/mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) and AP-1 signaling pathways. LH attenuated the RANKL-stimulated expression of osteoclast-related genes including NFATc1, tartrate resistant acid phosphatase (TRAP), cathepsin K, and osteoclast-associated receptor (OSCAR). Consistent with the in vitro results, LH administration attenuated osteoclast activity, thus preventing bone loss caused by estrogen deficiency in mice. In this study, LH suppressed RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis via RANK-TRAF6, NF-kappaB, and PI3K/Akt signaling. These data provide the first evidence that LH might be a promising therapeutic compound to treat osteoclast-related diseases, such as osteoporosis.
Leonurine hydrochloride induces apoptosis of H292 lung cancer cell by a mitochondria-dependent pathway.[Pubmed:25856714]
Pharm Biol. 2015;53(11):1684-90.
CONTEXT: Leonurine hydrochloride (LH), a major alkaloid compound extracted from Leonurus japonicas Houtt. (Labiatae), is considered to have antitumor roles. OBJECTIVE: This study investigated its effects on human non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) H292 cells and illustrated the possible mechanism involved. MATERIALS AND METHODS: After treatment with different concentrations of LH (0, 10, 25, and 50 mumol/L) for 6, 12, 24, 48, and 72 h, the cell viability was assessed by the MTT assay. After exposed to different doses of LH for 24 h, cell-cycle distribution, cell apoptosis, mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP), and reactive oxygen species (ROS) were monitored by flow cytometry. RT-PCR and western blot were used to detect the expression of apoptosis-related genes. RESULTS: LH significantly inhibited the proliferation of H292 cells in a time- and dose-dependent manner, and induced G0/G1 cell-cycle arrest. Coincidentally, LH treatment at a dose of 10, 25, and 50 mumol/L for 24 h increased apoptotic ratio from 4.9 +/- 0.43% to 11.5 +/- 1.12%, 19.3 +/- 1.16%, and 61.3 +/- 6.69%, respectively. The inhibition effect of LH on H292 cells was associated with the loss of MMP and the generation of ROS. The phosphorylation level of p38 was increased and Akt phosphorylation was reduced by LH treatment. Furthermore, LH treatment increased the expression levels of caspase-3, caspase-9 and Bax/Bcl-2. CONCLUSIONS: LH inhibits the proliferation and induces the apoptosis of H292 cells in a mitochondria-dependent pathway, and the specific mechanism need to be further explored.


