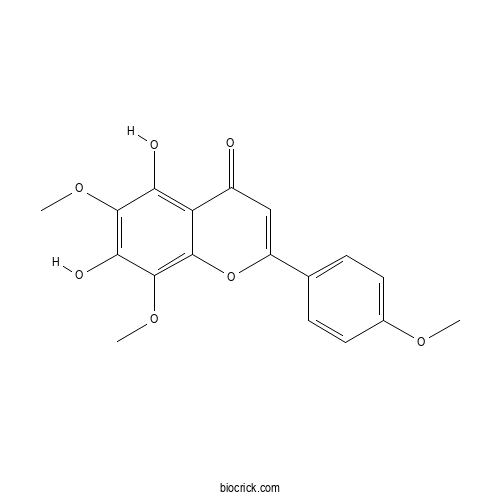
LysionotinCAS# 152743-19-6 |
- Nevadensin
Catalog No.:BCN6806
CAS No.:10176-66-6
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 152743-19-6 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 160921.0 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C18H16O7 | M.Wt | 344.32 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | 5,7-dihydroxy-6,8-dimethoxy-2-(4-methoxyphenyl)chromen-4-one | ||
| SMILES | COC1=CC=C(C=C1)C2=CC(=O)C3=C(C(=C(C(=C3O2)OC)O)OC)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | KRFBMPVGAYGGJE-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C18H16O7/c1-22-10-6-4-9(5-7-10)12-8-11(19)13-14(20)17(23-2)15(21)18(24-3)16(13)25-12/h4-8,20-21H,1-3H3 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

Lysionotin Dilution Calculator

Lysionotin Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.9043 mL | 14.5214 mL | 29.0428 mL | 58.0855 mL | 72.6069 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5809 mL | 2.9043 mL | 5.8086 mL | 11.6171 mL | 14.5214 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2904 mL | 1.4521 mL | 2.9043 mL | 5.8086 mL | 7.2607 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0581 mL | 0.2904 mL | 0.5809 mL | 1.1617 mL | 1.4521 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.029 mL | 0.1452 mL | 0.2904 mL | 0.5809 mL | 0.7261 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- 2-O-cinnamoyl-1-O-galloyl-β-D-glucose
Catalog No.:BCX0897
CAS No.:791836-69-6
- JioglutosideB
Catalog No.:BCX0896
CAS No.:124168-00-9
- Eucomicacid
Catalog No.:BCX0895
CAS No.:60449-48-1
- Malvidin-3-(6-caffeoyl-glucoside)-5-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCX0894
CAS No.:1374753-08-8
- Malvidin-3-O-(6''-O-coumaroyl)glucoside-5-O-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCX0893
CAS No.:144940-56-7
- Malvidin3-O-(6''-coumaroyl)glucoside
Catalog No.:BCX0892
CAS No.:158189-28-7
- petunidin-3-O-(6"-O-p-coumaroyl)glucoside-5-O-diglucoside
Catalog No.:BCX0891
CAS No.:1063818-55-2
- Peonidin3-O-(6-O-p-coumaroyl)glucoside
Catalog No.:BCX0890
CAS No.:305833-55-0
- peonidin-3-O-(6''-coumaroyl)glucoside-5-O-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCX0889
CAS No.:205505-30-2
- Delphinidin3-O-(6''-coumaroylglucoside)
Catalog No.:BCX0888
CAS No.:136031-08-8
- IsovitexinApigenin6-C-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCX0887
CAS No.:29702-25-8
- Lucenin-3 Luteolin-6-C-β-D-glucopyranosyl-8-C-β-D-xylopyranoside
Catalog No.:BCX0886
CAS No.:12656-83-6
- β-Gentiobiose
Catalog No.:BCX0899
CAS No.:554-91-6
- Rheochrysin
Catalog No.:BCX0900
CAS No.:29013-18-1
- Sodiumtaurodeoxylate
Catalog No.:BCX0901
CAS No.:1180-95-6
- TaurohyodeoxycholicAcid
Catalog No.:BCX0902
CAS No.:2958-04-5
- Sodium taurolithocholate
Catalog No.:BCX0903
CAS No.:6042-32-6
- 8-Methoxyquinoline-2-carboxylicacid
Catalog No.:BCX0904
CAS No.:21141-35-5
- 5-Hydroxytryptophan
Catalog No.:BCX0905
CAS No.:114-03-4
- Maltooctaose
Catalog No.:BCX0906
CAS No.:6156-84-9
- 1-Kestoheptaose
Catalog No.:BCX0907
CAS No.:62512-20-3
- Fructo-oligosaccharideDP8/GF7
Catalog No.:BCX0908
CAS No.:62512-21-4
- Isomaltotriose
Catalog No.:BCX0909
CAS No.:3371-50-4
- Sodiumnewhouttuyfonate
Catalog No.:BCX0910
CAS No.:83766-73-8
The abrogation of GRP78 sensitizes liver cancer cells to lysionotin by enhancing ER stress-mediated pro-apoptotic pathway.[Pubmed:37326827]
Cell Stress Chaperones. 2023 Jul;28(4):409-422.
Glucose-regulated protein 78 (GRP78) is frequently and highly expressed in various human malignancies and protects cancer cells against apoptosis induced by multifarious stresses, particularly endoplasmic reticulum stress (ER stress). The inhibition of GRP78 expression or activity could enhance apoptosis induced by anti-tumor drugs or compounds. Herein, we will evaluate the efficacy of Lysionotin in the treatment of human liver cancer as well as the molecular mechanism. Moreover, we will examine whether inhibition of GRP78 enhanced the sensitivity of hepatocellular carcinoma cells to Lysionotin. We found that Lysionotin significantly suppressed proliferation and induced apoptosis of liver cancer cells. TEM showed that Lysionotin-treated liver cancer cells showed an extensively distended and dilated endoplasmic reticulum lumen. Meanwhile, the levels of the ER stress hallmark GRP78 and UPR hallmarks (e.g., IRE1alpha and CHOP) were significantly increased in response to Lysionotin treatment in liver cancer cells. Moreover, the reactive oxygen species (ROS) scavenger NAC and caspase-3 inhibitor Ac-DEVD-CHO visibly attenuated the induction of GRP78 and attenuated the decrease in cell viability induced by Lysionotin. More importantly, the knockdown of GRP78 expression by siRNAs or treatment with EGCG, both induced remarkable increase in Lysionotin-induced PARP and pro-caspase-3 cleavage and JNK phosphorylation. In addition, knockdown of GRP78 expression by siRNA or suppression GRP78 activity by EGCG both significantly improved the effectiveness of Lysionotin. These data indicated that pro-survival GRP78 induction may contribute to Lysionotin resistance. The combination of EGCG and Lysionotin is suggested to represent a novel approach in cancer chemo-prevention and therapeutics.
Lysionotin exerts antinociceptive effects in various models of nociception induction.[Pubmed:37151635]
Heliyon. 2023 Apr 18;9(4):e15619.
BACKGROUND: Lysionotin, a natural flavonoid extracted from Lysionotus pauciflorus Maxim (Gesneriaceae), has several pharmacological effects including anti-bacterial, anti-hypertensive and anti-inflammatory effects. However, its analgesic effect has not been investigated. This study aimed to assess the antinociceptive activity of Lysionotin using chemically and thermally induced nociception in a mouse model. METHODS: The antinociceptive effects of various Lysionotin doses (50, 100, 150, and 200 mug/kg) were assessed in mice using the acetic acid-induced writhing test, hot plate test, and formalin-induced paw licking assay. The effects were compared to those of mice treated with acetylsalicylic acid or morphine in the presence or absence of naloxone (an opioid receptor antagonist). Capsaicin- and glutamate-induced paw licking tests were also used to evaluate the involvement of the vanilloid and glutamatergic systems, respectively. RESULTS: Lysionotin produced significant dose-dependent inhibition of nociceptive behavior in the acetic acid-induced writhing test, showing 60% inhibition at a dose of 200 mug/kg. Lysionotin also caused a significant increase in the latency period in response to the hot plate test (76.4% at 200 mug/kg), and significantly inhibited both the neurogenic and inflammatory phases in the formalin-induced paw licking test. Naloxone significantly reverses the effect of Lysionotin in both hot plate test and formalin-induced paw licking test. Moreover, Lysionotin significantly inhibited the neurogenic nociception induced by intraplantar injections of glutamate and capsaicin (57% and 67.2%, respectively at a dose of 200 mug/kg). Thus, Lysionotin exhibited peripheral and central antinociception through the modulation of vanilloid receptors, opioid receptors, and the glutamatergic system. CONCLUSION: Lysionotin possesses antinociceptive activity on adult mice that is mediated through both central and peripheral pathways.
Lysionotin Induces Ferroptosis to Suppress Development of Colorectal Cancer via Promoting Nrf2 Degradation.[Pubmed:35993016]
Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022 Aug 10;2022:1366957.
Extensive use of substances derived from natural sources has been documented in the treatment of colorectal cancer (CRC). Lysionotin (Lys) is a flavonoid present in the flowers and leaves of Gesneriaceae family plants. Despite its various pharmacological properties, which include neuroprotective, pro, antimalarial, and anticancer effects, the therapeutic advantages of Lys for CRC remain uncertain. In this present study, we demonstrated that Lys treatment successfully inhibited cell proliferation, migration, and invasion in HCT116 and SW480 CRC cells in vitro. Intriguingly, significant ferroptosis and reactive oxygen species (ROS) accumulation in CRC cells were induced by Lys treatment, whereas antagonism of ferroptosis by Liproxstatin-1 (Lip1) pretreatment retarded the anti-CRC effects of Lys. In addition, Lys reduced the amount of Nrf2 protein in CRC cells by increasing the rate at which it is degraded. Overexpression of Nrf2 rescued Lys reduced ferroptosis, suggesting the Nrf2 signaling is a crucial determinant of whether Lys induces ferroptosis in CRC cells. We also revealed that Lys suppressed tumor growth in vivo without obvious adverse effects on the main organs of mice. In conclusion, our results discovered that Lys treatment induced ferroptosis to exert antitumor effects in HCT116 and SW480 CRC cells by modulating Nrf2 signaling, providing a potential therapeutic approach for the prevention of colorectal cancer.
Lysionotin induces apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells via caspase-3 mediated mitochondrial pathway.[Pubmed:33989594]
Chem Biol Interact. 2021 Aug 1;344:109500.
As the sixth most prevalent cancer, liver cancer has been reported as the second cause of cancer-induced deaths globally. Lysionotin, a fl avonoid compound widely distributed in Lysionotus pauciflorus Maxim, has attracted considerable attention due to its multiple biological activities. The present study analyzes the anti-liver cancer effects of Lysionotin in cells and mouse models. In HepG2 and SMMC-7721 cells, Lysionotin significantly reduced the viability of cells, inhibited cell proliferation and migration, enhanced cell apoptosis, promoted the increase of intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels, decreased mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP), and alternated the content of apoptosis-related proteins. In HepG2-and SMMC-7721-xenograft tumor mouse models, Lysionotin inhibited tumor growth, reduced the expression levels of anti-apoptotic proteins and enhanced the expression levels of pro-apoptotic proteins in tumor tissues. Additionally, the pre-treatment of Ac-DEVD-CHO, an inhibitor of caspase-3, strongly restored the low cell viability, the enhanced apoptosis rate, the dissipation of MMP caused by Lysionotin exposure, as well as prevented the Lysionotin-caused enhancement on expressions of apoptosis related proteins, especially cleaved poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP), Fas Ligand (FasL), cleaved caspase-3 and Bax in both HepG2 and SMMC-7721 cells. Altogether, Lysionotin showed significant anti-liver cancer effects related to caspase-3 mediated mitochondrial apoptosis.
In vitro inhibitory effect of lysionotin on the activity of cytochrome P450 enzymes.[Pubmed:32673137]
Pharm Biol. 2020 Dec;58(1):695-700.
CONTEXT: Lysionotin, a major extraction of Lysionotus pauciflorus Maxim (Gesneriaceae), has a variety of pharmacological properties commonly used in the treatment of lung disease. A study of Lysionotin on the activity of human liver cytochrome P450 (CYP) enzymes can provide guidance on the clinical application of Lysionotin. OBJECTIVE: This study investigated the interaction between Lysionotin and CYPs. MATERIAL AND METHOD: The effects of 100 muM Lysionotin on eight human liver CYP isoforms (i.e., 1A2, 3A4, 2A6, 2E1, 2D6, 2C9, 2C19 and 2C8) were investigated in vitro using human liver microsomes (HLMs) with specific inhibitor as positive control and untreated HLMs as control. Meanwhile, the enzyme kinetic parameters were calculated. A time-dependent study was performed with a time interval of 5 min in 30 min. RESULTS: Lysionotin was found to inhibit the activity of CYP3A4, 2C19, and 2C8, with IC(50) values of 13.85, 24.95, and 30.05 muM, respectively. The inhibition of CYP3A4 was performed in a non-competitive manner with the Ki value of 6.83 muM, while the inhibition of CYP2C19 and 2C8 was performed in a competitive manner with Ki values of 12.41 and 14.51 muM. Moreover, it was found that the inhibition of CYP3A4 was time-dependent with K (I)/K (inact) value of 6.618/0.048 min/muM. Discussion and conclusions: The in vitro inhibitory effect of Lysionotin on the activity of CYP3A4, 2C19, and 2C8 indicated potential drug interactions between Lysionotin and drugs metabolised by CYP3A4, 2C19, and 2C8. Further in vivo experiments are needed to assess the potential interactions.
Determination of isosinensetin in rat plasma by UHPLC-MS/MS: Application to oral and intravenous pharmacokinetic study in healthy rats.[Pubmed:32126459]
J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2020 May 30;184:113210.
Isosinensetin is a polymethoxyflavone existing in various kinds of citrus. It has exhibited significant anti-proliferative activity and herb-drug interaction. To date, a specific determination method to quantify isosinensetin concentration in biological matrix has not been developed. In the present study, a highly specific, simple and sensitive ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (UHPLC-MS/MS) approach was developed and validated for quantification of isosinensetin in rat plasma with subsequent application to a pharmacokinetic study. Isosinensetin and Lysionotin (internal standard, IS) were extracted from rat plasma by a single step protein precipitation using acetonitrile as precipitation agent. The chromatographic separation was conducted using an Agilent C18 column with a gradient elution system (0.1 % formic acid aqueous solution and acetonitrile) within 3.5 min. An electrospray ionization (ESI) source operating in positive mode and multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) were used to monitor the transitions of m/z 373.1 --> 343.1 for isosinensetin and m/z 345.1 --> 315.1 for IS. The developed method was linear within the range of 1-1000 ng/mL and fully validated according to FDA guidelines. The accuracy values reported as relative errors were between 2.0 and 10.0 % for three quality control levels (2, 400 and 800 ng/mL) and lower limit of quantification (LLOQ). The precisions were
Activation of G protein-coupled receptor 30 by flavonoids leads to expression of acetylcholinesterase in cultured PC12 cells.[Pubmed:31034797]
Chem Biol Interact. 2019 Jun 1;306:147-151.
Flavonoids, considered as phytoestrogen mainly deriving from fruit and vegetable, are known to have beneficial effects in brain functions. The role of flavonoids in induction of a cholinergic enzyme, acetylcholinesterase (AChE), was being explored here. In cultured PC12 cells, twenty-four commonly found flavonoids were tested for its induction on AChE activity. Fourteen flavonoids showed induction, and five of them had robust effect, i.e. daidzin, alpinetin, irisflorentin, cardamonin and Lysionotin. The induction of AChE was fully blocked by pre-treatment of G15 (a selective G protein-coupled receptor 30 [GPR 30] antagonist), suggesting a direct involvement of a membrane-bound estrogen receptor, named as GPR 30, in the cultures. In addition, daidzin was further identified to induce expression of tetrameric globular form of proline-rich membrane anchor (PRiMA)-linked AChE. In parallel, application of daidzin in cultured PC12 cells significantly induced expression of neurofilaments, markers for neuronal differentiation. Taken together, flavonoids could induce the expression of AChE via GPR 30 in cultured PC12 cells, which could be a good candidate for possible treatment of the brain diseases.
Screening Five Qi-Tonifying Herbs on M2 Phenotype Macrophages.[Pubmed:30766614]
Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2019 Jan 15;2019:9549315.
Tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) with M2 phenotype play an essential role in tumor microenvironment (TME) during the progression and development of numerous cancers and associated with poor prognosis. Thus, regulation of TAMs polarization emerged as a new strategy for tumor immune therapy. According to Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) theory, herbs with Qi-tonifying character are involved in improving the defense capacity of immune system. In this study, we screened extracts and ingredients from five Qi-tonifying herbs exhibiting an inhibitory effect on M2 polarization of murine macrophages RAW264.7 induced by IL-4 and IL-13. Among these candidates, total flavonoids from Glycyrrhiza Radix et Rhizoma (TFRG) and ethanol extract of Ginseng Radix et Rhizoma significantly inhibited the expression of Arginase-1 (Arg-1) (above 90% at 100mug/mL), one of the phenotype markers of M2 macrophages. The inhibition of total saponins of Ginseng Radix et Rhizoma, ethanol extract of Cordyceps, ethanol extract of Acanthopanacis senticosi Radix et Rhizoma Seu caulis, and ethanol extract of Astragali Radix reached above 50% at 100mug/mL. The inhibition of ingredients including glabridin, isoliquiritin apioside, Lysionotin, cordycepin, astragaloside IV, and calycosin reached above 50% at 50muM. Then, we investigated the molecular mechanisms of TFRG. TFRG abolished the migration of murine breast cancer 4T1 stimulated by the conditioned medium from M2 macrophages (M2-CM). In addition to Arg-1, TFRG also antagonized the IL-4/13-mediated mRNA upregulation of the M2 markers including found in inflammatory zone 1 (FIZZ1), chitinase-3-like protein 3 (YM1), and mannose receptor (CD206) and upregulated the expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), one of the M1 markers. The further exploration showed that TFRG decreased the phosphorylation of STAT6 and increased the expression of miR-155. Our study provides a series of potential immune regulating natural products from five Qi-tonifying herbs on M2 phenotype. For instance, TFRG suppressed M2 polarization of macrophages partly by inactivating STAT6 pathway and enhanced the level of miR-155 to regulate the expressions of M1 and M2 markers.
Lysionotin attenuates Staphylococcus aureus pathogenicity by inhibiting alpha-toxin expression.[Pubmed:28710557]
Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2017 Sep;101(17):6697-6703.
alpha-Toxin, one of the best known pore-forming proteins produced by Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus), is a critical virulence factor in multiple infections. The necessity of alpha-toxin for S. aureus pathogenicity suggests that this toxin is an important target for the development of a potential treatment strategy. In this study, we showed that Lysionotin, a natural compound, can inhibit the hemolytic activity of culture supernatants by S. aureus by reducing alpha-toxin expression. Using real-time PCR analysis, we showed that transcription of hla (the gene encoding alpha-toxin) and agr (the locus regulating hla) was significantly inhibited by Lysionotin. Lactate dehydrogenase and live/dead assays indicated that Lysionotin effectively protected human alveolar epithelial cells against S. aureus, and in vivo studies also demonstrated that Lysionotin can protect mice from pneumonia caused by S. aureus. These findings suggest that Lysionotin is an efficient inhibitor of alpha-toxin expression and shows significant protection against S. aureus in vitro and in vivo. This study supports a potential strategy for the treatment of S. aureus infection by inhibiting the expression of virulence factors and indicates that Lysionotin may be a potential treatment for S. aureus pneumonia.
Pharmacokinetics of eupalinolide A, eupalinolide B and hyperoside from Eupatorium lindleyanum in rats by LC/MS/MS.[Pubmed:26011510]
J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2015 Jul 15;995-996:1-7.
A simple, selective, and sensitive LC/MS/MS method was developed and validated for simultaneous determination of eupalinolide A, eupalinolide B, and hyperoside in rat plasma. Plasma samples were processed by protein precipitation with acetonitrile. The three analytes, together with internal standard (IS, Lysionotin), were separated on a Venusil MP-C18 column (50mmx2.1mm, 3mum) using a mobile phase of methanol and 10mM ammonium acetate (45:55, v/v) with isocratic elution. Mass spectrometric detection was performed by multiple-reaction monitoring mode via electrospray ionization source. Linear calibration curves were obtained for the following concentration range: 1.28-640ng/mL for EA; 1.98-990ng/mL for EB; and 2.00-1000ng/mL for HYP. The intra- and inter-day precision was less than 10.25%, and the accuracy was between 89.16% and 110.63%. The extraction recovery of the analytes and IS from rat plasma was above 88.75%. The validated method has been successfully applied to pharmacokinetic studies of the three analytes following intragastric administration of Eupatorium lindleyanum extract at a single dose of 100, 250, and 625mg/kg to Sprague-Dawley rats, respectively. The pharmacokinetic results may help to better understand the pharmacological actions of the herb E. lindleyanum.
Simultaneous Determination of Seven Components from Hawthorn Leaves Flavonoids in Rat Plasma by LC-MS/MS.[Pubmed:25368407]
J Chromatogr Sci. 2015 Jul;53(6):909-14.
In this study, a simple, sensitive, and throughout liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) method was developed for the simultaneous determination of seven flavonoid compounds, namely, rutin, vitexin-4''-O-glucoside, vitexin-2''-O-rhamnoside, hyperoside, vitexin, shanyenoside A and quercetin in rat plasma after intravenous administration of hawthorn leaves flavonoids (HLF) using Lysionotin as an internal standard (IS). The target compounds were extracted using protein precipitation by methanol. The detection was achieved by LC-MS/MS in multiple reaction monitoring mode. The optimal mass transition ion pairs (m/z) for quantitation were 609.3/300.1 for rutin, 593.1/413.2 for vitexin-4''-O-glucoside, 577.3/413.2 for vitexin-2''-O-rhamnoside, 463.2/300.1 for hyperoside, 431.2/311.2 for vitexin, 407.2/245.1 for shanyenoside A, 301.1/151.1 for quercetin and 343.2/313.1 for the IS, respectively. The method was fully validated with respect to specificity, sensitivity, linearity, precision, accuracy, recovery and stability experiments. A sufficiently sensitive and selective LC-MS/MS method was first developed in this study to simultaneously evaluate the pharmacokinetics of seven flavonoids in rat plasma following intravenous administration of HLF.
Simultaneous determination and pharmacokinetic study of three isoflavones from Trifolium pratense extract in rat plasma by LC-MS/MS.[Pubmed:24898405]
Biomed Chromatogr. 2015 Feb;29(2):210-9.
A highly selective and sensitive liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry has been developed and validated for simultaneous determination of three isoflavones - ononin, formononetin and biochanin A - in rat plasma using Lysionotin as internal standard (IS). The plasma samples were pretreated and extracted by liquid-liquid extraction. Chromatographic separation was accomplished on a C18 column with the column temperature of 30 degrees C and a mobile phase of methanol-0.1% formic acid (75:25, v/v). The detection was accomplished by multiple-reaction monitoring scanning with positive/negative ion-switching electrospray ionization mode. The optimized mass transition ion pairs (m/z) for quantitation were 431.3/269.1 for ononin, 267.1/252.2 for formononetin, 283.2/268.2 for biochanin A and 343.2/313.3 for IS. The total run time was 8.0 min. Full validation of the assay was implemented, including selectivity, sensitivity, linearity, precision, accuracy, recovery, matrix effect and stability. This is the first report on simultaneous determination of the three major isoflavones in rat plasma after intragastric administration of Trifolium pratense extract. The results provided a significant basis for the clinical application of this herb Trifolium pratense.
Detection of interaction between lysionotin and bovine serum albumin using spectroscopic techniques combined with molecular modeling.[Pubmed:24398555]
Mol Biol Rep. 2014 Mar;41(3):1693-702.
A combination of fluorescence, UV-Vis absorption, circular dichroism (CD), Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) and molecular modeling approaches were employed to determine the interaction between Lysionotin and bovine serum albumin (BSA) at physiological pH. The fluorescence titration suggested that the fluorescence quenching of BSA by Lysionotin was a static procedure. The binding constant at 298 K was in the order of 10(5) L mol(-1), indicating that a high affinity existed between Lysionotin and BSA. The thermodynamic parameters obtained at different temperatures (292, 298, 304 and 310 K) showed that the binding process was primarily driven by hydrogen bond and van der Waals forces, as the values of the enthalpy change (DeltaH degrees ) and entropy change (DeltaS degrees ) were found to be -40.81 +/- 0.08 kJ mol(-1) and -35.93 +/- 0.27 J mol(-1) K(-1), respectively. The surface hydrophobicity of BSA increased upon interaction with Lysionotin. The site markers competitive experiments revealed that the binding site of Lysionotin was in the sub-domain IIA (site I) of BSA. Furthermore, the molecular docking results corroborated the binding site and clarified the specific binding mode. The results of UV-Vis absorption, CD and FT-IR spectra demonstrated that the secondary structure of BSA was altered in the presence of Lysionotin.
Development of an LC-MS/MS method for quantification of kadsurenone in rat plasma and its application to a pharmacokinetic study.[Pubmed:23843078]
Biomed Chromatogr. 2013 Dec;27(12):1754-8.
A sensitive and rapid LC-MS/MS method was developed and validated for the determination of kadsurenone in rat plasma using Lysionotin as the internal standard (IS). The analytes were extracted from rat plasma with acetonitrile and separated on a SB-C18 column (50 x 2.1 mm, i.d.; 1.8 microm) at 30 degrees C. Elution was achieved with a mobile phase consisting of methanol-water-formic acid (65:35:0.1, v/v/v) at a flow rate of 0.30 mL/min. Detection and quantification for analytes were performed by mass spectrometry in the multiple reaction monitoring mode with positive electrospray ionization m/z at 357.1 --> 178.1 for kadsurenone, and m/z 345.1 --> 315.1 for IS. Calibration curves were linear over a concentration range of 4.88-1464 ng/mL with a lower limit of quantification of 4.88 ng/mL. The intra- and inter-day accuracies and precisions were <8.9%. The LC-MS/MS assay was successfully applied for oral pharmacokinetic evaluation of kadsurenone using the rat as an animal model.


