5-HydroxytryptophanCAS# 114-03-4 |
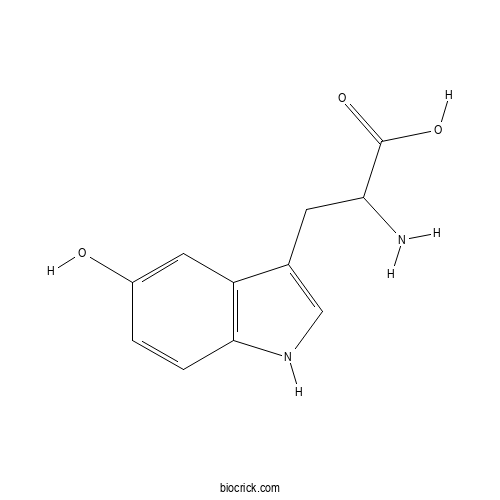
- L-5-Hydroxytryptophan
Catalog No.:BCC8106
CAS No.:4350-09-8
- DL-5-Hydroxytryptophan
Catalog No.:BCN1232
CAS No.:56-69-9
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 114-03-4 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 144.0 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C11H12N2O3 | M.Wt | 220.22 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | 2-amino-3-(5-hydroxy-1H-indol-3-yl)propanoic acid | ||
| SMILES | C1=CC2=C(C=C1O)C(=CN2)CC(C(=O)O)N | ||
| Standard InChIKey | LDCYZAJDBXYCGN-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C11H12N2O3/c12-9(11(15)16)3-6-5-13-10-2-1-7(14)4-8(6)10/h1-2,4-5,9,13-14H,3,12H2,(H,15,16) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

5-Hydroxytryptophan Dilution Calculator

5-Hydroxytryptophan Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 4.5409 mL | 22.7046 mL | 45.4091 mL | 90.8183 mL | 113.5228 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.9082 mL | 4.5409 mL | 9.0818 mL | 18.1637 mL | 22.7046 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.4541 mL | 2.2705 mL | 4.5409 mL | 9.0818 mL | 11.3523 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0908 mL | 0.4541 mL | 0.9082 mL | 1.8164 mL | 2.2705 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0454 mL | 0.227 mL | 0.4541 mL | 0.9082 mL | 1.1352 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- 8-Methoxyquinoline-2-carboxylicacid
Catalog No.:BCX0904
CAS No.:21141-35-5
- Sodium taurolithocholate
Catalog No.:BCX0903
CAS No.:6042-32-6
- TaurohyodeoxycholicAcid
Catalog No.:BCX0902
CAS No.:2958-04-5
- Sodiumtaurodeoxylate
Catalog No.:BCX0901
CAS No.:1180-95-6
- Rheochrysin
Catalog No.:BCX0900
CAS No.:29013-18-1
- β-Gentiobiose
Catalog No.:BCX0899
CAS No.:554-91-6
- Lysionotin
Catalog No.:BCX0898
CAS No.:152743-19-6
- 2-O-cinnamoyl-1-O-galloyl-β-D-glucose
Catalog No.:BCX0897
CAS No.:791836-69-6
- JioglutosideB
Catalog No.:BCX0896
CAS No.:124168-00-9
- Eucomicacid
Catalog No.:BCX0895
CAS No.:60449-48-1
- Malvidin-3-(6-caffeoyl-glucoside)-5-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCX0894
CAS No.:1374753-08-8
- Malvidin-3-O-(6''-O-coumaroyl)glucoside-5-O-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCX0893
CAS No.:144940-56-7
- Maltooctaose
Catalog No.:BCX0906
CAS No.:6156-84-9
- 1-Kestoheptaose
Catalog No.:BCX0907
CAS No.:62512-20-3
- Fructo-oligosaccharideDP8/GF7
Catalog No.:BCX0908
CAS No.:62512-21-4
- Isomaltotriose
Catalog No.:BCX0909
CAS No.:3371-50-4
- Sodiumnewhouttuyfonate
Catalog No.:BCX0910
CAS No.:83766-73-8
- Dehydrocostuslactone
Catalog No.:BCX0911
CAS No.:74299-48-2
- Graniline
Catalog No.:BCX0912
CAS No.:40737-97-1
- Oxysophoridine
Catalog No.:BCX0913
CAS No.:54809-74-4
- Climbazole
Catalog No.:BCX0914
CAS No.:38083-17-9
- Chlorine6
Catalog No.:BCX0915
CAS No.:19660-77-6
- PALATINOSE
Catalog No.:BCX0916
CAS No.:13718-94-0
- 8-Methoxyquinoline-2-carbaldehyde
Catalog No.:BCX0917
CAS No.:103854-64-4
A novel mechanism of idiopathic orthostatic hypotension and hypocatecholaminemia due to autoimmunity against aromatic l-Amino acid decarboxylase.[Pubmed:38677008]
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2024 Apr 16;714:149940.
Orthostatic hypotension (OH) is a common condition. Many potential etiologies of OH have been identified, but in clinical practice the underlying cause of OH is often unknown. In the present study, we identified a novel and extraordinary etiology of OH. We describe a first case of acquired severe OH with syncope, and the female patient had extremely low levels of catecholamines and serotonin in plasma, urine and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). Her clinical and biochemical evidence showed a deficiency of the enzyme aromatic l-amino acid decarboxylase (AADC), which converts l-DOPA to dopamine, and 5-Hydroxytryptophan to serotonin, respectively. The consequence of pharmacologic stimulation of catecholaminergic nerves and radionuclide examination revealed her catecholaminergic nerves denervation. Moreover, we found that the patient's serum showed presence of autoantibodies against AADC, and that isolated peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) from the patient showed cytokine-induced toxicity against AADC. These observations suggest that her autoimmunity against AADC is highly likely to cause toxicity to adrenal medulla and catecholaminergic nerves which contain AADC, resulting in hypocatecholaminemia and severe OH. Administration of vitamin B6, an essential cofactor of AADC, enhanced her residual AADC activity and drastically improved her symptoms. Our data thus provide a new insight into pathogenesis and pathophysiology of OH.
Plasma and milk metabolomics profiles in dairy cows with subclinical and clinical ketosis.[Pubmed:38608939]
J Dairy Sci. 2024 Apr 10:S0022-0302(24)00738-0.
Ketosis, a commonly observed energy metabolism disorder in dairy cows during the peripartal period, is distinguished by increased concentrations of beta-hydroxybutyrate (BHB) in blood. This condition has a negative impact on milk production and quality, causing financial losses. An untargeted metabolomics approach was performed on plasma samples from cows between 5 and 7 DIM diagnosed as controls (CON, BHB <1.2 mM, n = 30), subclinically ketotic (SCK, 1.2 < BHB <3.0 mM, n = 30), or clinically ketotic (CK, BHB >3.0 mM, n = 30). Cows were selected from a commercial farm of 214 Holstein cows (average 305-d yield in the previous lactation of 35.42 +/- 7.23 kg/d; parity, 2.41 +/- 1.12; body condition score, 3.1 +/- 0.45). All plasma and milk samples (n = 90) were subjected to Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS)-based metabolomic analysis. Statistical analyses was performed using the Graph Pad Prism 8.0, MetaboAnalyst 4.0 and R packages (version 4.1.3). Compared with the CON group, both SCK and CK groups had greater milk fat, freezing point, and fat-to-protein ratio and lower milk protein, lactose, solids-nonfat, and milk density. Within 21 d after calving, compared with CON, the SCK group experienced a reduction of 2.65 kg/d in milk yield, while the CK group experienced a decrease of 7.7 kg/d. Untargeted metabolomics analysis facilitated the annotation of a total of 5,259 and 8,423 metabolites in plasma and milk. Differentially affected metabolites were screened in CON vs. SCK, CON vs. CK, and SCK vs. CK (unpaired t-test, False discovery rate <0.05; and absolute value of log(2)-fold change >1.5). A total of 1,544 and 1,888 differentially affected metabolites were detected in plasma and milk. In plasma, glycerophospholipid metabolism, pyrimidine metabolism, tryptophan metabolism, sphingolipid metabolism, amino sugar and nucleotide sugar metabolism, phenylalanine metabolism, steroid hormone biosynthesis were identified as significant pathways. Weighted gene co-expression network analysis (WGCNA) indicated that tryptophan metabolism is a key pathway associated with the occurrence and development of ketosis. Increases in 5-Hydroxytryptophan and decreases in kynurenine and 3-indoleacetic acid in SCK and CK were suggestive of an impact at the gut level. The decrease of most glycerophospholipids indicated that ketosis is associated with disordered lipid metabolism. For milk, pyrimidine metabolism, purine metabolism, pantothenate and CoA biosynthesis, amino sugar and nucleotide sugar metabolism, nicotinate and nicotinamide metabolism, sphingolipid metabolism, fatty acid degradation were identified as significant pathways. The WGCNA indicated that purine and pyrimidine metabolism in plasma was highly correlated with milk yield during the peripartal period. Alterations in purine and pyrimidine metabolism characterized ketosis, with lower levels of these metabolites in both milk and blood underscoring reduced efficiency in nitrogen metabolism. Our results may help to establish a foundation for future research investigating mechanisms responsible for the occurrence and development of ketosis in peripartal cows.
Sepiapterin Reductase Deficiency Misdiagnosed as Neurological Sequelae of Meningitis.[Pubmed:38585541]
Mol Syndromol. 2024 Mar;15(2):130-135.
INTRODUCTION: Sepiapterin reductase deficiency (SRD) is an exceedingly rare neurotransmitter disease caused by an enzyme error involved in the synthesis of tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4). It has been described in nearly 60 cases so far. The clinical manifestations include motor and speech delay, axial hypotonia, dystonia, weakness, oculogyric crises, diurnal fluctuation, and improvement of symptoms during sleep. Molecular genetic analysis can demonstrate pathogenic mutations in the SPR gene, allowing for a definitive diagnosis. Levodopa/carbidopa and 5-Hydroxytryptophan are used for treatment. CASE PRESENTATION: We present a 19-year-old male patient who was evaluated for dysarthria, axial hypotonia, limb dystonia, and movement disorder. The parents described the current patient's history with febrile seizures since 9 months of age, as well as speech and neuromotor developmental retardation, which indicated that the disease began in infancy. The basal metabolic work-up was normal except for hyperprolactinemia. The definitive diagnosis of SRD was confirmed by whole exome sequencing (WES) analysis, which revealed a homozygous pathogenic mutation c.655C>T (p.Arg219*) (rs779204655) in the SPR gene. After treatment, we noted significant improvements in dystonia, axial hypotonia, and dysarthria. CONCLUSION: WES analysis offers a more expeditious and dependable method for diagnosing difficult cases exhibiting neurodevelopmental problems and thus renders the possibilities of early management.
Monoaminergic Systems in Flight-Induced Potentiation of Phonotactic Behavior in Female Crickets Gryllus bimaculatus.[Pubmed:38535378]
Insects. 2024 Mar 9;15(3):183.
We have recently shown that experience of flight remarkably enhanced subsequent terrestrial phonotaxis in females in response to the male calling song. Here, we elucidated the possible roles of octopamine and serotonin in the enhancing effect of flying on phonotactic behavior. Octopamine is known to be released into the hemolymph during flight in insects; however, the octopamine receptor antagonist epinastine did not abolish the effects of flight in our study. On the contrary, the drug significantly potentiated the influence of flying on phonotactic behavior. The octopamine receptor agonist chlordimeform, at a concentration of 2 mM, which was previously found to activate aggression in crickets, dramatically reduced the phonotactic response. However, at a 10-times-lower dose, chlordimeform produced a light but significant decrease in the time that females took to reach the source of the calling song. A similar effect was produced by octopamine itself, which hardly passes the blood-brain barrier in insects. The effect of flight was completely abolished in female crickets treated with alpha-methyl tryptophan (AMTP). AMPT suppresses the synthesis of serotonin, decreasing its content in the nervous systems of insects, including crickets. An activation of the serotonin synthesis with 5-Hydroxytryptophan mimicked the effect of flight by increasing the number of visits to and the time spent in the zone near the source of the calling song. The 5-HT content in the third thoracic ganglion was significantly higher in flyers compared to the control group. In contrast, no changes in the octopamine level were observed in the third thoracic ganglion, which is known to play a crucial role in decision-making involved in intraspecific interactions. Therefore, the results suggest that although octopamine is known to be released into the hemolymph during flight, it is likely to inhibit rather than activate the central mechanisms related to phonotaxis. The weak facilitating effect of a low dose of chlordimeform can be attributed to the activation of peripheral octopaminergic receptors. Our results suggest that the serotoninergic system may contribute to the facilitation of female phonotactic behavior by flying. We suggest that both flying and serotonin enhance sexual motivation in females and, by these means, impact their behavioral response to the male calling song.
5-hydroxytryphophan mitigates ergot alkaloid-induced suppression of serotonin and feed intake in cattle.[Pubmed:38520304]
J Anim Sci. 2024 Jan 3;102:skae083.
The impact of ergot toxicosis on livestock industries is detrimental and treatments are needed in many countries. The objective of this study was to evaluate the effects of acute exposure to ergot alkaloids and 5-Hydroxytryptophan (5-HTP) supplementation on feed intake, serotonin metabolism, and blood metabolites in cattle. Eight Holstein steers (538 +/- 18 kg) fitted with ruminal cannulas were used in a replicated 4 x 4 Latin Square design experiment with a 2 x 2 factorial treatment structure. The treatments were the combination of 0 (E-) or 15 microg ergovaline/kg BW (E+) and 0 (5HTP-) or 0.5 mg of 5-hydroxy-l-tryptophan/kg BW (5HTP+) administered daily for 6 d. Toxic endophyte-infected tall fescue seed was used to supply the daily dose of ergovaline. Endophyte-free seed was used to equalize seed intake between treatments. Ground seed was placed into the rumen immediately before feeding. The 5-HTP was dissolved in water and infused into the abomasum via the reticulo-omasal orifice. Blood was collected from a jugular vein catheter at 0, 1, 2, 4, 8, and 24 h after treatment administration. Ergovaline without 5-HTP (E+/5HTP-) decreased dry matter intake (DMI) in comparison to steers without ergovaline and 5-HTP (E-/5HTP-). However, 5-HTP infusion in association with ergovaline (E+/5HTP+) normalized the DMI. Although E + did not affect (P > 0.05) the area under the curve (AUC) of serum 5-HTP, 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid, tryptophan, and kynurenine, serum and plasma serotonin concentrations were decreased (P < 0.05). The infusion of 5-HTP increased (P < 0.05) the AUC of serum 5-HTP, serum and plasma serotonin, and serum 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid. In conclusion, acute exposure to ergot alkaloids reduced DMI and circulating serotonin in cattle but 5-HTP administration showed potential to normalize both circulating serotonin and feed intake.
First trimester maternal tryptophan metabolism and embryonic and fetal growth: the Rotterdam Periconceptional Cohort (Predict Study).[Pubmed:38498837]
Hum Reprod. 2024 Mar 18:deae046.
STUDY QUESTION: What is the association between first trimester maternal tryptophan (TRP) metabolites and embryonic and fetal growth? SUMMARY ANSWER: Higher 5-Hydroxytryptophan (5-HTP) concentrations are associated with reduced embryonic growth and fetal growth and with an increased risk of small-for-gestational age (SGA), while higher kynurenine (KYN) concentrations are associated with a reduced risk of SGA. WHAT IS KNOWN ALREADY: The maternal TRP metabolism is involved in many critical processes for embryonic and fetal growth, including immune modulation and regulation of vascular tone. Disturbances in TRP metabolism are associated with adverse maternal and fetal outcomes. STUDY DESIGN, SIZE, DURATION: This study was embedded within the Rotterdam Periconceptional Cohort (Predict Study), an ongoing prospective observational cohort conducted at a tertiary hospital from November 2010 onwards. PARTICIPANTS/MATERIALS, SETTING, METHODS: A total of 1115 women were included before 11 weeks of gestation between November 2010 and December 2020. Maternal serum samples were collected between 7 and 11 weeks of gestation, and TRP metabolites (TRP, KYN, 5-HTP, 5-hydroxytryptamine, and 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid) were determined using a validated liquid chromatography (tandem) mass spectrometry method. Serial 3D ultrasound scans were performed at 7, 9, and 11 weeks of gestation to accurately assess features of embryonic growth, including crown-rump length (CRL) and embryonic volume (EV) offline using virtual reality systems. Fetal growth parameters were retrieved from medical records and standardized according to Dutch reference curves. Mixed models were used to assess associations between maternal TRP metabolites and CRL and EV trajectories. Linear and logistic regression models were utilized to investigate associations with estimated fetal weight (EFW) and birthweight, and with SGA, respectively. All analyses were adjusted for potential confounders. MAIN RESULTS AND THE ROLE OF CHANCE: Maternal 5-HTP concentrations and the maternal 5-HTP/TRP ratio were inversely associated with embryonic growth (5-HTP, radicalCRL: beta = -0.015, 95% CI = -0.028 to -0.001; 5-HTP 3 radicalEV: beta = -0.009, 95% CI = -0.016 to -0.003). An increased maternal 5-HTP/TRP ratio was also associated with lower EFW and birthweight, and with an increased risk of SGA (odds ratio (OR) = 1.006, 95% CI = 1.00-1.013). In contrast, higher maternal KYN concentrations were associated with a reduced risk of SGA in the unadjusted models (OR = 0.548, 95% CI = 0.320-0.921). LIMITATIONS, REASONS FOR CAUTION: Residual confounding cannot be ruled out because of the observational design of this study. Moreover, this study was conducted in a single tertiary hospital, which assures high internal validity but may limit external validity. WIDER IMPLICATIONS OF THE FINDINGS: The novel finding that maternal 5-HTP concentrations are associated with a smaller embryo and fetus implies that disturbances of the maternal serotonin pathway in the first trimester of pregnancy are potentially involved in the pathophysiology of fetal growth restriction. The association between higher maternal KYN concentrations and a reduced risk of SGA substantiate the evidence that the KYN pathway has an important role in fetal growth. More research is needed to delve deeper into the potential role of the maternal TRP metabolism during the periconception period and pregnancy outcome for mother and offspring. STUDY FUNDING/COMPETING INTEREST(S): This study was funded by the Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology and the Department of Clinical Chemistry of the Erasmus MC, University Medical Center, Rotterdam, the Netherlands. The authors have no competing interests to disclose. TRIAL REGISTRATION NUMBER: N/A.
Tryptophan-kynurenine metabolic pathway and daytime dysfunction in women with HIV.[Pubmed:38472641]
J Neurovirol. 2024 Mar 12.
Sleep disturbances are prevalent in women with HIV (WWH). Tryptophan-kynurenine (T-K) pathway metabolites are associated with alterations in actigraphy derived sleep measures in WWH, although may not always correlate with functional impairment. We investigated the relationship between T-K pathway metabolites and self-reported daytime dysfunction in WWH and women without HIV (WWoH). 141 WWH on stable antiretroviral therapy and 140 demographically similar WWoH enrolled in the IDOze Study had targeted plasma T-K metabolites measured using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. We utilized the daytime dysfunction component of the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI) to assess functional impairment across HIV-serostatus. Lower levels of 5-Hydroxytryptophan and serotonin were associated with greater daytime dysfunction in all women. In WWH, daytime dysfunction was associated with increased kynurenic acid (R = 0.26, p < 0.05), and kynurenic acid-tryptophan (KA-T) ratio (R = 0.28, p < 0.01). WWH with daytime dysfunction had a 0.7 log fold increase in kynurenic acid compared to WWH without daytime dysfunction. Kynurenic acid levels and the KA-T ratio were associated with daytime dysfunction in WWH but not in WWoH. Longitudinal studies are needed to establish a causal relationship and directionality between T-K metabolic changes and sleep impairment in WWH.
5-Hydroxytryptophan acts as a gap junction inhibitor to limit the spread of chemotherapy-induced cardiomyocyte injury and mitochondrial dysfunction.[Pubmed:38462693]
Aging (Albany NY). 2024 Mar 10;16(5):4889-4903.
Anthracycline chemotherapeutics like doxorubicin (DOX) are widely used against various cancers but are accompanied by severe cardiotoxic effects that can lead to heart failure. Through whole transcriptome sequencing and pathological tissue analysis in a murine model, our study has revealed that DOX impairs collagen expression in the early phase, causing extracellular matrix anomalies that weaken the mechanical integrity of the heart. This results in ventricular wall thinning and dilation, exacerbating cardiac dysfunction. In this work, we have identified 5-Hydroxytryptophan (5-HTP) as a potent inhibitor of gap junction communication. This inhibition is key to limiting the spread of DOX-induced cardiotoxicity. Treatment with 5-HTP effectively countered the adverse effects of DOX on the heart, preserving ventricular structure and ejection fraction. Moreover, 5-HTP enhanced mitochondrial respiratory function, as shown by the O2k mitochondrial function assay, by improving mitochondrial complex activity and ATP production. Importantly, the cardioprotective benefits of 5-HTP did not interfere with DOX's ability to combat cancer. These findings shed light on the cardiotoxic mechanisms of DOX and suggest that 5-HTP could be a viable strategy to prevent heart damage during chemotherapy, offering a foundation for future clinical development. This research opens the door for 5-HTP to be considered a dual-purpose agent that can protect the heart without compromising the oncological efficacy of anthracycline chemotherapy.
Safety evaluation of 5-hydroxytryptophan and S-(2-aminoethyl)isothiouronium bromide hydrobromide on rodent lungs.[Pubmed:38454586]
Indian J Pharmacol. 2024 Jan 1;56(1):28-36.
OBJECTIVES: During the past few decades, various compounds have been researched for their potential as radioprotectants, and many of them were found to be safe and effective in several preclinical models. However, many of these compounds were found to have serious adverse effects when evaluated in clinical settings, thereby making them unsuitable for human applications. 5-Hydroxytryptophan (5-HTP) and S-(2-aminoethyl) isothiouronium bromide hydrobromide (AET) act in a synergistic fashion to promote radioprotection. The present study primarily emphasizes the safety of fixed dose of 5-HTP + AET in the lungs of C57BL/6 mice, a well-known model used in drug safety studies. MATERIALS AND METHODS: Post-administration of the combination of HTP+AET at specific time points, blood and bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) were collected for the analysis of inflammatory and oxidative stress markers of the lungs. Thereafter, the mice were sacrificed and the lungs were dissected out, weighed, and fixed in formalin for histopathological studies. RESULTS: The inflammatory biomarkers: tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-10 and oxidative stress biomarkers: 8-isoprostane and 8-hydroxy-2'-deoxyguanosine were found to have normal levels in blood and BALF in both control and treatment groups, which was further supported by normal histological findings. In addition, other endpoints such as food and water intake were found to be within normal limits. CONCLUSION: The present safety study reflects that the combination has no adverse effects on the lungs of the experimental mouse. Further, evaluation in higher mammals including nonhuman primates is essential prior to validation of the safety of the combination in humans.
Directed evolution of the fluorescent protein CGP with in situ biosynthesized noncanonical amino acids.[Pubmed:38446072]
Appl Environ Microbiol. 2024 Apr 17;90(4):e0186323.
The incorporation of noncanonical amino acids (ncAAs) into proteins can enhance their function beyond the abilities of canonical amino acids and even generate new functions. However, the ncAAs used for such research are usually chemically synthesized, which is expensive and hinders their application on large industrial scales. We believe that the biosynthesis of ncAAs using metabolic engineering and their employment in situ in target protein engineering with genetic code expansion could overcome these limitations. As a proof of principle, we biosynthesized four ncAAs, O-L-methyltyrosine, 3,4-dihydroxy-L-phenylalanine, 5-Hydroxytryptophan, and 5-chloro-L-tryptophan using metabolic engineering and directly evolved the fluorescent consensus green protein (CGP) by combination with nine other exogenous ncAAs in Escherichia coli. After screening a TAG scanning library expressing 13 ncAAs, several variants with enhanced fluorescence and stability were identified. The variants CGP(V3pMeoF/K190pMeoF) and CGP(G20pMeoF/K190pMeoF) expressed with biosynthetic O-L-methyltyrosine showed an approximately 1.4-fold improvement in fluorescence compared to the original level, and a 2.5-fold improvement in residual fluorescence after heat treatment. Our results demonstrated the feasibility of integrating metabolic engineering, genetic code expansion, and directed evolution in engineered cells to employ biosynthetic ncAAs in protein engineering. These results could further promote the application of ncAAs in protein engineering and enzyme evolution. IMPORTANCE: Noncanonical amino acids (ncAAs) have shown great potential in protein engineering and enzyme evolution through genetic code expansion. However, in most cases, ncAAs must be provided exogenously during protein expression, which hinders their application, especially when they are expensive or have poor cell membrane penetration. Engineering cells with artificial metabolic pathways to biosynthesize ncAAs and employing them in situ for protein engineering and enzyme evolution could facilitate their application and reduce costs. Here, we attempted to evolve the fluorescent consensus green protein (CGP) with biosynthesized ncAAs. Our results demonstrated the feasibility of using biosynthesized ncAAs in protein engineering, which could further stimulate the application of ncAAs in bioengineering and biomedicine.
Enhancing thermostability of tryptophan hydroxylase via protein engineering and its application in 5-hydroxytryptophan production.[Pubmed:38437933]
Int J Biol Macromol. 2024 Apr;264(Pt 1):130609.
5-Hydroxytryptophan (5-HTP), as the precursor of serotonin and melatonin in animals, can regulate mood, sleep, and behavior, which is widely used in pharmaceutical and health products industry. The enzymatic production of 5-Hydroxytryptophan (5-HTP) from L-tryptophan (L-Trp) using tryptophan hydroxylase (TPH) show huge potential in application due to its advantages, such as mild reaction conditions, avoidance of protection/deprotection processes, excellent regioselectivity and considerable catalytic efficiency, compared with chemical synthesis and natural extraction. However, the low thermostability of TPH restricted its hydroxylation efficiency toward L-Trp. In this study, we aimed to improve the thermostability of TPH via semi-rational design guided by (folding free energy) DeltaDeltaG fold calculation. After two rounds of evolution, two beneficial mutants M1 (S422V) and M30 (V275L/I412K) were obtained. Thermostability evaluation showed that M1 and M30 possessed 5.66-fold and 6.32-fold half-lives (t(1/2)) at 37 degrees C, and 4.2 degrees C and 6.0 degrees C higher melting temperature (T(m)) than the WT, respectively. The mechanism behind thermostability improvement was elucidated with molecular dynamics simulation. Furthermore, biotransformation of 5-HTP from L-Trp was performed, M1 and M30 displayed 1.80-fold and 2.30-fold than that of WT, respectively. This work provides important insights into the thermostability enhancement of TPH and generate key mutants that could be robust candidates for practical production of 5-HTP.
Genotype characterization of tetrahydrobiopterin deficiency in two Tibetan children.[Pubmed:38434370]
Heliyon. 2024 Feb 24;10(5):e27050.
BACKGROUND: Tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4) deficiency is a rare cause of hyperphenylalaninemia (HPA). The incidence of this condition varies based on region and ethnicity. In the early stages, patients typically do not exhibit any symptoms, and HPA is identified only through newborn screening for diseases. It is important to distinguish BH4 deficiency from phenylketonuria (PKU, MIM # 261600). Timely diagnosis and treatment of BH4 deficiency are crucial for the prognosis of patients. CASE PRESENTATION: We present two rare cases of Chinese Tibetan children with BH4D, diagnosed through biochemical tests and genetic sequencing. Case 1 is a male infant, 2 months old, with a newborn screening (NBS) Phe level of 1212 mumol/L (reference range <120 mumol). The biopterin(B) level was 0.19 mmol/molCr (reference range: 0.42-1.92 mmol/molCr), with a B% of 5.67% (reference range: 19.8%-50.3%). Gene sequencing revealed a homozygous missense variant [NM_000317.3 (PTS): c.259C > T (p.Pro87Ser), rs104894276, ClinVar variation ID: 480]. The patient was treated with a Phe-reduced diet and oral sapropterin, madopar and is currently 3 years and 4 months old, showing mild global developmental delay. Case 2 is a 40-day-old female infant with a Phe level of 2442.11 mumol/L and dihydropteridine reductase (DHPR) activity of 0.84 nmol/(min. 5 mm disc) (reference range: 1.02-3.35 nmol/min.5 mm disc. Gene sequencing revealed a compound heterozygous genotype [NM_000320.3(QDPR): c.68G > A (p.Gly23Asp), rs104893863, ClinVar Variation ID: 490] and [NM_000320.3(QDPR) c.419C > A (p. Ala140Asp), ClinVar ID: 2444501]. The patient was treated with a Phe-reduced diet and oral madopar, 5-Hydroxytryptophan. At the age of 1 year, she exhibited severe global developmental delay with seizures. CONCLUSION: We identified and treated two cases of BH4D in Tibetan populations in China, marking the first confirmed instances. Our report emphasizes the significance of conducting differential diagnosis tests for BH4D.
The kynurenine and serotonin pathway, neopterin and biopterin in depressed children and adolescents: an impact of omega-3 fatty acids, and association with markers related to depressive disorder. A randomized, blinded, prospective study.[Pubmed:38414497]
Front Psychiatry. 2024 Feb 13;15:1347178.
Depressive disorder is a severe mental condition. In addition to genetic factors, immunological-inflammatory factors, oxidative stress, and disturbances in neurotransmitter metabolism, kynurenine and serotonin pathways may play a role. The exact mechanisms, especially in depressed children and adolescents, are not fully understood. Our primary hypothesis was whether the metabolites of tryptophan degradation in children and adolescents with depressive disorder might be influenced by omega-3 FAs compared to omega-6 FAs during a 12-week supplementation. A secondary hypothesis was to investigate whether tryptophan metabolites in children and adolescents are associated with markers of inflammatory response, oxidative stress, cortisol, and the serum omega-6/omega-3 FA ratio. Metabolites of tryptophan degradation and pteridines, neopterin, and biopterin in urine were analyzed with an HPLC system. Surprisingly, omega-3 FAs stimulated both kynurenine (kynurenine/tryptophan ratio) and serotonin (5-Hydroxytryptophan) pathways, whereas omega-6 FAs only increased the kynurenine/tryptophan ratio. Neopterin and biopterin were not different from the healthy controls. Biopterin increased after omega-3 FA supplementation. Serotonin was positively correlated with lipoperoxidation and a marker of oxidative protein damage. Of the monitored tryptophan metabolites, only 5-hydroxyindolacetic acid was positively correlated with the severity of depression, total cholesterol, and negatively with brain-derived neurotrophic factor and glutathione peroxidase. In conclusion, in children and adolescents, both supplemented FAs stimulated the kynurenine pathway (kynurenine/tryptophan ratio) and kynurenine formation. However, the serotonin pathway (5-Hydroxytryptophan) was stimulated only by omega-3 FA. Tryptophan metabolism is associated with oxidative stress, inflammation, total cholesterol, and cortisol. We are the first to point out the association between the kynurenine pathway (KYN/TRP ratio) and the omega-6/omega-3 FA ratio. The metabolite 5-HIAA could play a role in the pathophysiology of depressive disorder in children and adolescents. CLINICAL TRIAL REGISTRATION: https://www.isrctn.com/ISRCTN81655012, identifier ISRCTN81655012.
Successful treatment of a severe 5-hydroxytrytophan intoxication using carbon hemoperfusion, hemodiafiltration, and mechanical ventilation in a dog.[Pubmed:38407445]
J Vet Emerg Crit Care (San Antonio). 2024 Mar-Apr;34(2):186-192.
OBJECTIVE: To describe the successful use of carbon hemoperfusion and hemodiafiltration in combination with mechanical ventilation (MV) to treat a severe intoxication of 5-Hydroxytryptophan (5-HTP) in a dog. CASE SUMMARY: A dog ingested a minimum of 550 mg/kg of extended-release 5-HTP, resulting in serotonin syndrome that progressed to a comatose state and severe hypoventilation requiring MV. Extracorporeal carbon hemoperfusion coupled with hemodiafiltration was performed to remove 5-HTP from this patient. A carbon hemoperfusion cartridge was placed in series upstream in the extracorporeal circuit from the hemodialyzer. A total of 46.5 L of blood (4.89 L/kg) was processed during a 4.85-hour treatment. Serial plasma samples were obtained at 0, 60, 90, and 150 minutes during the session and 14 hours after the session. These samples were later analyzed for 5-HTP and serotonin concentrations. The extraction ratio of 5-HTP was 93.6%-98.9% through the carbon filter. The dog was weaned from MV within 8 hours after extracorporeal therapy and, after a full recovery, was successfully discharged. NEW OR UNIQUE INFORMATION PROVIDED: Despite an extensive review of the available literature, this appears to be the first reported case of using a carbon hemoperfusion, hemodiafiltration, and MV to treat severe serotonin syndrome secondary to 5-HTP intoxication in a dog. The combination of carbon hemoperfusion and hemodiafiltration can significantly reduce plasma 5-HTP concentrations after acute intoxication and may serve to decrease morbidity and mortality in patients with severe intoxication.


