Acer truncatum
Acer truncatum
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Acer truncatum
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
BCC9217
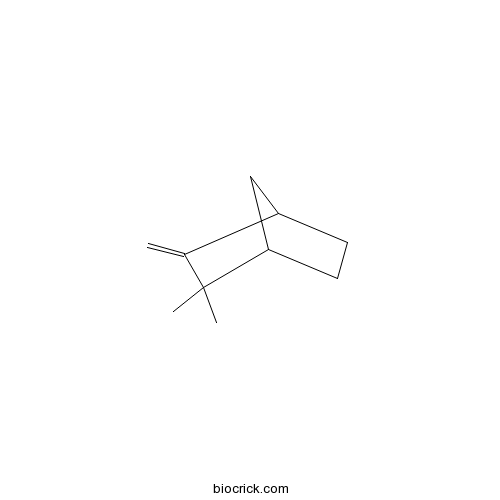
Camphene79-92-5
Instructions
The leaf phenophase of deciduous species altered by land pavements.[Pubmed: 29404687]
It has been widely reported that the urban environment alters leaf and flowering phenophases; however, it remains unclear if land pavement is correlated with these alterations. In this paper, two popular deciduous urban trees in northern China, ash (Fraxinus chinensis) and maple (Acer truncatum), were planted in pervious and impervious pavements at three spacings (0.5 m × 0.5 m, 1.0 m × 1.0 m, and 2.0 m × 2.0 m apart). The beginning and end dates of the processes of leaf budburst and senescence were recorded in spring and fall of 2015, respectively. The results show that leaf budburst and senescence were significantly advanced in pavement compared to non-pavement lands. The date of full leaf budburst was earlier by 0.7-9.3 days for ash and by 0.3-2.3 days for maple under pavements than non-pavements, respectively. As tree spacing increases, the advanced days of leaf budburst became longer. Our results clearly indicate that alteration of leaf phenophases is attributed to land pavement, which should be taken into consideration in urban planning and urban plant management.
Effect of Fatty Acid Chain Length on the Crystallization Behavior of Trans-free Margarine Basestocks during Storage.[Pubmed: 28381787]
In order to obtain margarine free of trans-fatty acids, four interesterified basestocks were prepared by chemical interesterification (CIE) of oil blends. Different ratios of palm stearin, palm olein and soybean oil were mixed without and with 1) fully hydrogenated Acer truncatum oil (FHATO), 2) fully hydrogenated rapeseed oil or 3) palm kernel oil containing a similar amount of saturated, monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fatty acids, but different saturated fatty acid length for CIE. Compared to the physical blends, the CIE samples demonstrated lower slip melting points and decreased solid fat contents, especially at high temperatures, indicating that the CIE samples might have improved mouthfeel. In all CIE samples, the β crystal form disappeared and only the β' crystal form was observed, except for sample 2, which contained a mixed β and β' forms. Furthermore, in all CIE samples, except sample 1, the β' crystal forms began transforming to β form after only two cycles of higher temperature treatments indicating that the CIE sample with FHATO had the most resistance to temperature fluctuation during storage which may be attributed to its longer saturated chains. In conclusion, the CIE basestocks containing longer saturated fatty acids could be more suitable for margarine use.
[Atmospheric Particle Retaining Function of Common Deciduous Tree Species Leaves in Beijing].[Pubmed: 26387301]
In order to explore the atmospheric particle-retaining function of common deciduous tree species leaves in Beijing, six typical tree species (Populus, Robinia pseudoacacia, Koelreuteria paniculata, Salix babylonica, Acer truncatum, Ginkgo biloba) were chosen to measure retaining amount of unit leaf area of air total suspended particles (TSP), coarse particles and fine particulate with aerosol generator (QRJZFSQ-I). The results showed that (1) All six tree species leaves had a certain level of retaining ability to different sizes of atmospheric particles, and different species exhibited some differences. For different sizes of atmospheric particle, retaining amounts of unit leaf area were higher in Koelreuteria paniculata and Robinia pseudoacacia than those of other four species, and the amount of Populus was the lowest among all tree species; (2) The retaining amount of unit leaf area for different tree species was not entirely increased with sampling time. The retaining amounts of TSP and coarse particles for all tree species on the eighth day after rain were significantly higher than those on the fifth day after rain, however, the retaining amount of fine particles was not significantly different under different sampling times. In order to select deciduous tree species for ecological management of air pollution in Beijing, Koelreuteria paniculata should be considered as the priority, followed by Robinia pseudoacacia, compared with Ginkgo biloba, Salix babylonica, Acer truncatum and Populus.
Chronic drought stress reduced but not protected Shantung maple (Acer truncatum Bunge) from adverse effects of ozone (O3) on growth and physiology in the suburb of Beijing, China.[Pubmed: 25765971]
A two-year experiment exposing Acer truncatum Bunge seedlings to elevated ozone (O3) concentrations above ambient air (AO) and drought stress (DS) was carried out using open-top chambers (OTCs) in a suburb of Beijing in north China in 2012-2013. The results suggested that AO and DS had both significantly reduced leaf mass area (LMA), stomatal conductance (Gs), light saturated photosynthetic rate (Asat) as well as above and below ground biomass at the end of the experiment. It appeared that while drought stress mitigated the expression of foliar injury, LMA, leaf photosynthetic pigments, height growth and basal diameter, due to limited carbon fixation, the O3 - induced reductions in Asat, Gs and total biomass were enhanced 23.7%. 15.5% and 8.1% respectively. These data suggest that when the whole plant was considered that drought under the conditions of this experiment did not protect the Shantung maple seedlings from the effects of O3.
[Study on the weight-reducing effect of Acer truncatum leave extract in alimentary obesity rat].[Pubmed: 23057325]
To investigate the weight-reducing effect of Acer truncatum leave extract on alimentary obesity rats and its effect on fatty acid synthase (FAS).
Effects of penta-O-galloyl-β-D-glucose on human neutrophil function: significant down-regulation of L-selectin expression.[Pubmed: 22899541]
Penta-O-galloyl-β-D-glucose (PGG) occurrs in high concentrations in medicinal herbs such as Rhus chinensis, Paeonia suffruticosa, Acer truncatum and Terminalia chebula, which demonstrate anti-inflammatory activity. We investigated the effect of PGG on stimulated and non-stimulated neutrophils in processes which included reactive oxygen species generation (ROS), metalloproteinase-9 and interleukin-8 secretion (IL-8), β₂ integrin (CD11b) and L-selectin (CD62L) expression and apoptosis. In concentrations of 5 μM-20 μM, PGG demonstrated statistically significant inhibition of ROS generation, IL-8 secretion and β₂ integrin expression in stimulated neutrophils. The inhibition of L-selectin expression by PGG resulted in prevention in neutrophils' endothelial attachment. The result obtained may explain the anti-inflammatory activity of this compound and underline the contribution of PGG in the activity of PGG rich plant extracts.
[Community structure and distribution pattern of a natural secondary forest in Beigou forest farm].[Pubmed: 22007439]
Taking the 4 hm2 fixed sampling plot in the Beigou forest farm of Weichang County in Hebei Province as test object, and by adopting the parameters (point pattern distribution, mingling, and size differentiation), this paper analyzed the community structure and distribution pattern of a natural secondary forest in the farm. There were eleven populations in the arbor layer of the forest, among which, Populus davidiana and Betula platyphylla had the obvious advantage in population density and basal area, being the dominant and constructive species of the arbor layer. Spatially, these two species all presented cluster modes remarkably, and competed each other greatly. The main accompanying species Larix principis-rupprechti and Acer truncatum also presented cluster modes, but the density and volume were significantly lower than the two dominant species', not able to compete with the dominate species. Affected by the low mingling of dominant species, the average mingling of the whole stand was only 0.40, while the mingling of accompanying species generally presented moderate or high. The mean size differentiation of the whole stand was 0.49, and P. davidiana, B. platyphylla, L. principis-rupprechti, and Quercus mongolica were of dominance or sub-dominance in the spatial structural units, while the other accompanying species had no obvious dominance.
[Study on the seasonal variations of the active components in Acer truncatum leaves and the inhibitory ability on fatty acid synthase].[Pubmed: 21434437]
To study the dynamic variations of the contents of total polyphenols, flvonoids and chlorogenic acid from Acer truncatum leaves in different months, and their inhibitory activities on fatty acid synthase.


