Aesculus chinensis
Aesculus chinensis
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Aesculus chinensis
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
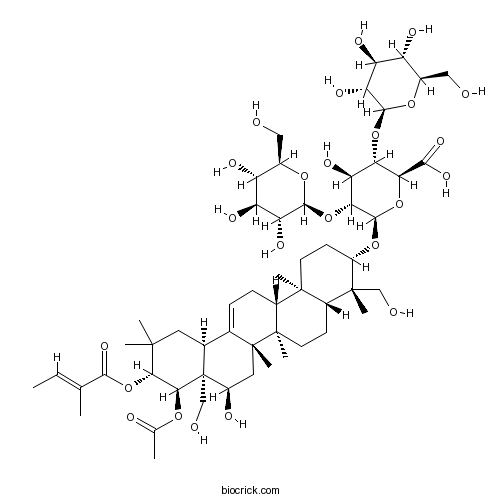
BCN3862
Escin IA123748-68-5
Instructions
-
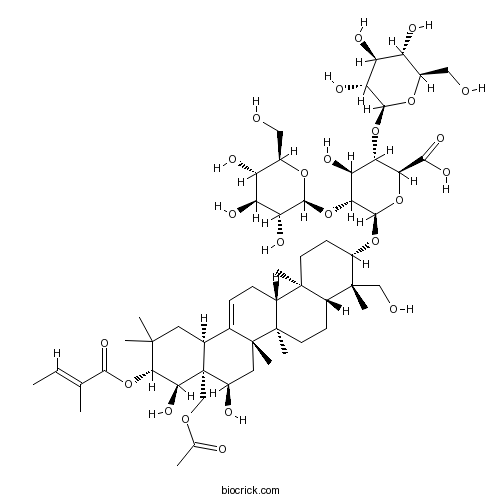
BCN2968
Isoescin IA219944-39-5
Instructions
-
BCN2970
Escin IB26339-90-2
Instructions

Triterpenoid Saponins from the Seeds of Aesculus chinensis and Their Cytotoxicities.[Pubmed: 29285602]
None
Escin Ia suppresses the metastasis of triple-negative breast cancer by inhibiting epithelial-mesenchymal transition via down-regulating LOXL2 expression.[Pubmed: 27008697]
The saponin fraction of Aesculus chinensis Bunge fruits (SFAC) could inhibit the invasion and migration of MDA-MB-231 cells. Among which, escin Ia showed more potent inhibition of the invasion than other five main saponin constituents. It selectively reduced the expression of LOXL2 mRNA and promoted the expression of E-cadherin mRNA, and prevented the EMT process of MDA-MB-231 cells and TNF-α/TGF-β-stimulated MCF-7 cells. Moreover, it reduced the LOXL2 level in MDA-MB-231 cells but not in MCF-7 cells. When MCF-7 cells were stimulated with TNF-α/TGF-β, transfected with LOXL2 or treated with hypoxia, escin Ia down-regulated the level of LOXL2 in MCF-7 cells. Meanwhile, escin Ia suppressed the EMT process in LOXL2-transfected or hypoxia-treated MCF-7 cells. Of interest, escin Ia did not alter the level of HIF-1α in hypoxia-induced MCF-7 cells. In TNBC xenograft mice, the metastasis and EMT of MDA-MB-231 cells were suppressed by escin Ia. In conclusion, escin Ia was the main active ingredient of SFAC for the anti-TNBC metastasis activity, and its action mechanisms involved inhibition of EMT process by down-regulating LOXL2 expression.
Transpiration rates of urban trees, Aesculus chinensis.[Pubmed: 23513449]
Transpiration patterns of Aesculus chinensis in relation to explanatory variables in the microclimatic, air quality, and biological phenomena categories were measured in Beijing, China using the thermal dissipation method. The highest transpiration rate measured as the sap flux density of the trees took place from 10:00 am to 13:00 pm in the summer and the lowest was found during nighttime in the winter. To sort out co-linearity, principal component analysis and variation and hierarchical partitioning methods were employed in data analyses. The evaporative demand index (EDI) consisting of air temperature, soil temperature, total radiation, vapor pressure deficit, and atmospheric ozone (O3), explained 68% and 80% of the hourly and daily variations of the tree transpiration, respectively. The independent and joint effects of EDI variables together with a three-variable joint effect exerted the greatest influences on the variance of transpiration rates. The independent effects of leaf area index and atmospheric O3 and their combined effect exhibited minor yet significant influences on tree transpiration rates.
In vivo anthelmintic activity of crude extracts of Radix angelicae pubescentis, Fructus bruceae, Caulis spatholobi, Semen aesculi, and Semen pharbitidis against Dactylogyrus intermedius (Monogenea) in goldfish (Carassius auratus).[Pubmed: 20191290]
In search of a natural antiparasitic, in vivo anthelmintic activity of petroleum ether, chloroform, ethyl acetate, methanol, and aqueous extracts of Angelica pubescens roots (Radix angelicae pubescentis), Brucea javanica fruits (Fructus bruceae), Spatholobus suberectus stems (Caulis spatholobi), Aesculus chinensis Bge. seeds (Semen aesculi), and Pharbitis purpurea (L.) Voigt seeds (Semen pharbitidis) were tested against Dactylogyrus intermedius (Monogenea) in goldfish (Carassius auratus). Among the extracts tested, the methanolic and aqueous extracts of S. aesculi were observed to be more efficient than the other plant extracts with EC(50) and EC(90) values of 5.23 and 7.33 mg/L and 6.48 and 12.29 mg/L after 48 h, respectively, followed by methanolic extracts of Fructus bruceae, Radix angelicae pubescentis, Caulis spatholobi, and Semen pharbitidis with EC(50) 49.96, 57.45, 64.92, and 309.47 mg/L. The methanolic and aqueous extracts of S. aesculi exhibited potential results and can be exploited as a preferred natural antiparasitic for the control of D. intermedius.
[Time lag characteristics of stem sap flow of common tree species during their growth season in Beijing downtown].[Pubmed: 20030130]
From April to September in 2008, the stem sap flow velocity (Js) of several common tree species (Ginkgo biloba, Aesculus chinensis, Magnolia denudata, Robinia pseudoacacia, Pinus tabulaeformis and Cedrus deodara) in Beijing was measured by thermal dissipation method. Crosscorrelation analysis was used to estimate the time lag between the stem sap flow and the driving factors of canopy transpiration among the tree species. The Js of the six tree species was significantly correlated with the total radiation (Rs) and vapor pressure deficit (D), and the Js was lagged behind Rs but ahead of D. The maximum correlation coefficient of Js with Rs (0.74-0.93) was often higher than that of Js with D (0.57-0.79), indicating that the diurnal Js was more dependent on Rs than on D. The sampled tree species except P. tabulaeformis had a shorter time lag of Js with Rs (10-70 min) than with D (47-130 min), and there existed significant differences among R. pseudoacacia, P. tabulaeformis, and C. deodara. The time lag between the Js and the driving factors of canopy transpiration was mainly correlated with the tree features (DBH, tree height, canopy area, and sapwood area) and the nocturnal water recharge, regardless of tree species.
RETRACTED ARTICLE[Pubmed: 18452082]
Beta-aescin, a natural triterpenoid saponin isolated from the seed of Chinese horse chestnut (Aesculus chinensis), is known to generate a wide variety of biochemical and pharmacological effects. In the present study, the authors investigated the anti-proliferative and apoptotic effects of beta-aescin in human chronic myeloid leukemia K562 cell line in vitro. The anti-proliferative effects were detected by CFU-K562 colony formation and cell viability assay. The apoptotic effects were analysed by morphological analysis, annexin V assay, DNA fragmentation assay and flow cytometry DNA content analysis. The results showed that beta-aescin exhibited potent dose- and time-dependent anti-proliferative effects in K562 cells. Morphological evidence of apoptosis, a significant increase of annexin V+ and PI- cells (early apoptotic) and apoptotic DNA fragmentation, were observed in cells treated with beta-aescin. Flow cytometry analysis revealed that beta-aescin could lead to an accumulation of sub G1 population in K562 cells, and suggesting a potential G1 phase accumulation in cell cycle profile of K562 cells. Our findings revealed that beta-aescin is a potent natural inhibitor of proliferation and inducer of apoptosis in K562 cells, and beta-aescin may be a candidate lead compound to explore potential antileukemia drugs.
Determination of four major saponins in the seeds of Aesculus chinensis Bunge using accelerated solvent extraction followed by high-performance liquid chromatography and electrospray-time of flight mass spectrometry.[Pubmed: 17631106]
A new method based on accelerated solvent extraction (ASE) followed by a reliable high-performance liquid chromatography-diode array detector (HPLC-DAD) and positive ion electrospray-time of flight mass spectrometry (ESI-TOF/MS) analysis has been developed for the characterization and quantification of four major saponins in extracts of the seeds of Aesculus chinensis Bunge (semen aesculi). The saponins escin Ia, escin Ib, isoescin Ia and isoescin Ib were extracted from seeds of A. chinesis Bunge via ASE, and the operational parameters of ASE were optimized, such as extraction solvent, extraction temperature, static extraction time and extraction cycles. The optimized procedure employed 70% MeOH as extraction solvent, 120 degrees C of extraction temperature, 7 min of static extraction time, 60% flush volume and the extraction recoveries of the four compounds were nearly to 100% for two cycles. The HPLC conditions are as follows: SinoChrom ODS BP C18 (4.6 mm x 200 mm, 5 microm) column, acetonitrile and 0.10% phosphoric acid solution as mobile phase, flow rate is 1.0 mL min(-1), detection length of UV is 203 nm, injection volume is 10 microL. The results indicated that the developed HPLC method is simple, sensitive and reliable for the determination of four major saponins in seeds of A. chinesis Bunge with a good linearity (r2 > 0.9994), precision (relative standard deviation (R.S.D.) < 1.5%) and the recovery ranges of 95.2-97.3%. The limits of detection (LOD) of the four compounds were in the range of 0.40-0.75 microg mL(-1). This assay can be readily utilized as a quality control method for semen aesculi and other related medicinal plants.
Synthesis of 3-O-(beta-D-xylopyranosyl-(1-->2)-beta-D-glucopyranosyl)-3'-O-(beta-D-glucopyranosyl)tamarixetin, the putative structure of aescuflavoside A from the seeds of Aesculus chinensis.[Pubmed: 16580652]
3-O-(beta-D-xylopyranosyl-(1-->2)-beta-D-glucopyranosyl)-3'-O-(beta-D-glucopyranosyl)tamarixetin, the putative flavonal glycoside named aescuflavoside A, isolated from the seeds of Aesculus chinensis, is synthesized via regioselective glycosylation of 7-O-benzyltamarixetin with glycosyl bromides under phase-transfer-catalyzed conditions.
Triterpenoid saponins from the fruits of Aesculus pavia.[Pubmed: 16497343]
The compounds, named aesculiosides Ia-Ie, IIa-IId, and IVa-IVc, were isolated from an ethanol extract of the fruits of North American Aesculus pavia, along with two known compounds. Their structures were characterized as polyhydroxyoleanene pentacyclic triterpenoid saponins by spectroscopic and chemical analyses. These saponins were divided into three elution zones by chromatography according to the polarity because of the acyl substitution at C-21 and C-22 of the aglycone saponins moiety. These are structurally different from those isolated from Eurasian Aesculus hippocastanum and Aesculus chinensis in their oligosaccharide moieties.


