Isoescin IACAS# 219944-39-5 |
- Isoescin IB
Catalog No.:BCN2969
CAS No.:219944-46-4
Quality Control & MSDS
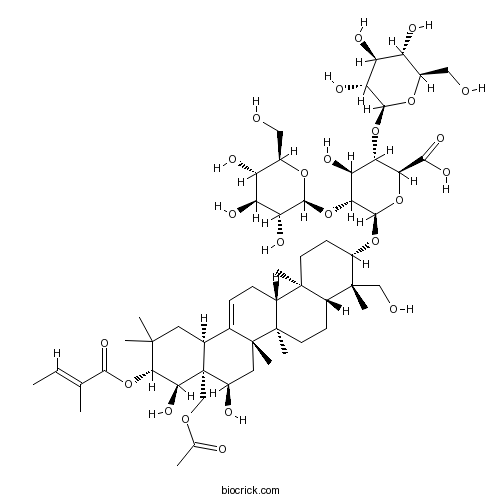
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 219944-39-5 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 6476032 | Appearance | White - beige powder |
| Formula | C55H86O24 | M.Wt | 1131.3 |
| Type of Compound | Triterpenoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Aescin C; Escin IVa | ||
| Solubility | Soluble in methanol; slightly soluble in water | ||
| Chemical Name | (2S,3S,4S,5R,6R)-6-[[(3S,4S,4aR,6aR,6bS,8R,8aR,9R,10R,12aS,14aR,14bR)-8a-(acetyloxymethyl)-8,9-dihydroxy-4-(hydroxymethyl)-4,6a,6b,11,11,14b-hexamethyl-10-[(E)-2-methylbut-2-enoyl]oxy-1,2,3,4a,5,6,7,8,9,10,12,12a,14,14a-tetradecahydropicen-3-yl]oxy]-4-hydroxy-3,5-bis[[(2S,3R,4S,5S,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxy]oxane-2-carboxylic acid | ||
| SMILES | CC=C(C)C(=O)OC1C(C2(C(CC1(C)C)C3=CCC4C5(CCC(C(C5CCC4(C3(CC2O)C)C)(C)CO)OC6C(C(C(C(O6)C(=O)O)OC7C(C(C(C(O7)CO)O)O)O)O)OC8C(C(C(C(O8)CO)O)O)O)C)COC(=O)C)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | YOSIWGSGLDDTHJ-IVKVKCDBSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C55H86O24/c1-10-23(2)46(71)79-44-43(68)55(22-72-24(3)59)26(17-50(44,4)5)25-11-12-30-51(6)15-14-32(52(7,21-58)29(51)13-16-53(30,8)54(25,9)18-31(55)60)75-49-41(77-48-38(66)36(64)34(62)28(20-57)74-48)39(67)40(42(78-49)45(69)70)76-47-37(65)35(63)33(61)27(19-56)73-47/h10-11,26-44,47-49,56-58,60-68H,12-22H2,1-9H3,(H,69,70)/b23-10+/t26-,27+,28+,29+,30+,31+,32-,33+,34+,35-,36-,37+,38+,39-,40-,41+,42-,43-,44-,47-,48-,49+,51-,52+,53+,54+,55-/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Escin Ia and Isoescin IA have been traditionally used clinically as the chief active ingredients of escin, a major triterpene saponin isolated from horse chestnut (Aesculus hippocastanum) seeds for the treatment of chronic venous insufficiency, hemorrhoids, inflammation and edema. |
| In vivo | Comparative pharmacokinetics and bioavailability of escin Ia and isoescin Ia after administration of escin and of pure escin Ia and isoescin Ia in rat.[Pubmed: 22094055 ]J Ethnopharmacol. 2012 Jan 6;139(1):201-6.Escin Ia and Isoescin IA have been traditionally used clinically as the chief active ingredients of escin, a major triterpene saponin isolated from horse chestnut (Aesculus hippocastanum) seeds for the treatment of chronic venous insufficiency, hemorrhoids, inflammation and edema.
To establish a sensitive LC-MS/MS method and investigate the pharmacokinetic properties of escin Ia and Isoescin IA in rats and the pharmacokinetics difference of sodium escinate with pure escin Ia and Isoescin IA. The absolute bioavailability of escin Ia and Isoescin IA and the bidirectional interconversion of them in vivo were also scarcely reported.
|
| Structure Identification | Adv Pharm Bull. 2015 Nov;5(4):587-91.Determination of Four Major Saponins in Skin and Endosperm of Seeds of Horse Chestnut (Aesculus Hippocastanum L.) Using High Performance Liquid Chromatography with Positive Confirmation by Thin Layer Chromatography.[Pubmed: 26819933]To separate and quantify four major saponins in the extracts of the skin and the endosperm of seeds of horse chestnut (Aesculus hippocastanum L.) using ultrasonic solvent extraction followed by a high performance liquid chromatography-diode array detector (HPLC-DAD) with positive confirmation by thin layer chromatography (TLC). |

Isoescin IA Dilution Calculator

Isoescin IA Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 0.8839 mL | 4.4197 mL | 8.8394 mL | 17.6788 mL | 22.0985 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.1768 mL | 0.8839 mL | 1.7679 mL | 3.5358 mL | 4.4197 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.0884 mL | 0.442 mL | 0.8839 mL | 1.7679 mL | 2.2098 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0177 mL | 0.0884 mL | 0.1768 mL | 0.3536 mL | 0.442 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0088 mL | 0.0442 mL | 0.0884 mL | 0.1768 mL | 0.221 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- 3-Methyl-1-(2-piperidinophenyl)butylamine N-acetylglutamate salt
Catalog No.:BCC8635
CAS No.:219921-94-5
- 5,8,9,14-Tetraacetoxy-3-benzoyloxy-10,15-dihydroxypepluane
Catalog No.:BCN7657
CAS No.:219916-77-5
- MPEP Hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1777
CAS No.:219911-35-0
- 2,2',3'-Trihydroxy-4,6-dimethoxybenzophenone
Catalog No.:BCN1488
CAS No.:219861-73-1
- Escitalopram Oxalate
Catalog No.:BCC5040
CAS No.:219861-08-2
- Merresectine B
Catalog No.:BCN1918
CAS No.:219829-75-1
- Consiculine
Catalog No.:BCN1903
CAS No.:219829-73-9
- BTB06584
Catalog No.:BCC5106
CAS No.:219793-45-0
- Bombiprenone
Catalog No.:BCN4940
CAS No.:21978-49-4
- ANA 12
Catalog No.:BCC6287
CAS No.:219766-25-3
- Taxezopidine L
Catalog No.:BCN6946
CAS No.:219749-76-5
- 14-Deoxy-12-hydroxyandrographolide
Catalog No.:BCN4673
CAS No.:219721-33-2
- Isoescin IB
Catalog No.:BCN2969
CAS No.:219944-46-4
- Fmoc-β-Homo-Tyr(tBu)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2621
CAS No.:219967-69-8
- Ixabepilone
Catalog No.:BCC1666
CAS No.:219989-84-1
- Nu 6027
Catalog No.:BCC1154
CAS No.:220036-08-8
- Vincetoxicoside B
Catalog No.:BCN2864
CAS No.:22007-72-3
- Imatinib Mesylate (STI571)
Catalog No.:BCC1115
CAS No.:220127-57-1
- Eichlerialactone
Catalog No.:BCN4941
CAS No.:2202-01-9
- O-Methyldauricine
Catalog No.:BCC8225
CAS No.:2202-17-7
- Triptohairic acid
Catalog No.:BCN8060
CAS No.:220209-71-2
- Cinnamamide
Catalog No.:BCN4942
CAS No.:22031-64-7
- 5-[2-[Tert-butyl(dimethyl)silyl]oxyethyl]-2,2-dimethyl-3a,6a-dihydrofuro[2,3-d][1,3]dioxol-6-one
Catalog No.:BCC8592
CAS No.:220328-03-0
- 3,11,12-Trihydroxyspirovetiv-1(10)-en-2-one
Catalog No.:BCN1487
CAS No.:220328-04-1
Determination of Four Major Saponins in Skin and Endosperm of Seeds of Horse Chestnut (Aesculus Hippocastanum L.) Using High Performance Liquid Chromatography with Positive Confirmation by Thin Layer Chromatography.[Pubmed:26819933]
Adv Pharm Bull. 2015 Nov;5(4):587-91.
PURPOSE: To separate and quantify four major saponins in the extracts of the skin and the endosperm of seeds of horse chestnut (Aesculus hippocastanum L.) using ultrasonic solvent extraction followed by a high performance liquid chromatography-diode array detector (HPLC-DAD) with positive confirmation by thin layer chromatography (TLC). METHODS: The saponins: escin Ia, escin Ib, Isoescin IA and isoescin Ib were extracted using ultrasonic extraction method. The optimized extraction conditions were: 70% methanol as extraction solvent, 80 degrees C as extraction temperature, and the extraction time was achieved in 4 hours. The HPLC conditions used: Zorbax SB-ODS-(150 mm x 2.1 mm, 3 mum) column, acetonitrile and 0.10% phosphoric acid solution (39:61 v/v) as mobile phase, flow rate was 0.5 mL min(-1) at 210 nm and 230 nm detection. The injection volume was 10 muL, and the separation was carried out isothermally at 30 degrees C in a heated chamber. RESULTS: The results indicated that the developed HPLC method is simple, sensitive and reliable. Moreover, the content of escins in seeds decreased by more than 30% in endosperm and by more than 40% in skin upon storage for two years. CONCLUSION: This assay can be readily utilized as a quality control method for horse chestnut and other related medicinal plants.
Comparative pharmacokinetics and bioavailability of escin Ia and isoescin Ia after administration of escin and of pure escin Ia and isoescin Ia in rat.[Pubmed:22094055]
J Ethnopharmacol. 2012 Jan 6;139(1):201-6.
ETHNOPHARMACOLOGICAL RELEVANCE: Escin Ia and Isoescin IA have been traditionally used clinically as the chief active ingredients of escin, a major triterpene saponin isolated from horse chestnut (Aesculus hippocastanum) seeds for the treatment of chronic venous insufficiency, hemorrhoids, inflammation and edema. AIM OF THE STUDY: To establish a sensitive LC-MS/MS method and investigate the pharmacokinetic properties of escin Ia and Isoescin IA in rats and the pharmacokinetics difference of sodium escinate with pure escin Ia and Isoescin IA. The absolute bioavailability of escin Ia and Isoescin IA and the bidirectional interconversion of them in vivo were also scarcely reported. MATERIALS AND METHODS: Wister rats were administrated an intravenous (i.v.) dose (1.7 mg/kg) of sodium escinate (corresponding to 0.5mg/kg of escin Ia and 0.5mg/kg of Isoescin IA, respectively) and an i.v. dose (0.5mg/kg) or oral dose (4mg/kg) of pure escin Ia or Isoescin IA, respectively. At different time points, the concentrations of escin Ia and Isoescin IA in rat plasma were determined by LC-MS/MS method. Main pharmacokinetic parameters including t(1/2), MRT, CL, V(d), AUC and F were estimated by non-compartmental analysis using the TopFit 2.0 software package (Thomae GmbH, Germany) and statistical analysis was performed using the Student's t-test with P<0.05 as the level of significance. RESULTS: After administration of sodium escinate, the t(1/2) and MRT values for both escin Ia and Isoescin IA were larger than corresponding values for the compounds given alone. Absorption of escin Ia and Isoescin IA was very low with F values both <0.25%. Escin Ia and Isoescin IA were found to form the other isomer in vivo with the conversion of escin Ia to Isoescin IA being much extensive than from Isoescin IA to escin Ia. CONCLUSION: Comparison of the pharmacokinetics of escin Ia and Isoescin IA given alone and together in rat suggest that administration of herbal preparations of escin for clinical use may provide longer duration of action than administration of single isomers. The interconversion of escin Ia and Isoescin IA when given alone indicates that administration of one isomer leads to exposure to the other.


